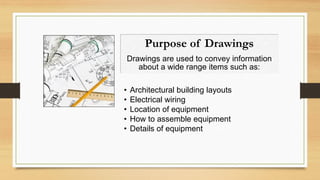
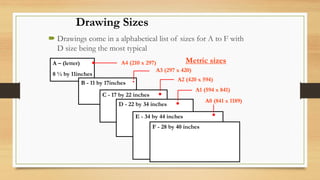
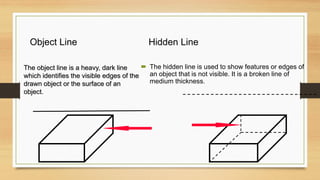
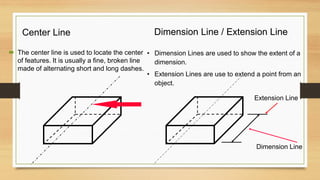
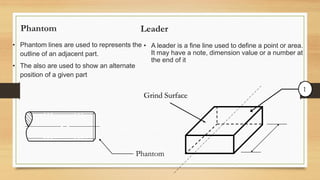
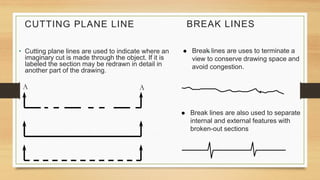
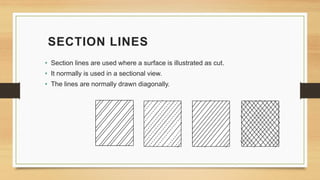
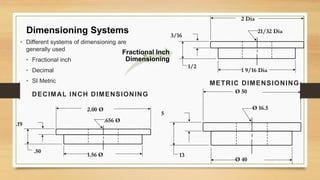
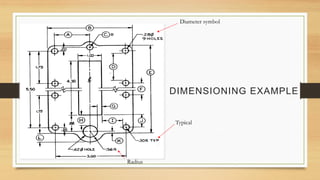
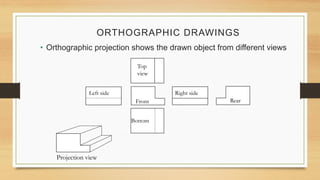
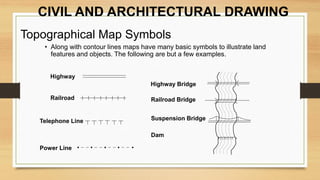
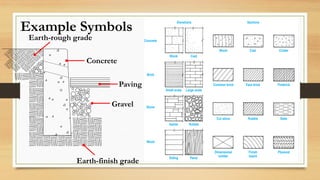
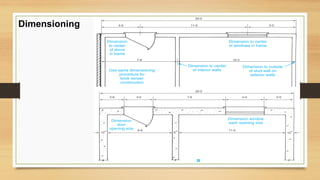
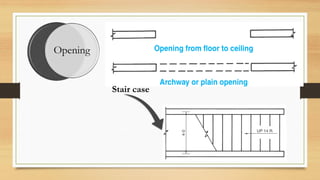
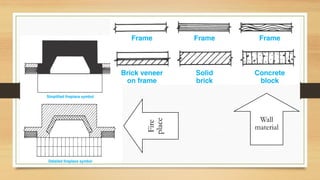
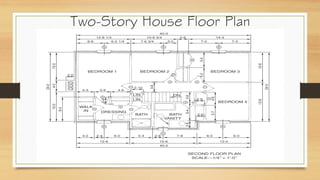
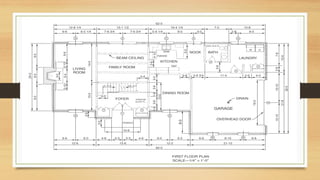
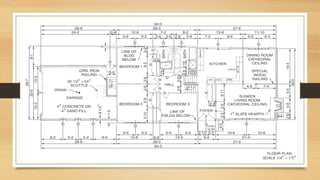
This document provides an overview of engineering drawings, including their purpose and typical components. It discusses drawing sizes, basic line types like object lines and hidden lines, dimensioning systems, orthographic projections, and examples of civil and architectural drawings like floor plans and topographic maps. The key information conveyed through engineering drawings includes layouts, wiring, equipment details and assembly instructions.