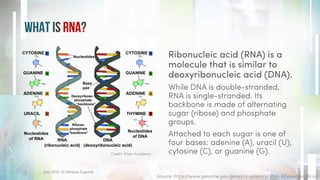
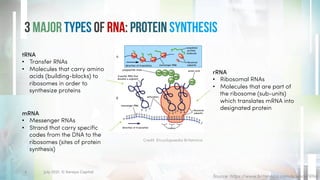
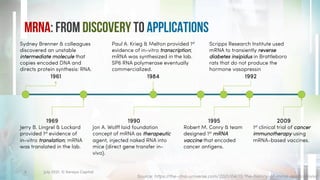
This document discusses the significance and applications of RNA technologies in life sciences, particularly highlighting their roles in vaccines, therapeutics, and agriculture. It covers the history of mRNA, the impact of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, and advancements in RNA therapies for various diseases. Additionally, it introduces innovative RNA-based solutions for crop biocontrol with minimal environmental impact.