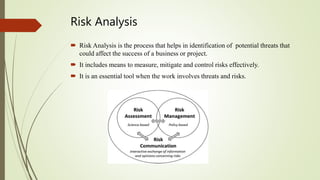
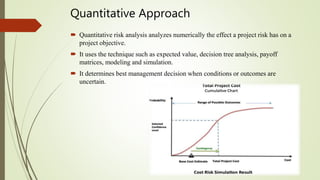
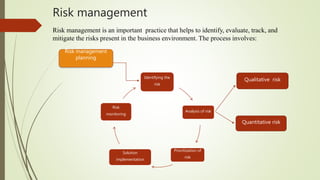
This document discusses project risk management. It defines project risk as an uncertain event that may positively or negatively impact project objectives. There are various types of risks including external risks outside a manager's control, cost risks, schedule risks, technology risks, and operational risks. The document outlines qualitative and quantitative approaches to risk analysis and describes methods for risk identification, response planning including risk avoidance, transfer, mitigation and acceptance, monitoring and control. Regular risk management is important to identify uncertainties and minimize their impacts to help projects meet their objectives on time and on budget.