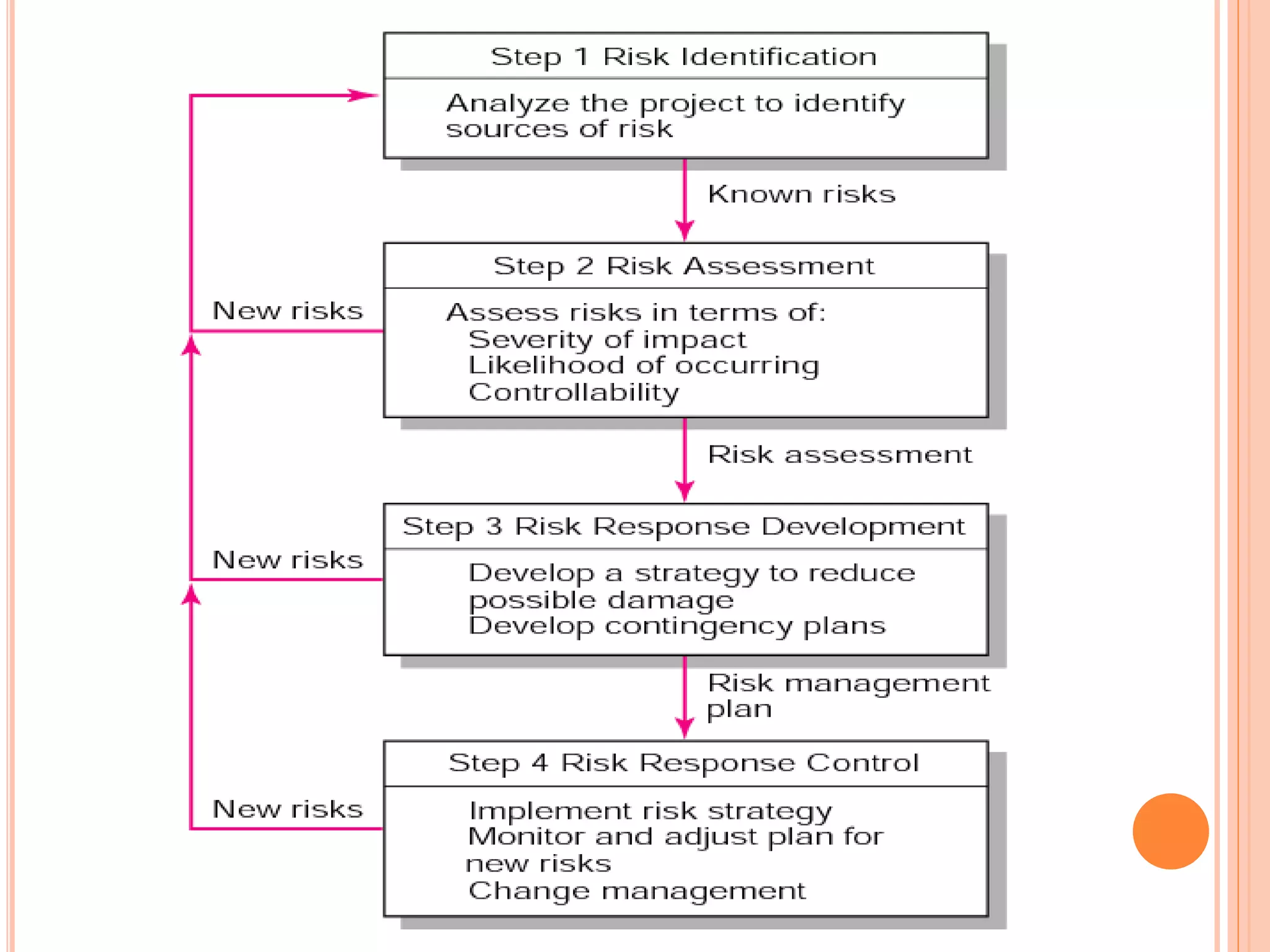
The document outlines a risk management process including risk identification, assessment, response planning, and control. It discusses internal risks like technical and market risks as well as external risks outside a project manager's control. Risks are identified and assessed based on probability and impact. Responses include transferring risk, avoiding risk through plan changes, reducing risk through contingency planning, and accepting some level of risk. The overall process helps manage risks to meet schedule, budget and technical objectives.