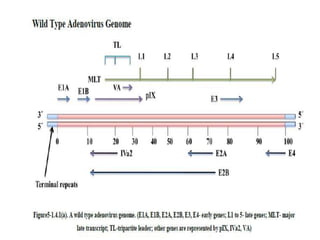
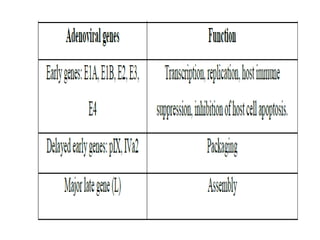
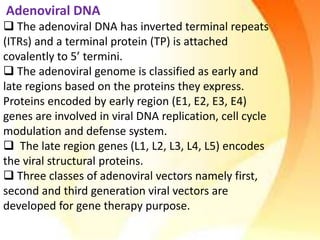
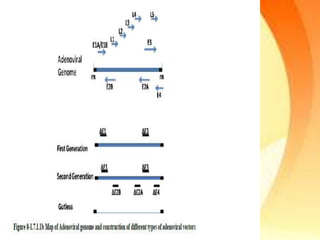
Adenoviral vectors are modified adenoviruses that can deliver genetic material into host cells. Adenoviruses are medium-sized, non-enveloped viruses containing double-stranded DNA. They can efficiently transfer DNA/RNA into cells and have been used to construct viral vectors. Wild type adenoviruses are modified by deleting non-essential genes and adding exogenous genetic material to create viral vectors. Three generations of adenoviral vectors have been developed for gene therapy, with later generations having improved safety profiles and ability to carry larger DNA payloads.