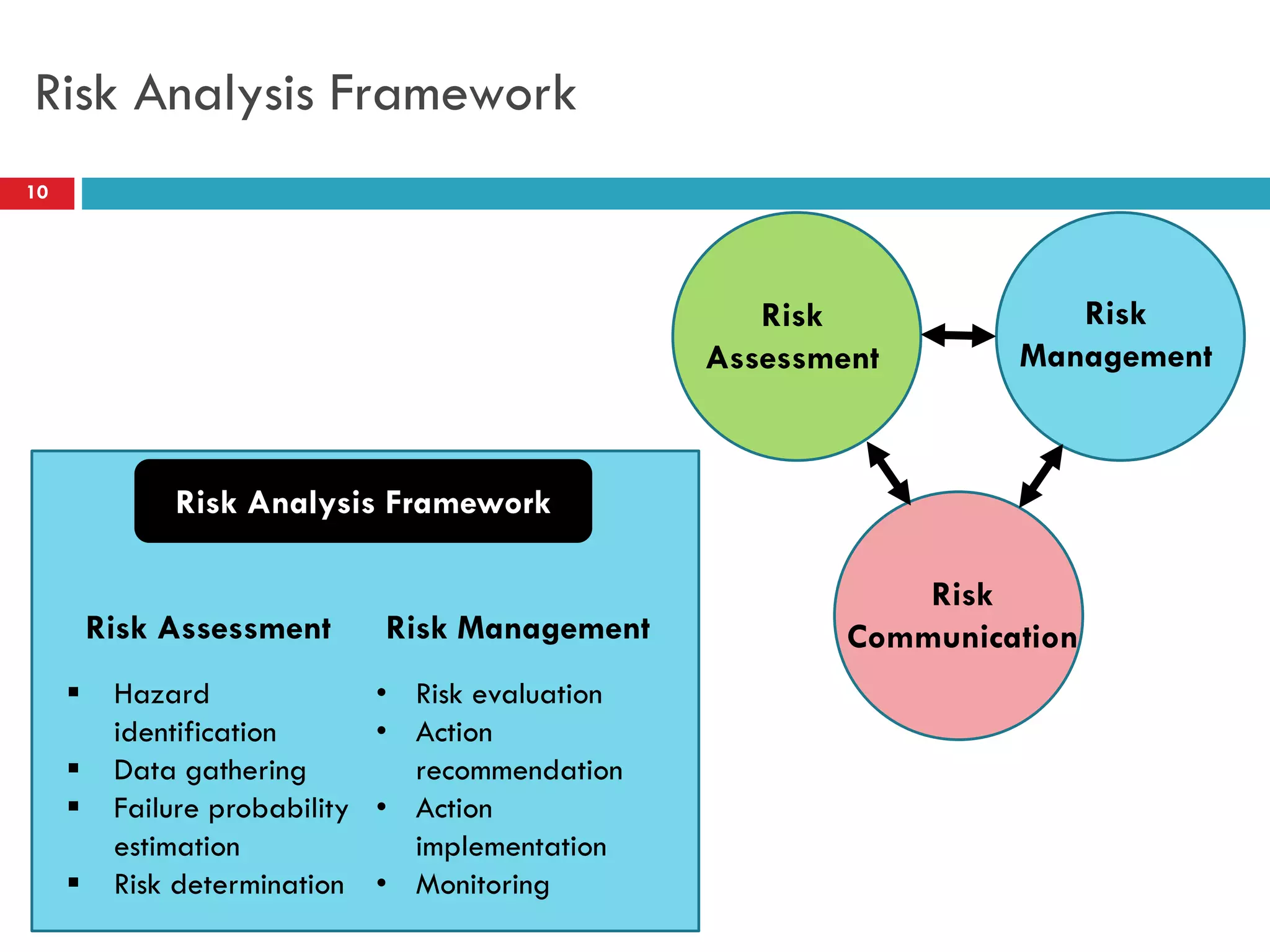
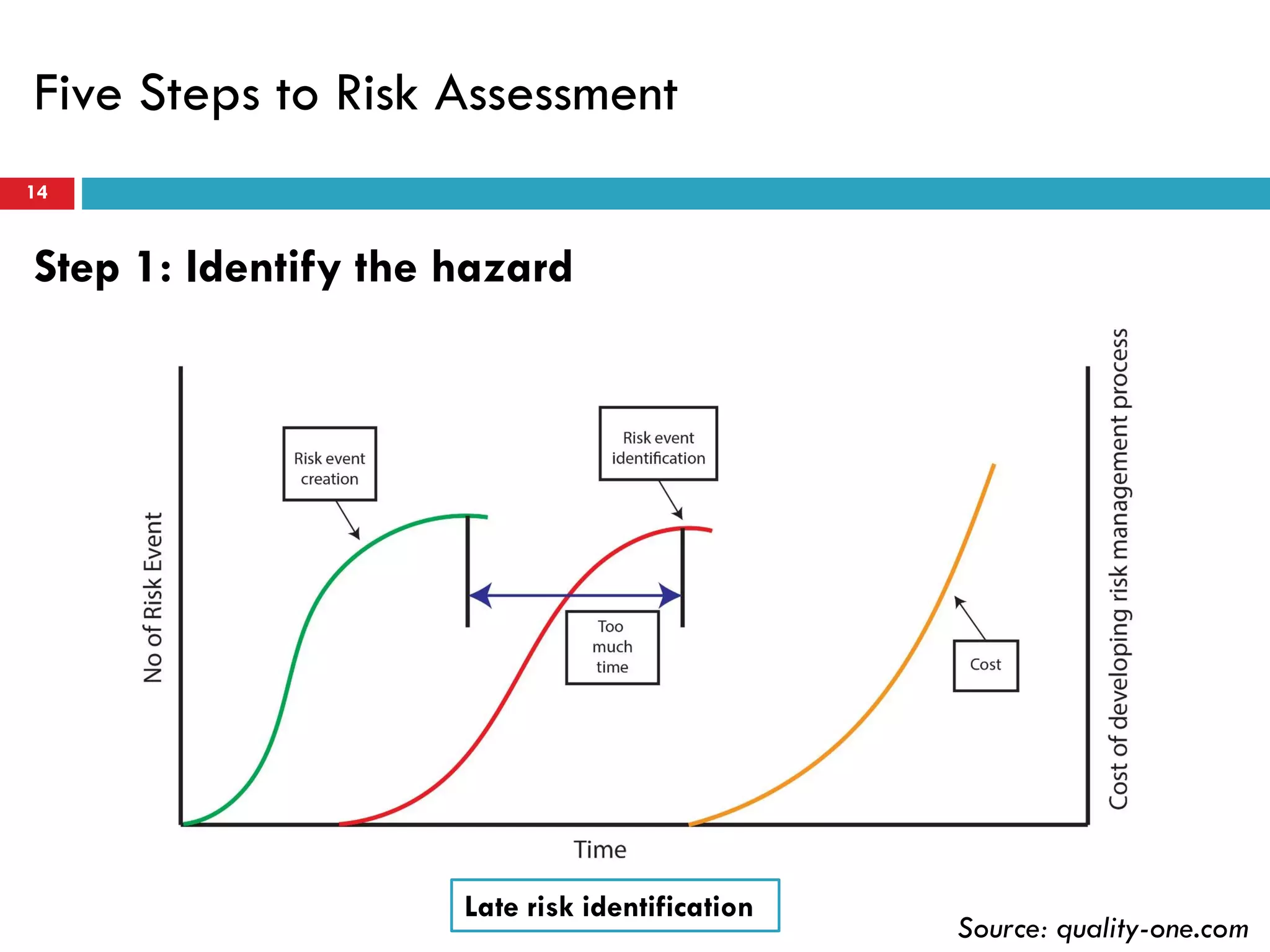
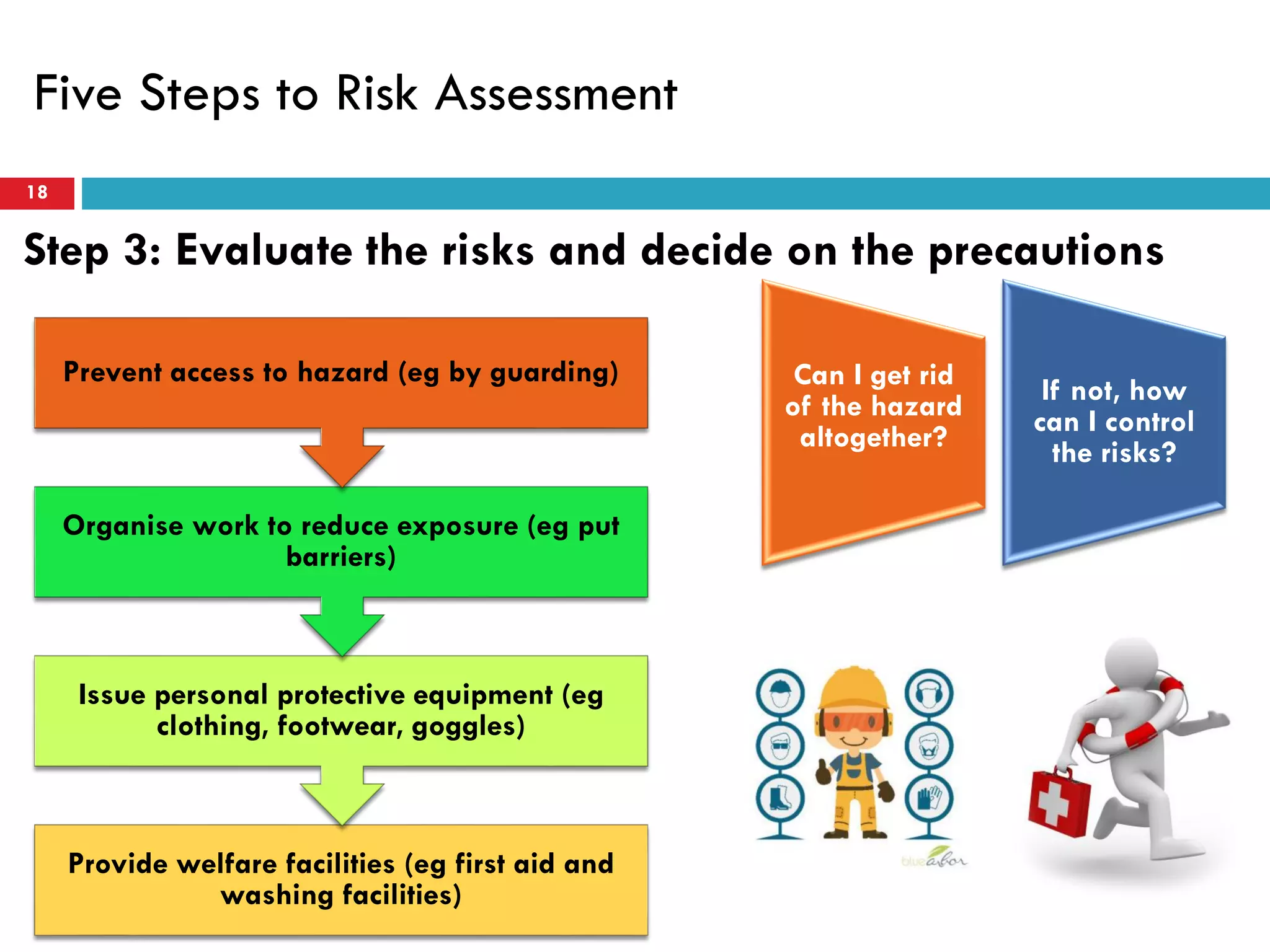
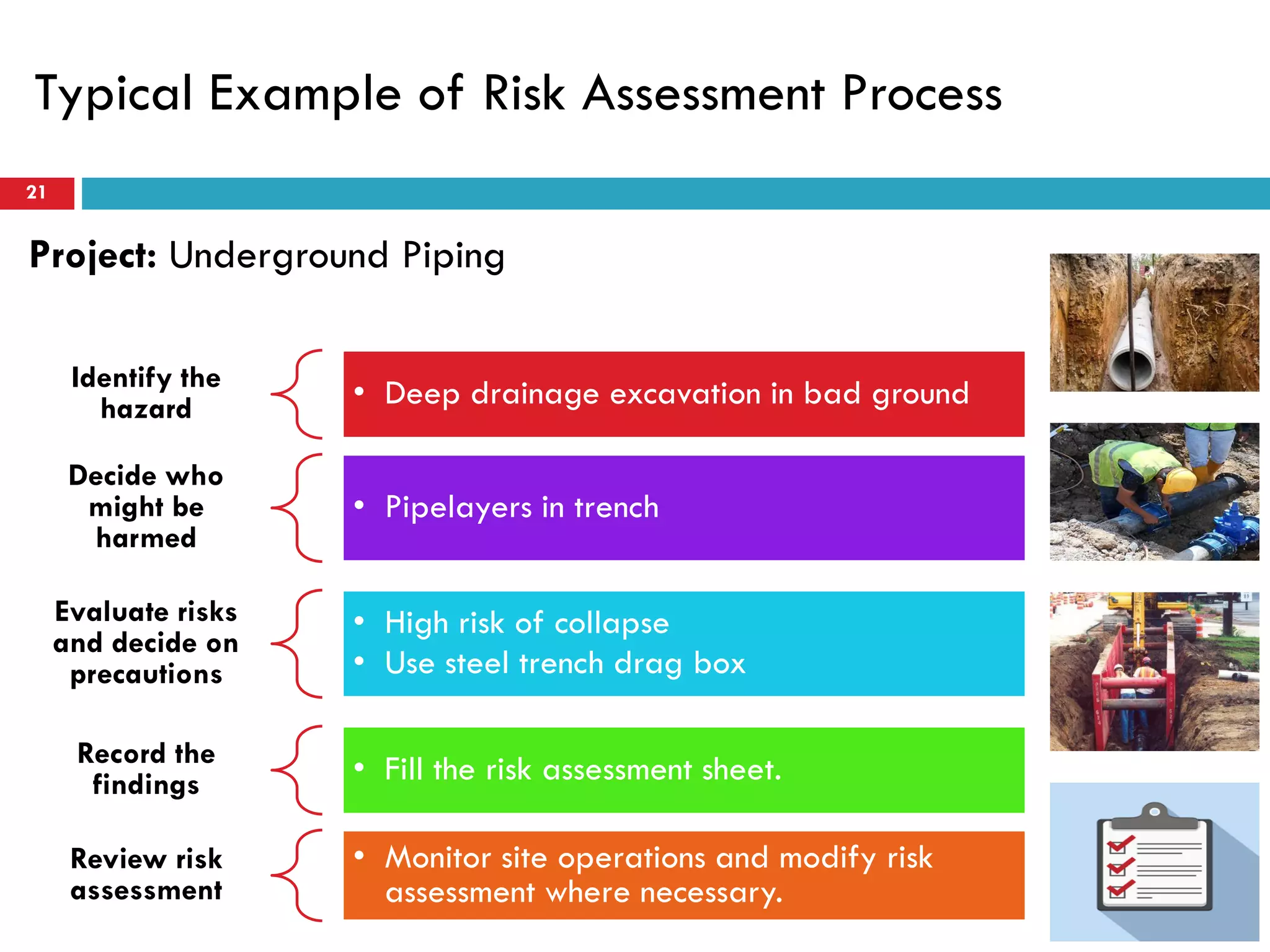
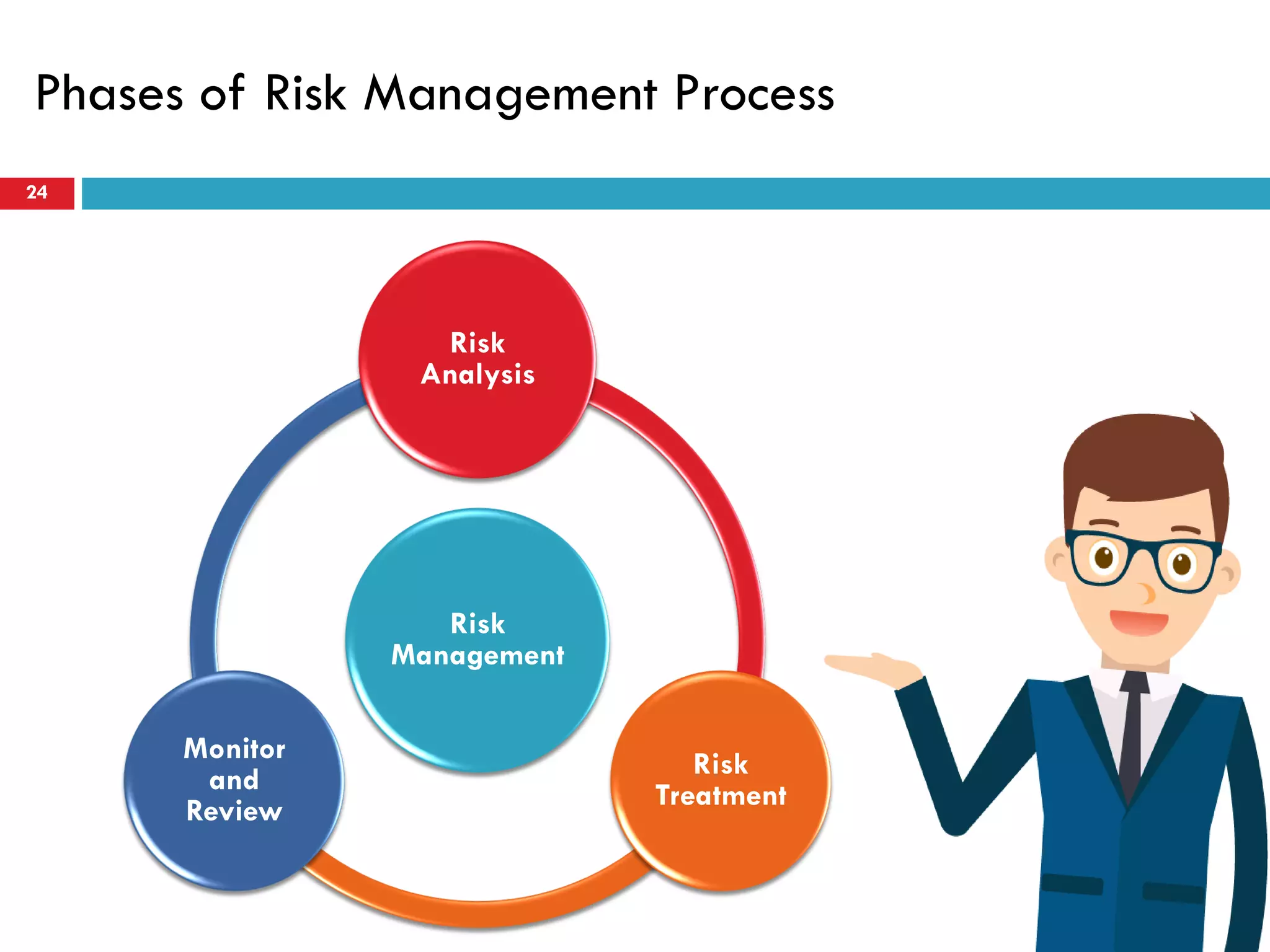
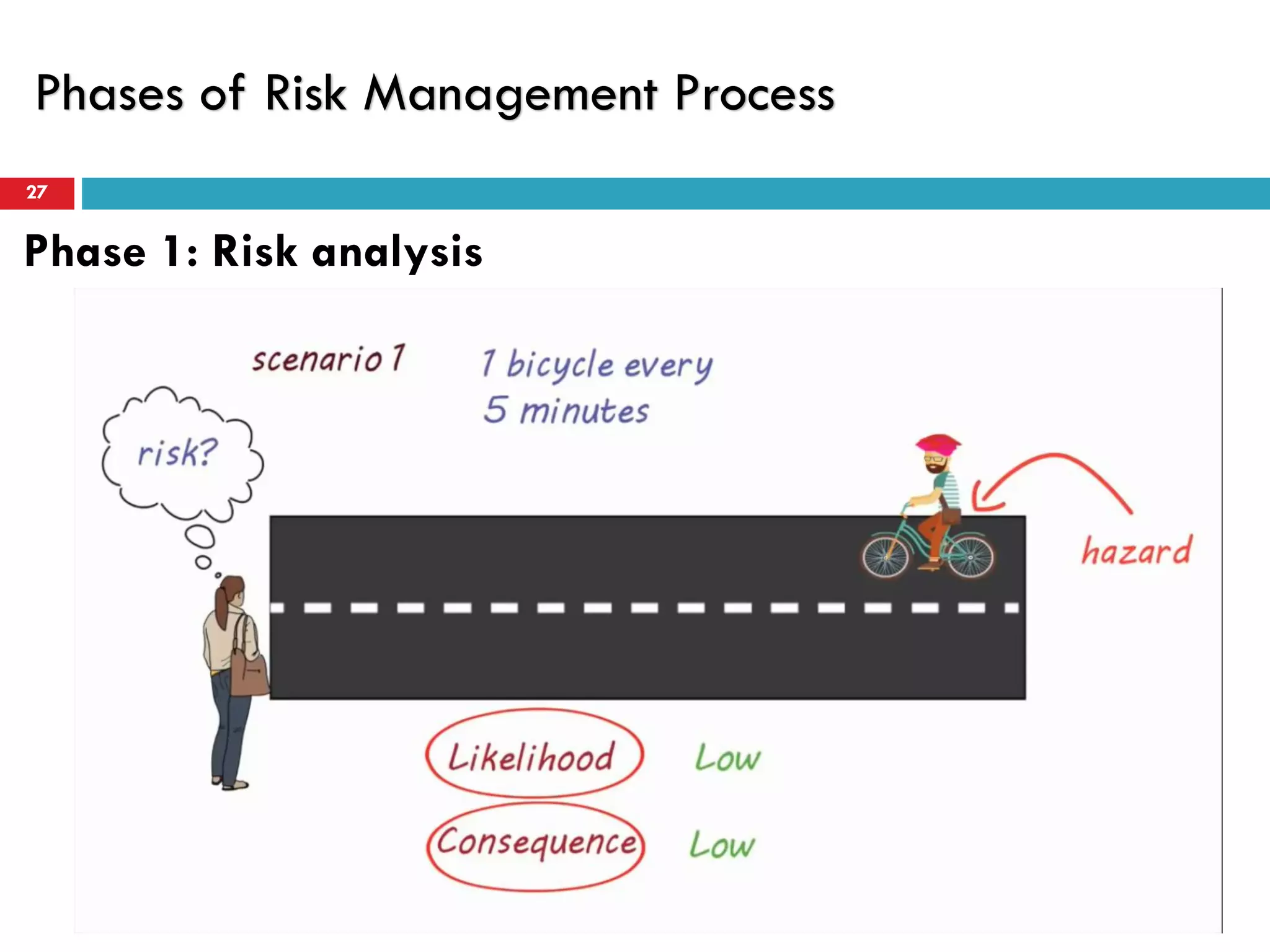
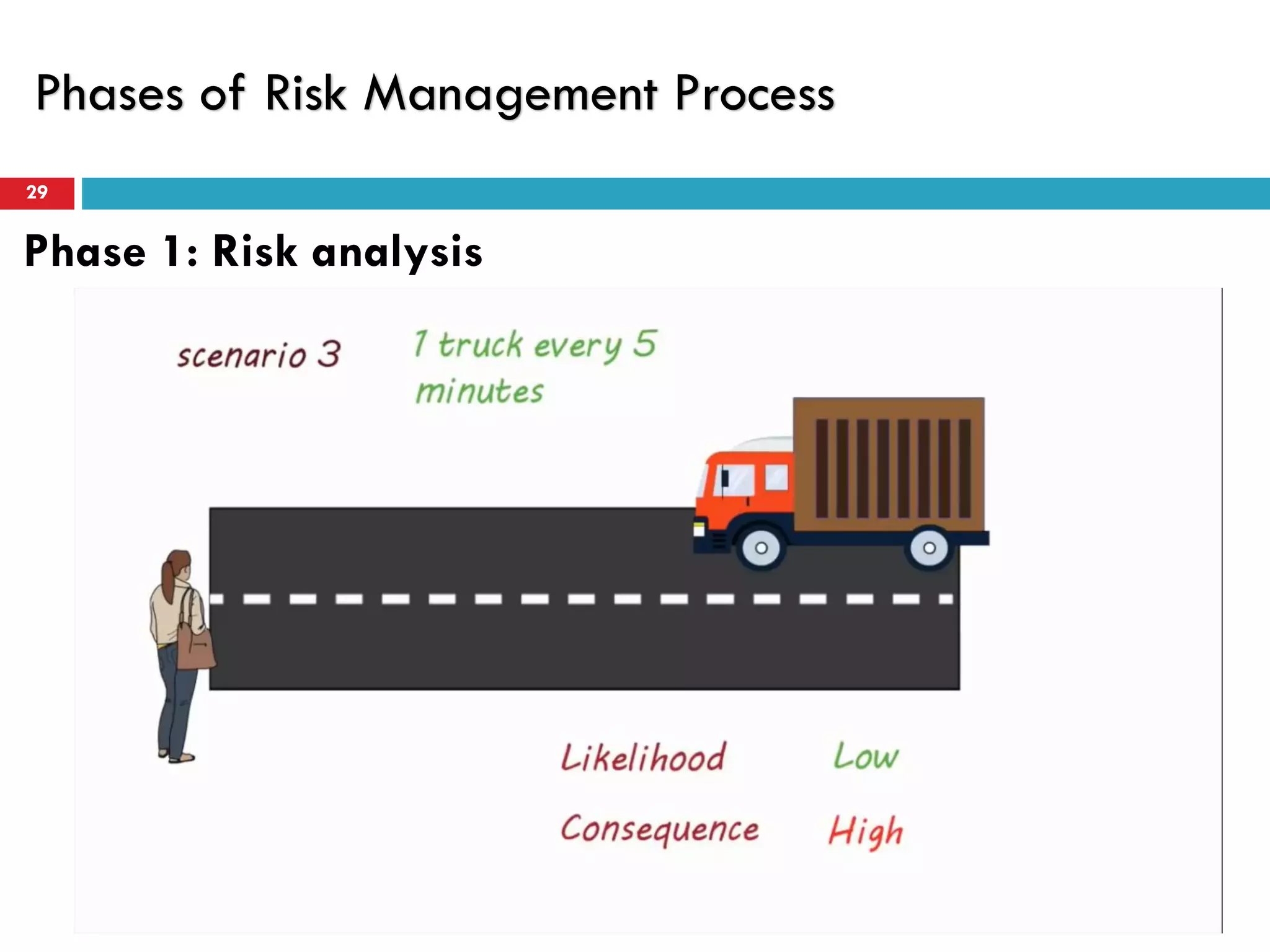
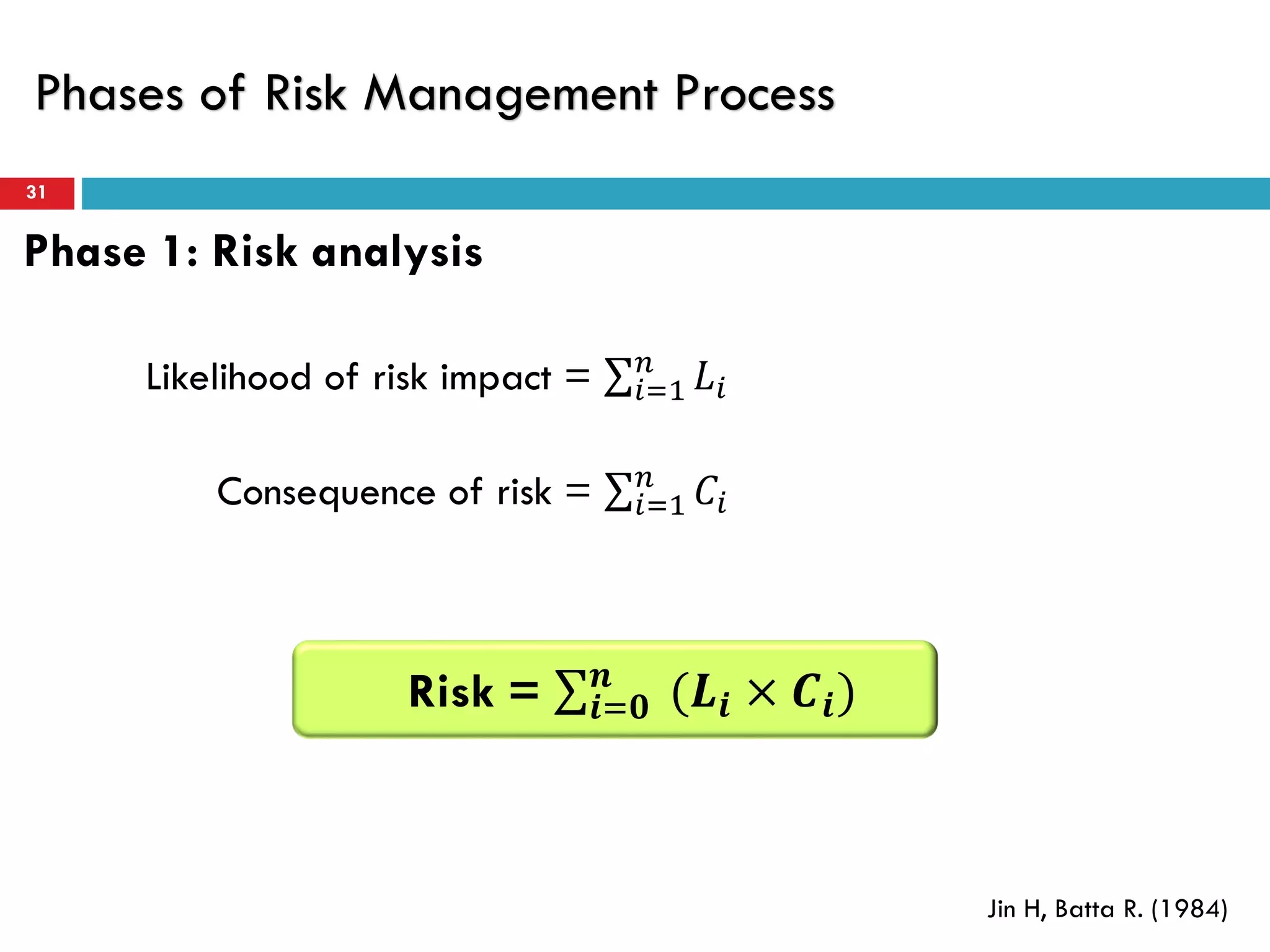
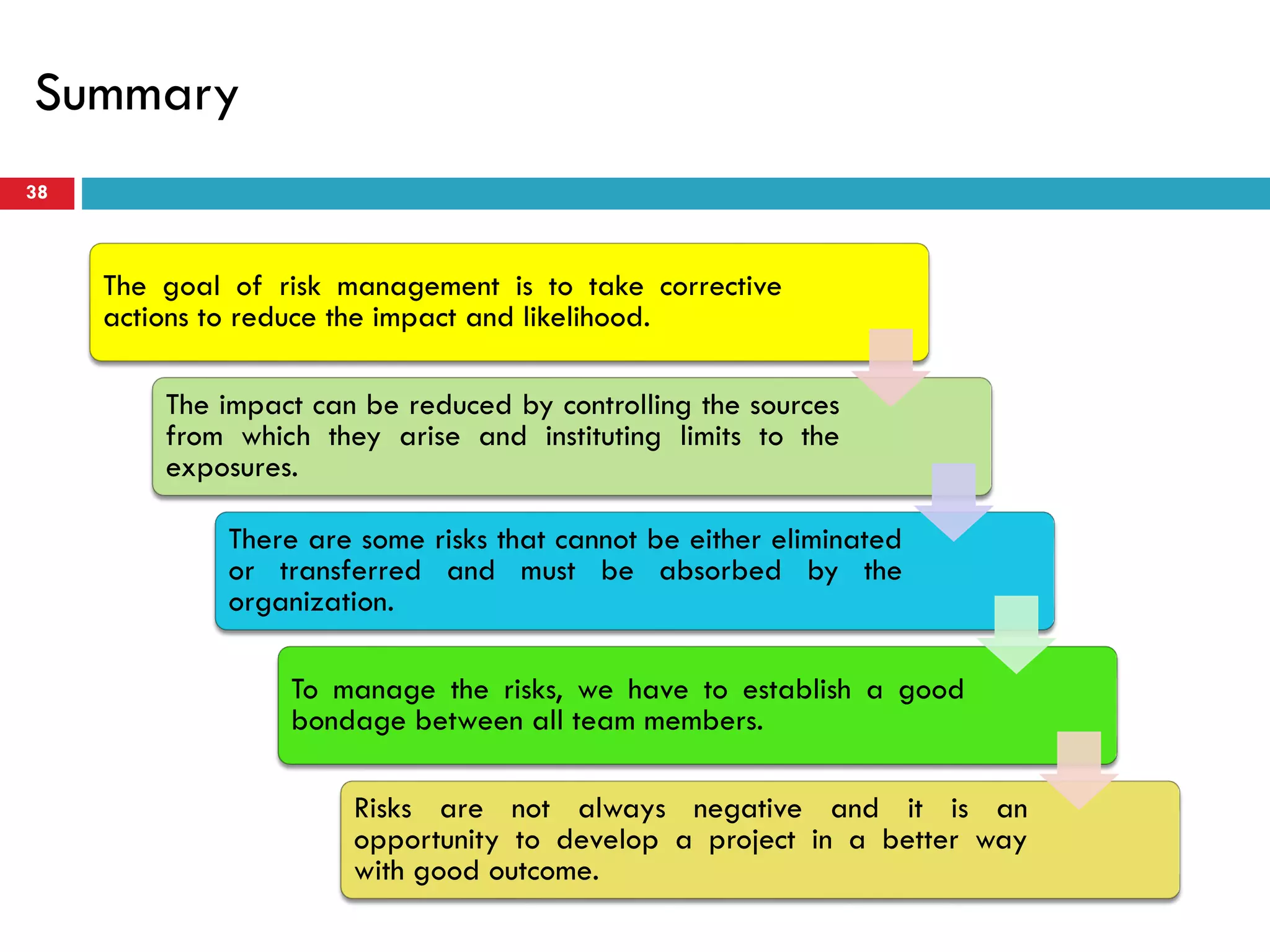
Risk assessment and management involves five key steps: 1) identifying hazards, 2) deciding who might be harmed, 3) evaluating risks and precautions, 4) recording findings, and 5) reviewing assessments. A typical risk assessment process first identifies hazards like trench collapse, then evaluates who may be harmed (pipe layers), assesses risks, decides on controls like trench boxes, records findings, and reviews assessments during monitoring. Risk management aims to reduce likelihood and consequences of risks through analysis, treatment, and ongoing monitoring and review to control risks.