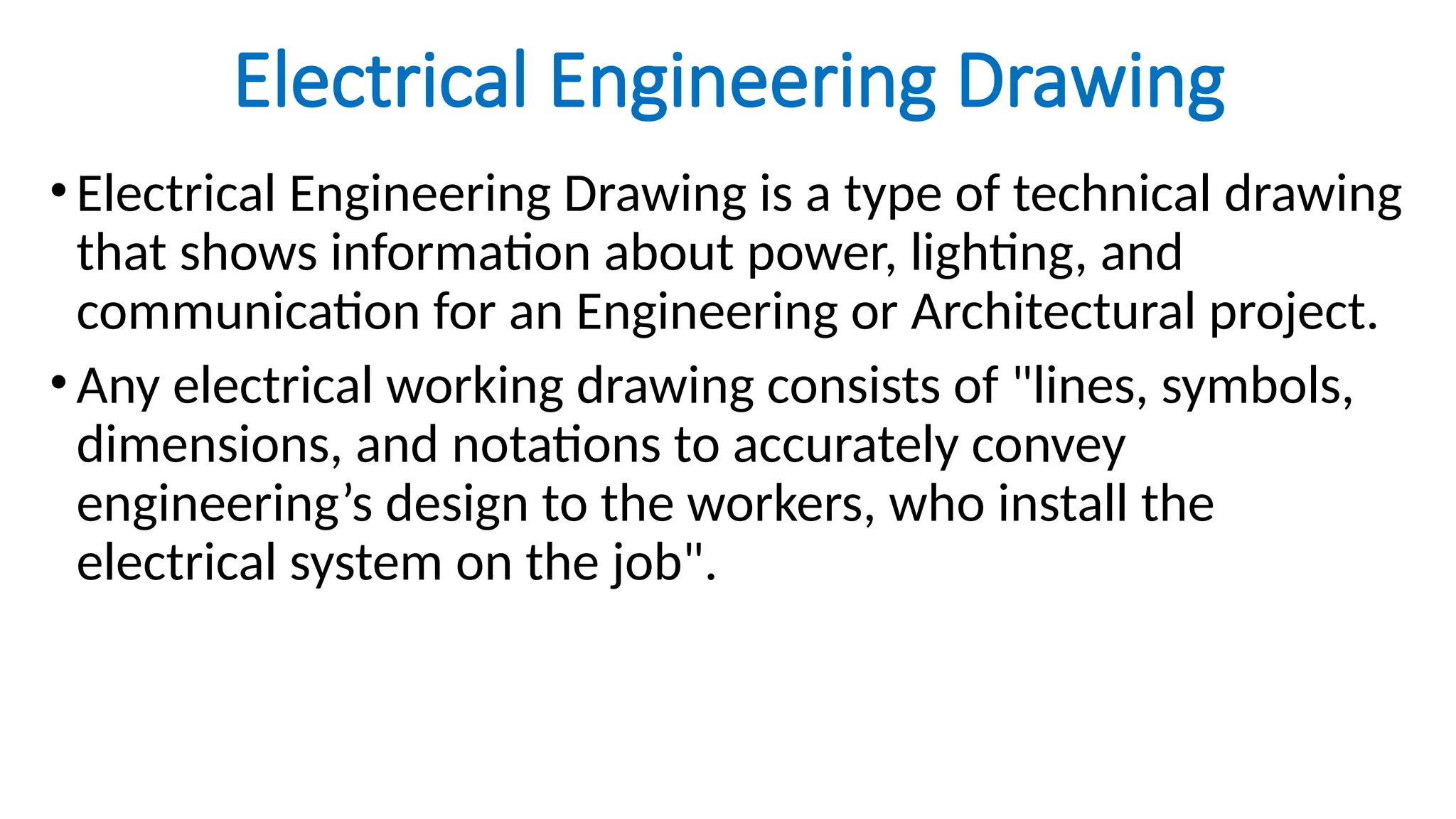
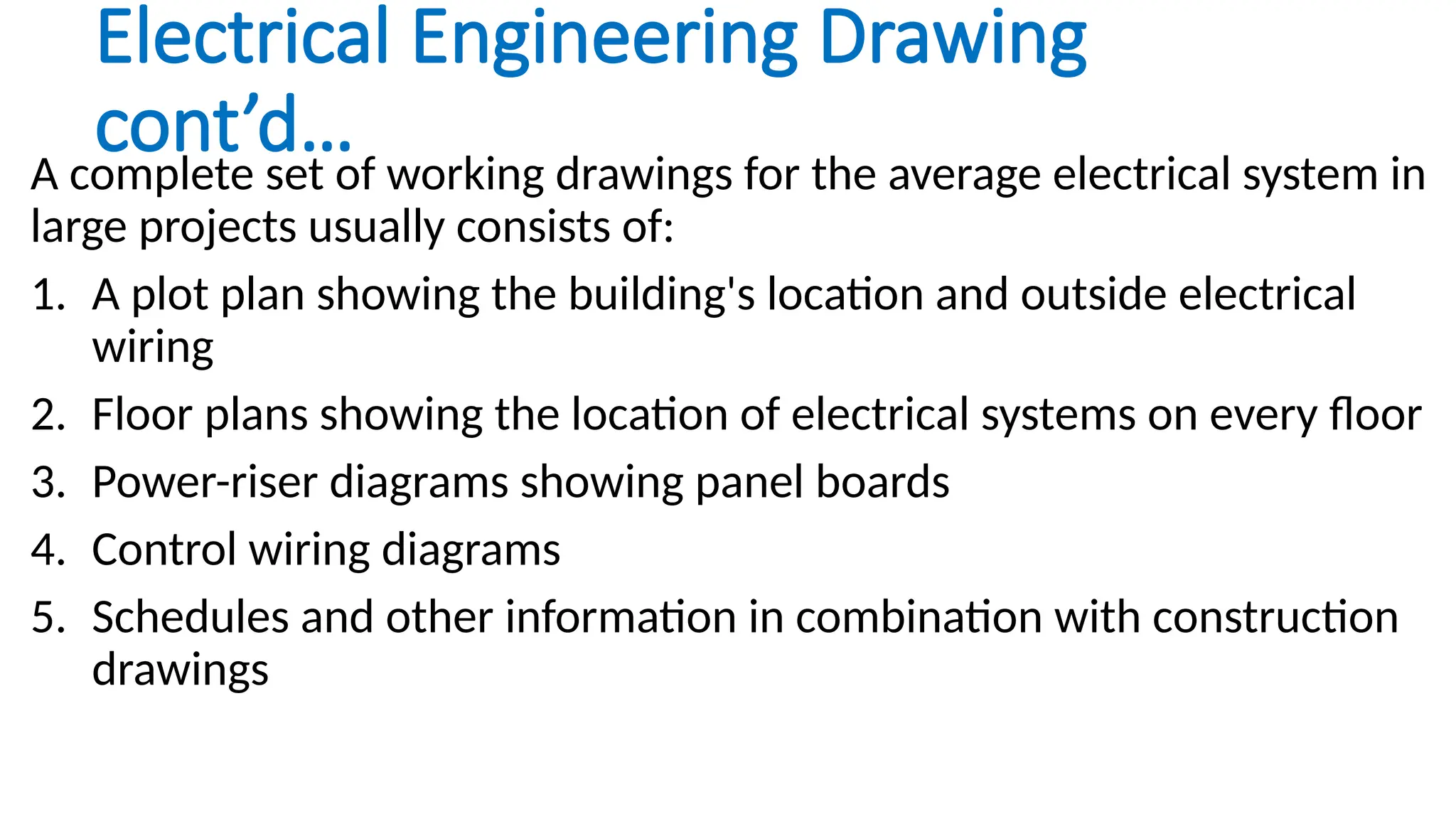
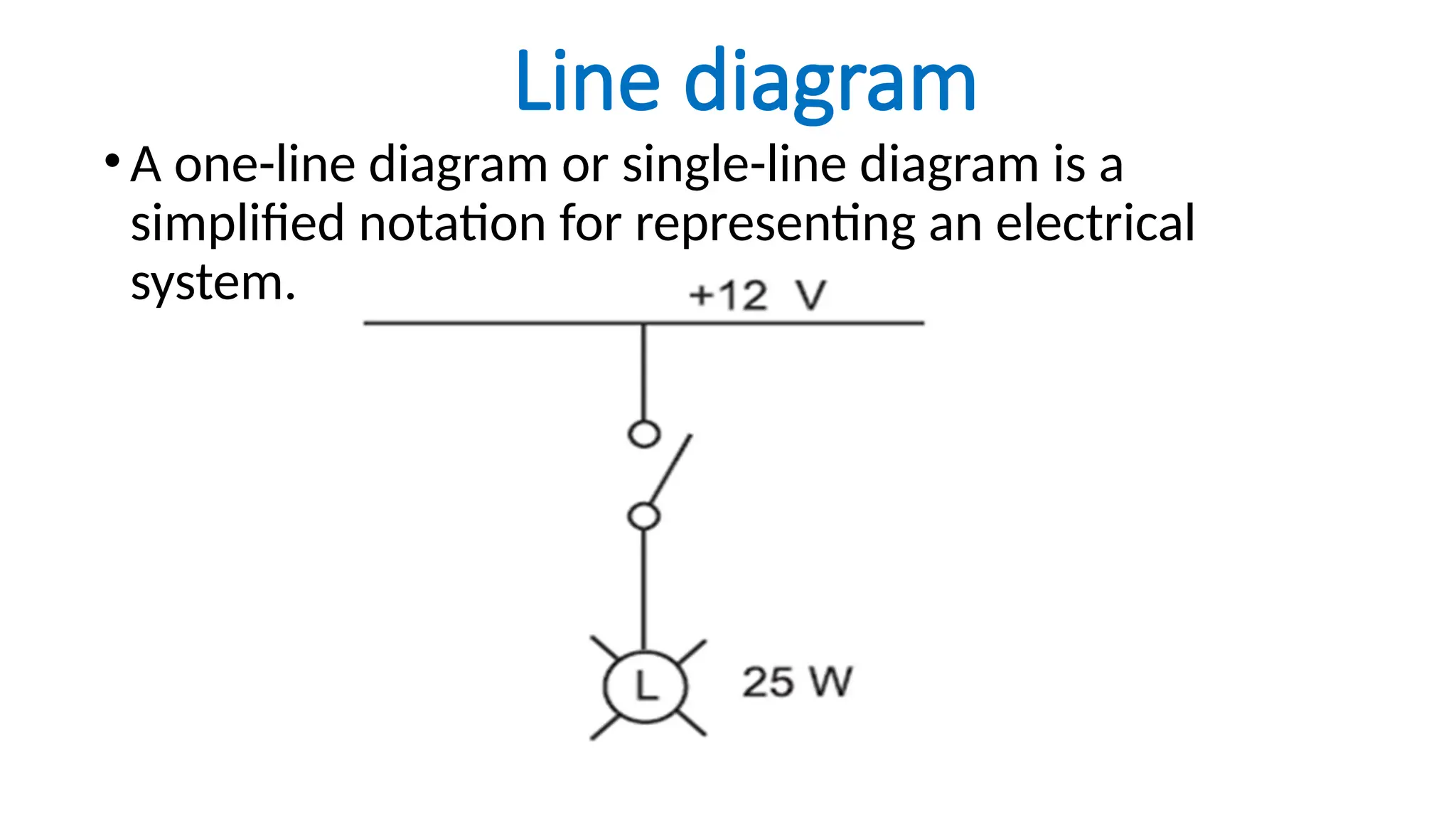
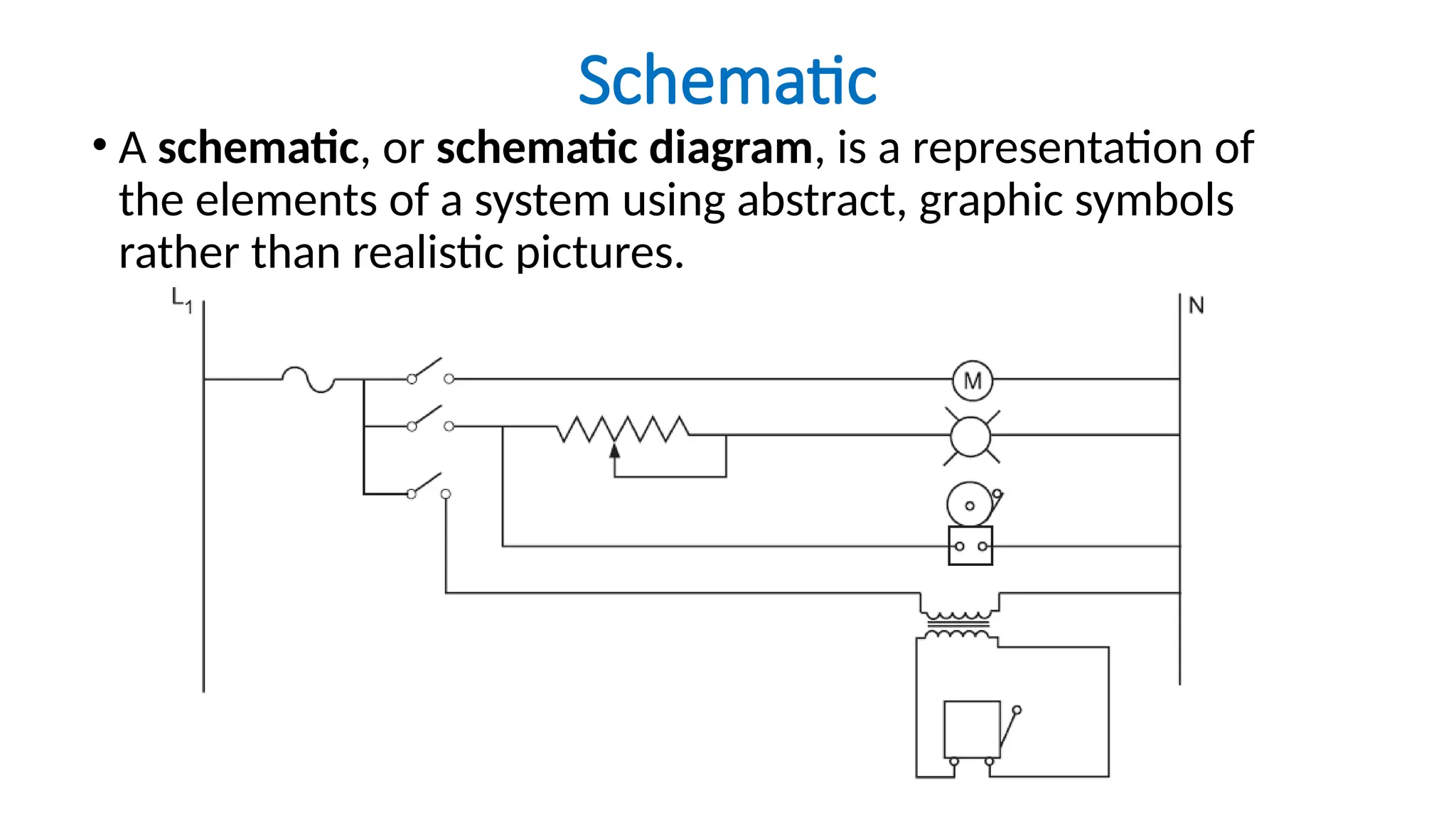
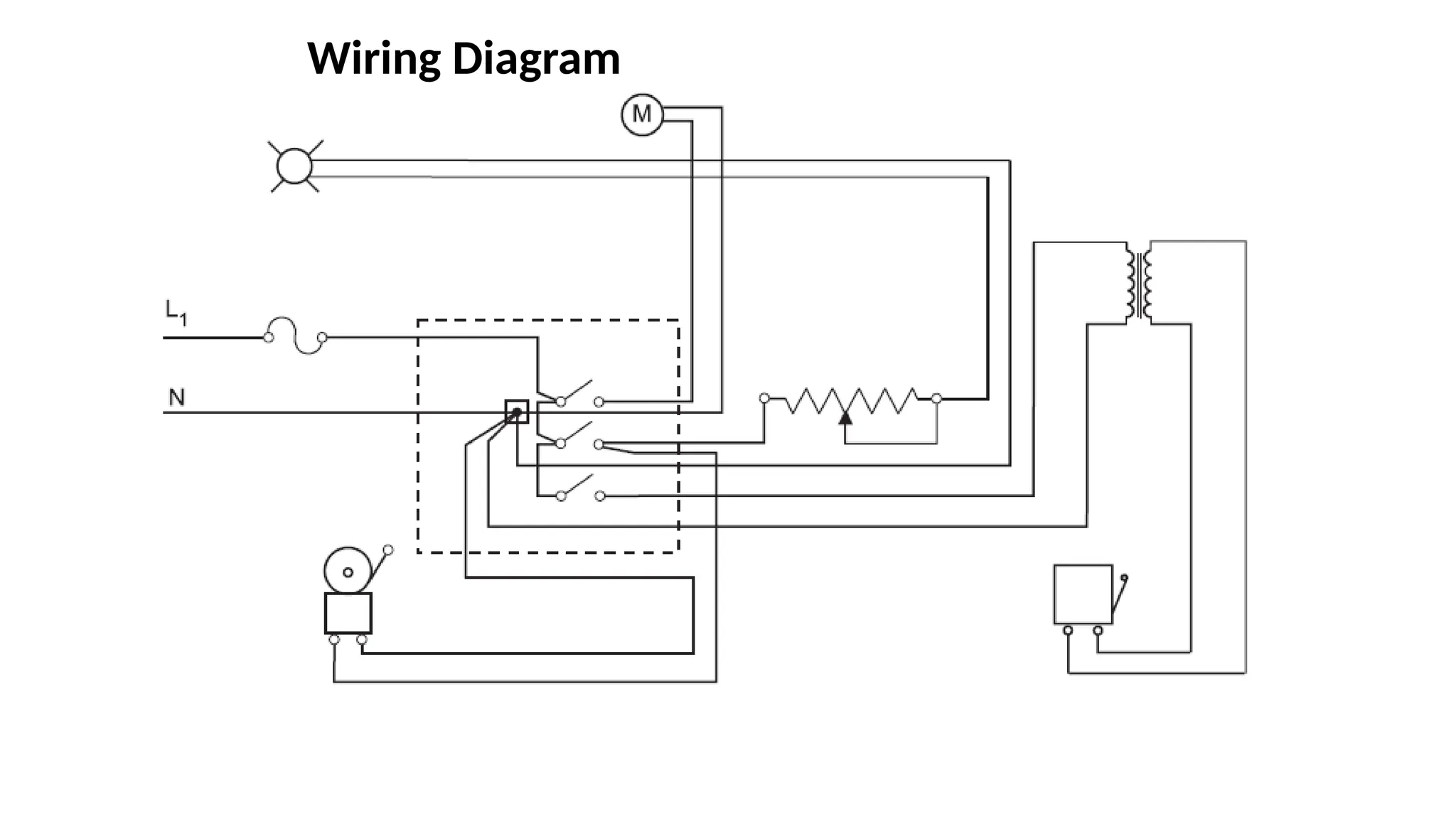
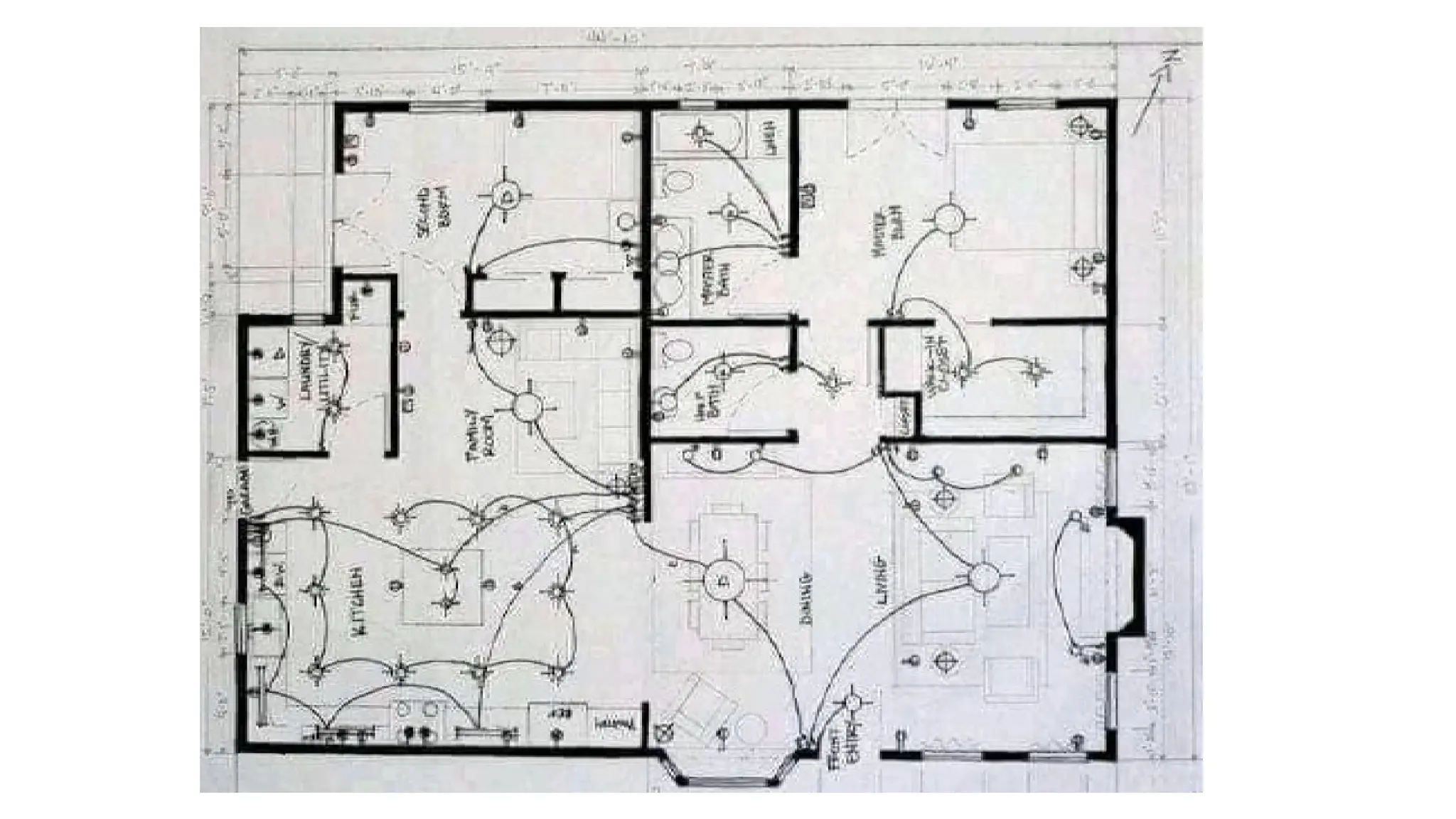
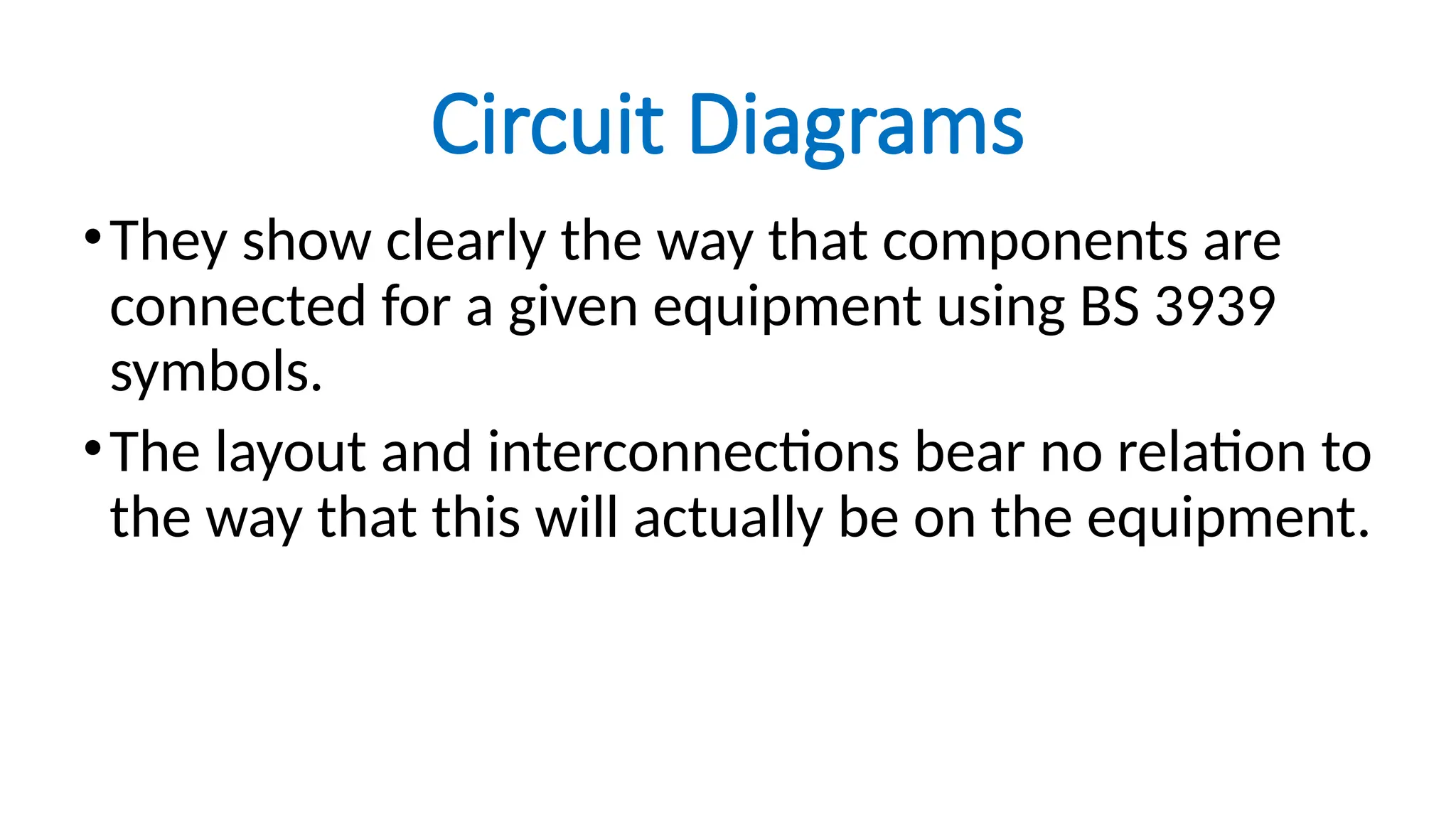
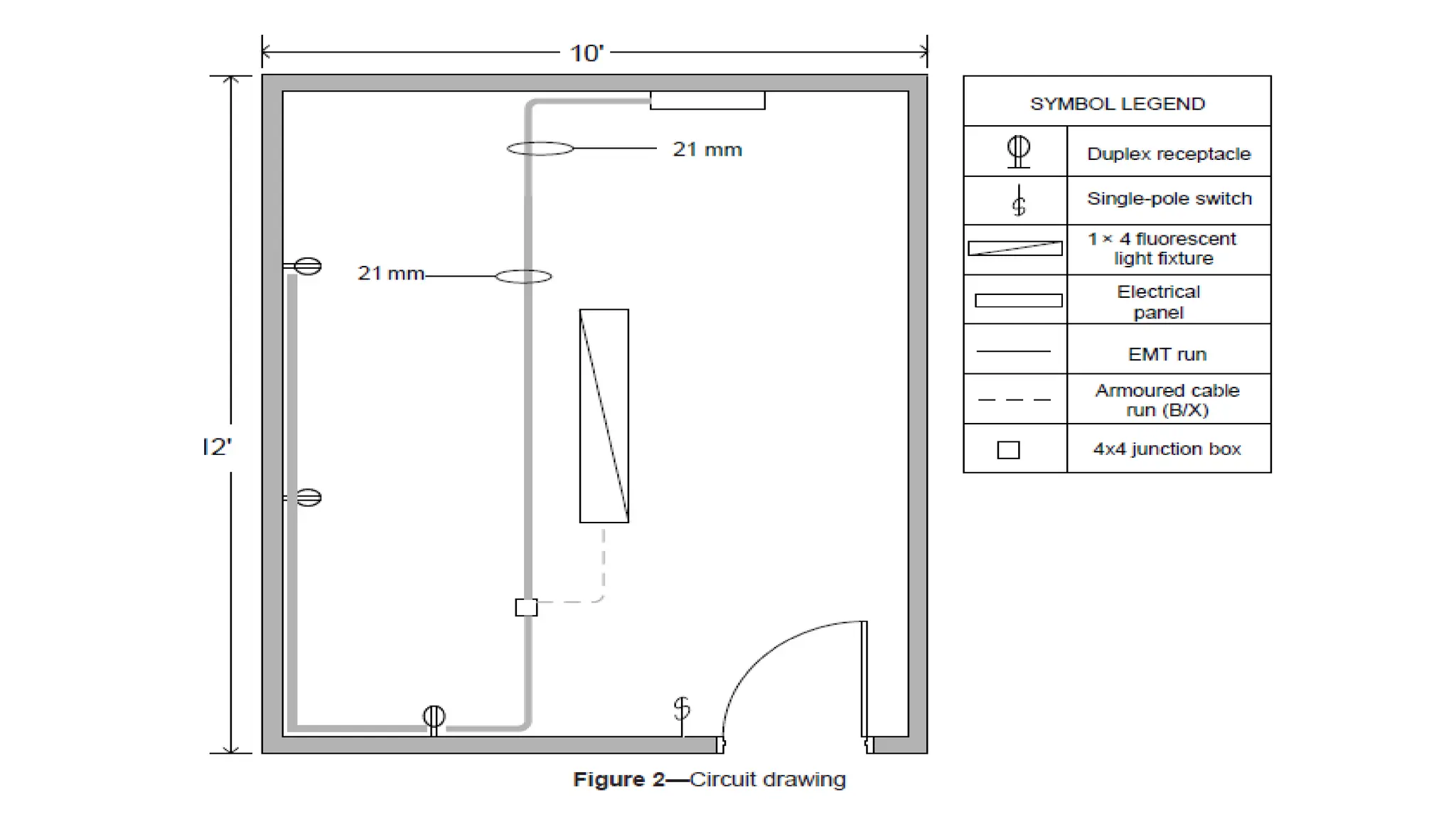
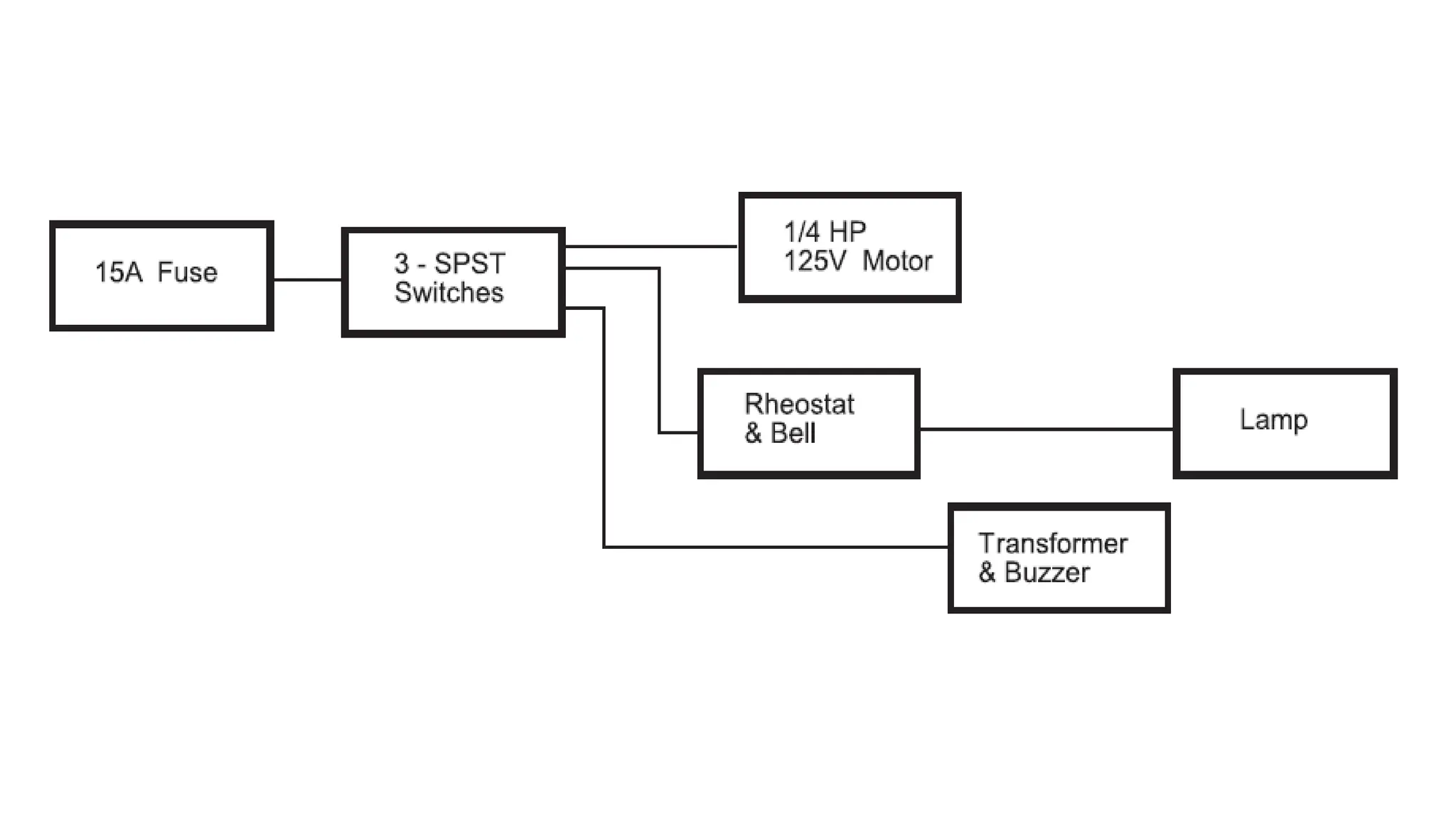
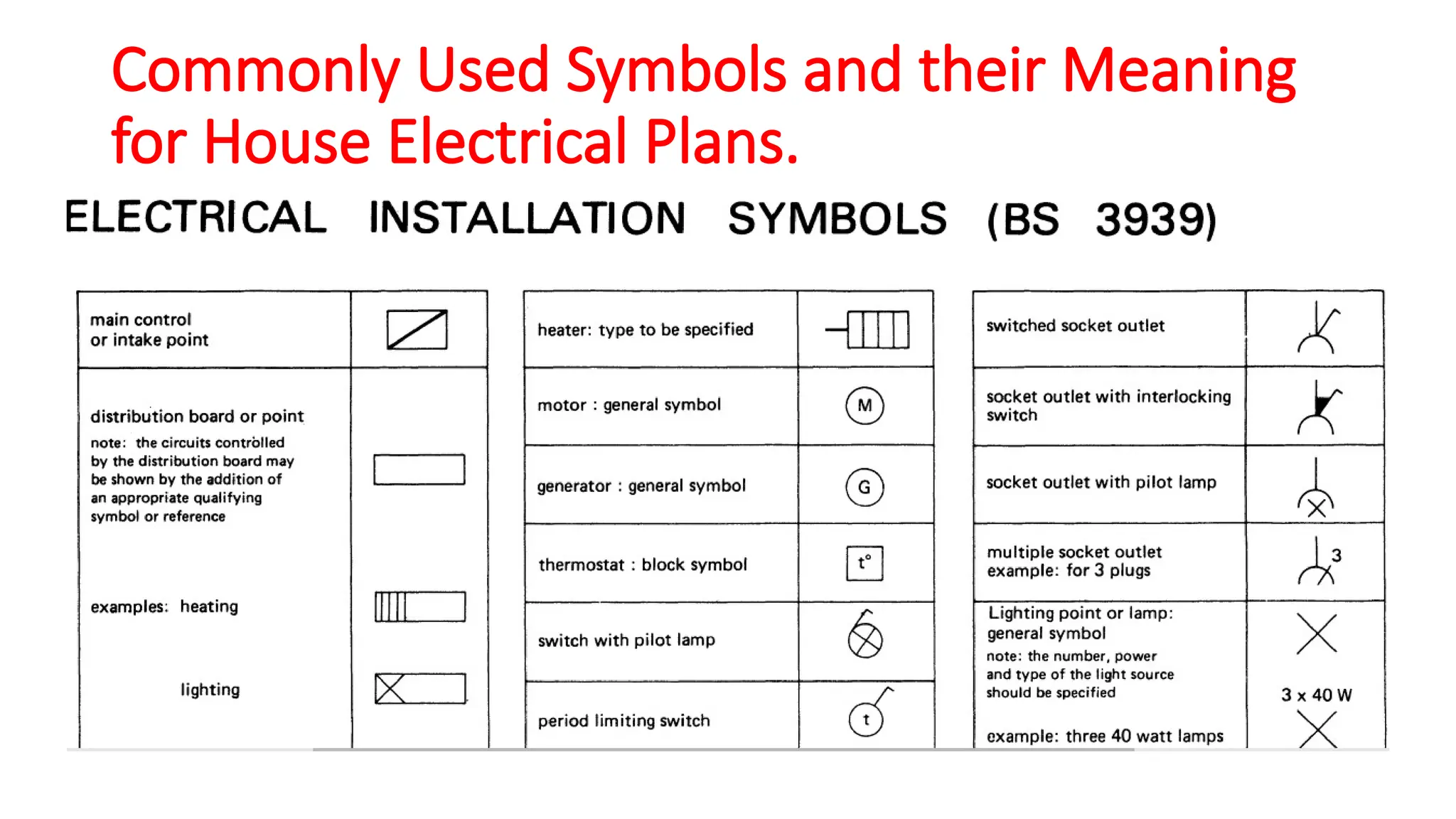
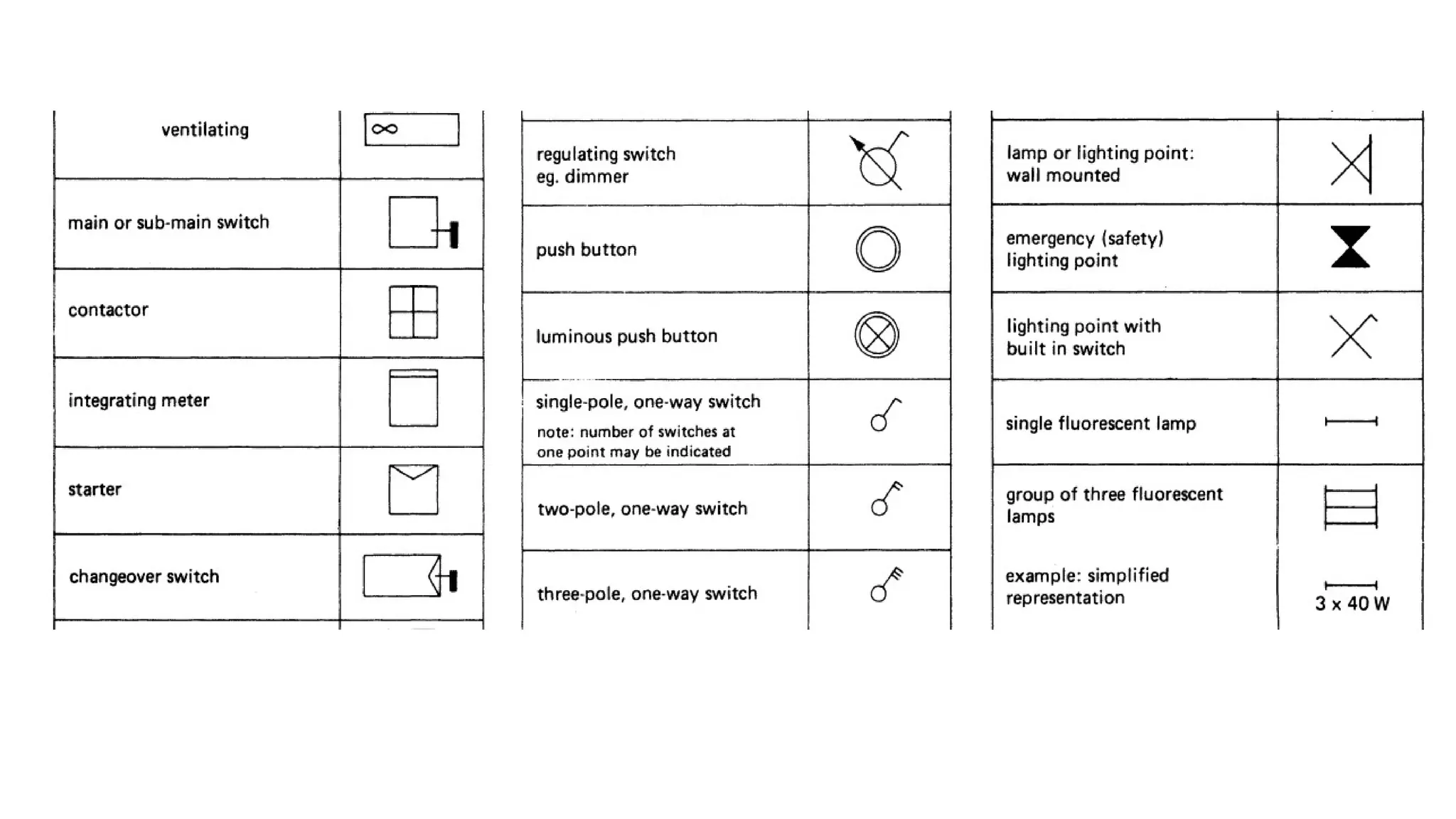
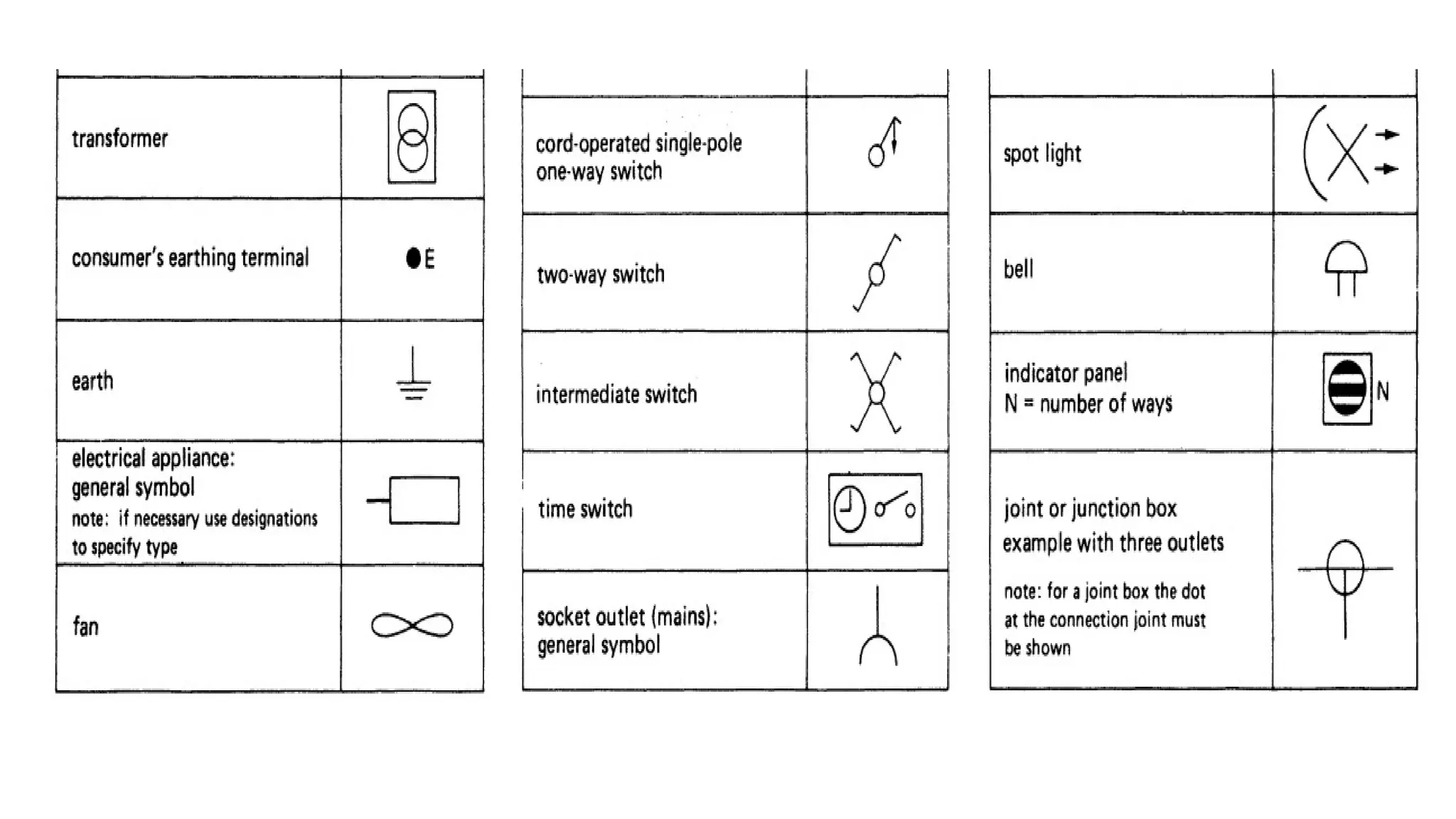
The document discusses electrical engineering drawing, highlighting its purpose as a graphical language to convey information for construction or analysis of systems. It outlines various types of drawings, methods of drafting, and necessary requirements, including symbols and dimensions, to create effective technical designs. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of these drawings in the electro-technical industry for design, maintenance, installation, and cost estimation.