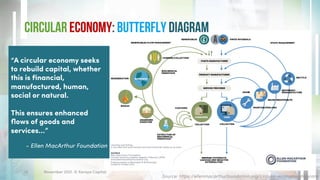
The document outlines the concept of a circular economy, defined as a sustainable model for production and consumption that prioritizes reusing and recycling materials to minimize waste. It emphasizes the benefits of such an economy, including reduced carbon emissions, prolonged product life, and economic opportunities. Moreover, Xeraya Capital is committed to investing in initiatives that promote circular economy practices.