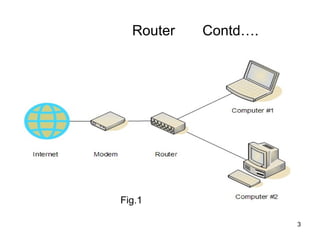
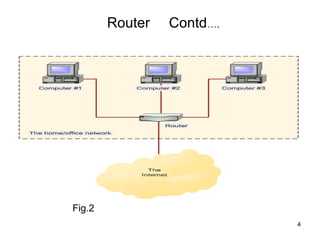
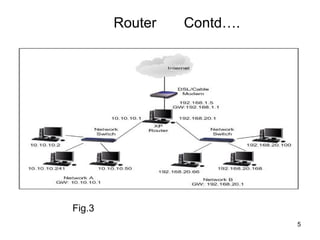
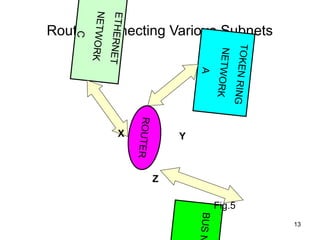
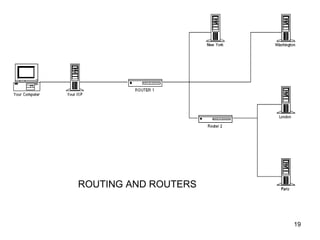
Routers connect multiple computer networks together and allow data to be sent between networks. Routers contain specialized operating systems, memory, and processors to perform routing and forwarding of information. Routers operate in both a control plane, where they learn the best paths between networks, and a forwarding plane, where they actually send packets along the paths. Common types of routers include edge routers, border routers, core routers, and access routers. Routing is the process of selecting the best path for sending data packets between source and destination devices across multiple networks using routers.