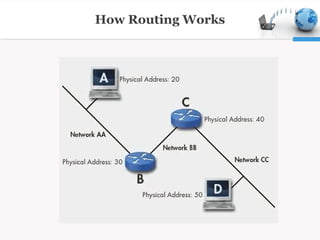
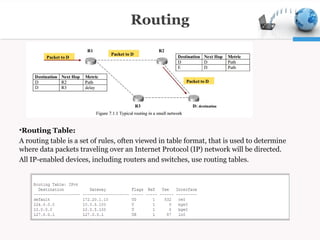
Routing is the process of selecting the best paths in a network. It is performed for many kinds of networks like telephone, electronic data, and transportation networks. Routers are networking devices that forward data packets between different computer networks. Routing involves using IP addresses to identify hosts, protocols like RIP, EIGRP, OSPF and BGP to exchange routing information between routers, and algorithms to determine the optimal path to send packets through a network. Routing tables stored in routers and switches determine the path for packets to travel based on metrics like bandwidth and reliability.