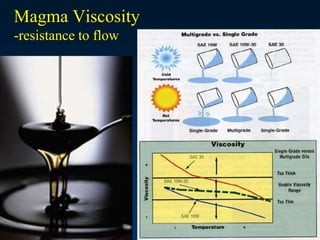
The document discusses the formation and characteristics of igneous rocks, explaining the differences between intrusive and extrusive types based on magma and lava behavior. It details the composition, textures, and the processes involved in magma evolution, including conditions leading to the formation of various magma types. Additionally, it covers the role of plate tectonics in the distribution and differentiation of igneous rocks.


![Lava flow in Hawaii
[magma @ the Earth’s
surface]
Pyroclastic Flow
Montserrat Volcano](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/igneousrocks-140416070648-phpapp02/85/Igneous-rocks-3-320.jpg)
![What is a rock? [Yes, you really do care.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/igneousrocks-140416070648-phpapp02/85/Igneous-rocks-4-320.jpg)
![The Nature of Igneous Rocks
• Form from Magma [Greek=“paste”]
– Hot, partially molten mixture of solid
liquid and gas
– Gases: H2O, CO2, etc.
– less dense than
solid rock
– solidify upon
cooling](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/igneousrocks-140416070648-phpapp02/85/Igneous-rocks-6-320.jpg)






























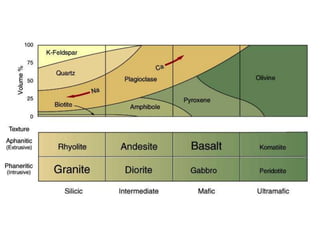
![IGNEOUS COMPOSITIONS
Granitic versus basaltic compositions
Granitic [felsic] composition
Light-colored silicates
Termed felsic (feldspar and silica) in composition
High silica (SiO2) content
Major constituent of continental crust
Basaltic [mafic] composition
Dark silicates and Ca-rich feldspar
Termed mafic (magnesium and ferrum, for iron) in
composition
Higher density than granitic rocks
Comprise the ocean floor and many volcanic islands](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/igneousrocks-140416070648-phpapp02/85/Igneous-rocks-40-320.jpg)











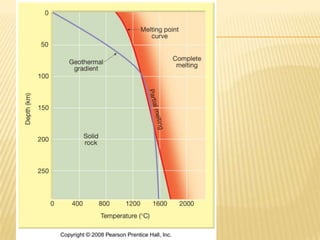
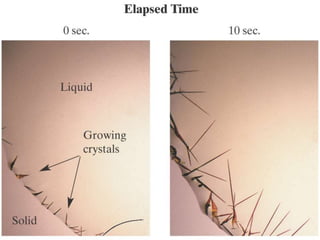

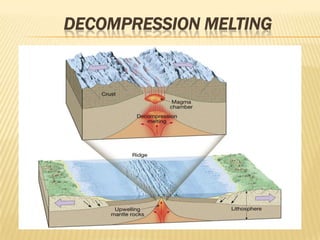
![Origin of Magmas
Generating magma from solid rock
• Role of heat
Temperature increases in the upper crust (geothermal gradient) average
between 20oC to 30oC per kilometer
Rocks in the lower crust and upper mantle are near their melting points
Additional heat may induce melting
• Role of pressure
Increases in confining pressure increases a rock’s melting temperature
When confining pressures drop, decompression melting occurs
• Role of volatiles
Volatiles (primarily water) cause melting at lower temperatures
Important factor where oceanic lithosphere descends into the mantle
• Solid rock is at equilibrium with its surrounding
• Changes in the surroundings cause solid rock magma [melting]
• Lowering P
Mantle convection moves deep mantle rocks upwards
• Raising T
Hot mafic magma intrudes into the crust
• Changing composition
Adding small amounts of water](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/igneousrocks-140416070648-phpapp02/85/Igneous-rocks-56-320.jpg)
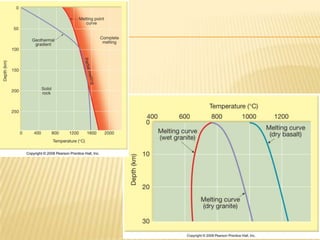
![How do rocks melt?
Heat: Geothermal Gradient
Temperature of most
Silicic magmas [600-800oC]
-about the base of crust
Temperature of Mafic
Magmas [1100-1200oC]
-upper mantle conditions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/igneousrocks-140416070648-phpapp02/85/Igneous-rocks-58-320.jpg)

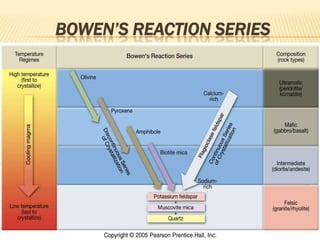


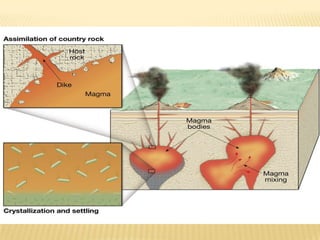

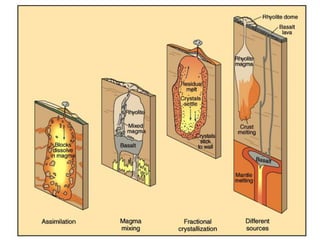
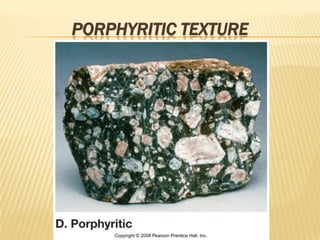
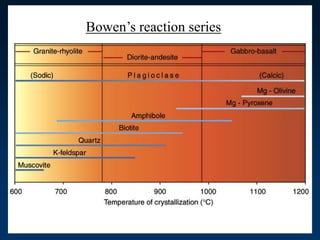
![• Partial Melting
– Individual minerals in source rock melt at
different T
– Magma is enriched in many elements,
especially SiO2
How do we know this?
Norman Bowen [1887-1956]
-Experimental Petrologist
-developed Bowen’s Reaction Series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/igneousrocks-140416070648-phpapp02/85/Igneous-rocks-66-320.jpg)
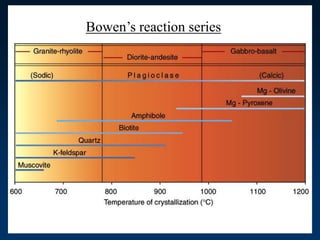
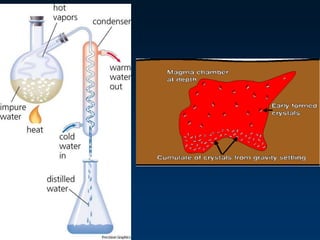
![• Fractional Crystallization
– Individual minerals precipitate from
magma at different T
– Magma is enriched in many elements,
especially SiO2
– Magma may migrate [buoyancy]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/igneousrocks-140416070648-phpapp02/85/Igneous-rocks-68-320.jpg)
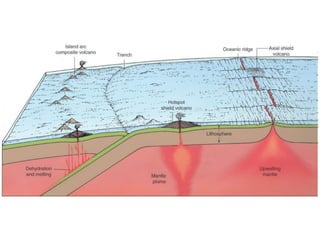
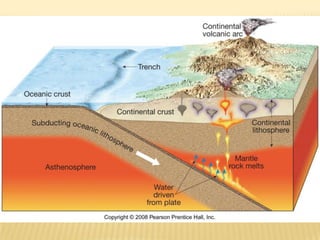
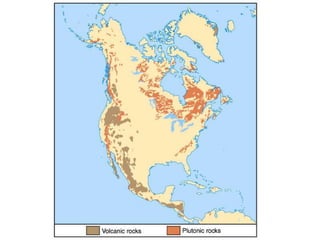
![Plate Tectonic Setting of Igneous Rocks
• Divergent Plate Boundaries
– Partial melting of mantle produces basaltic magma
• Convergent Plate Boundaries
– Subduction produces partial melting of basalt, sediments, parts of mantle
– Andesitic and rhyolitic magma
– Ascending magma assimilates lower crustal material
• Mantle Plumes
– Partial melting of plumes of mantle material
– Basaltic magma is produced
– Rising magma produce
• Intraplate island chains
• Flood basalt [Columbia River Basalts]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/igneousrocks-140416070648-phpapp02/85/Igneous-rocks-71-320.jpg)