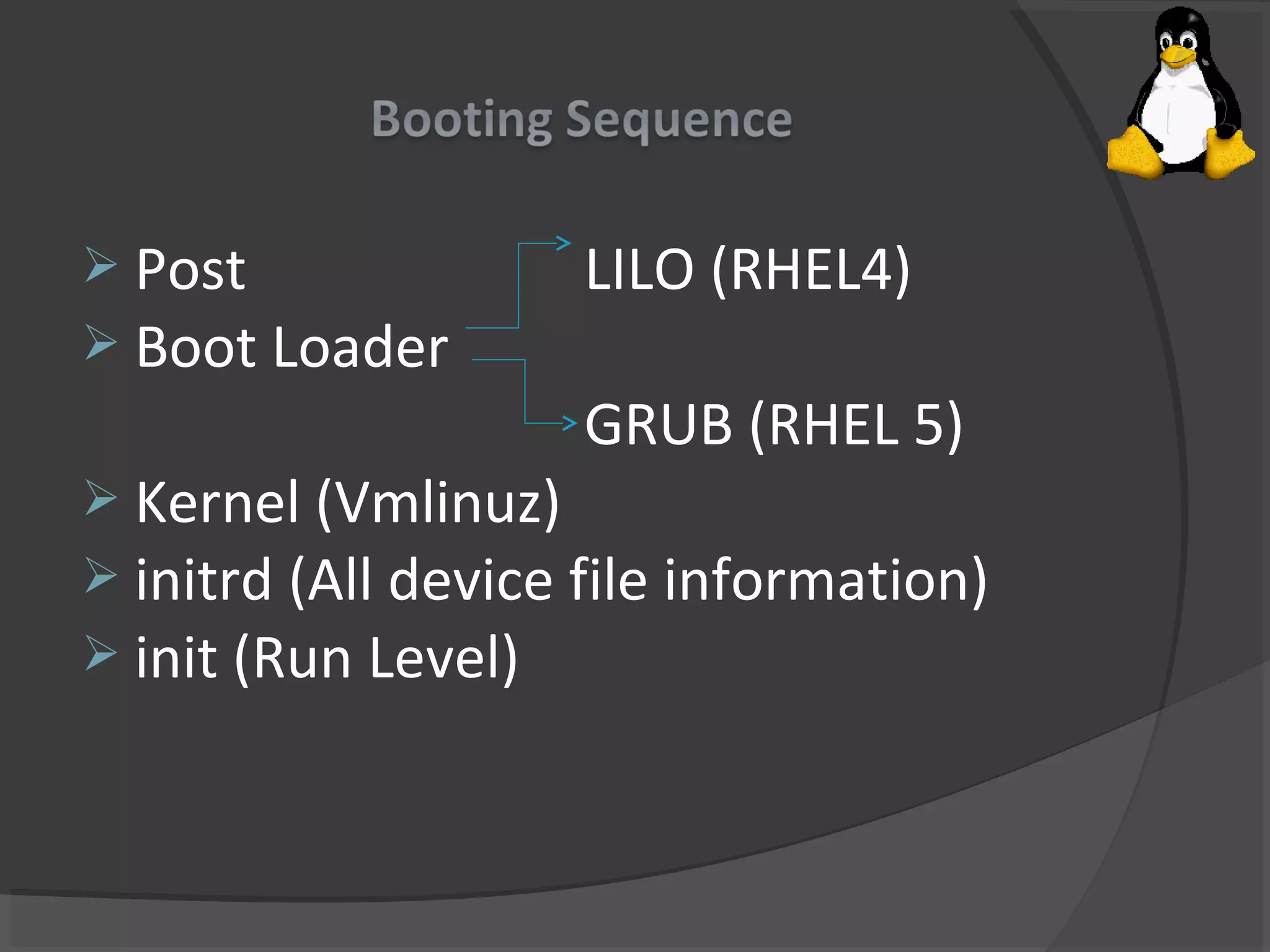
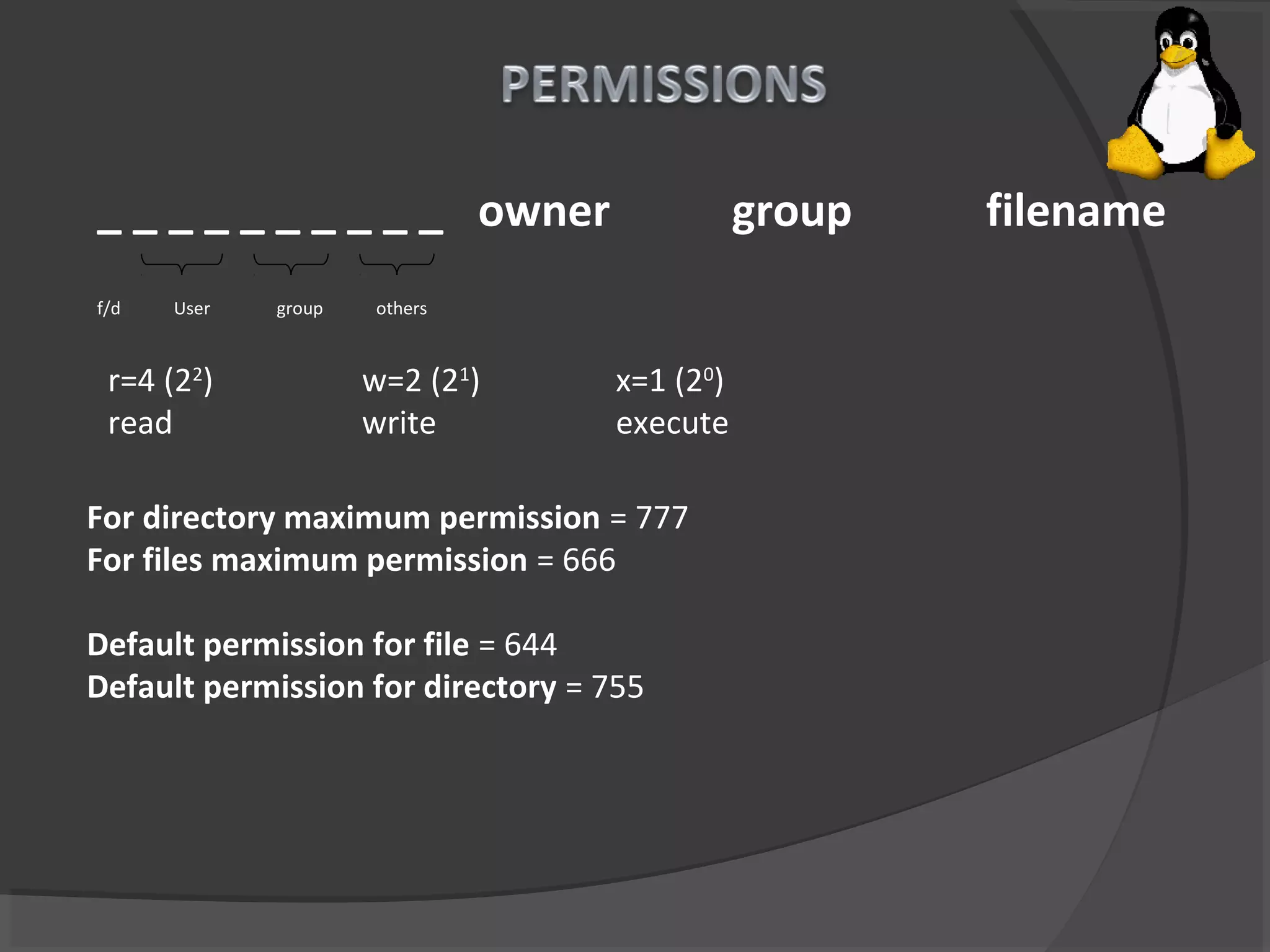
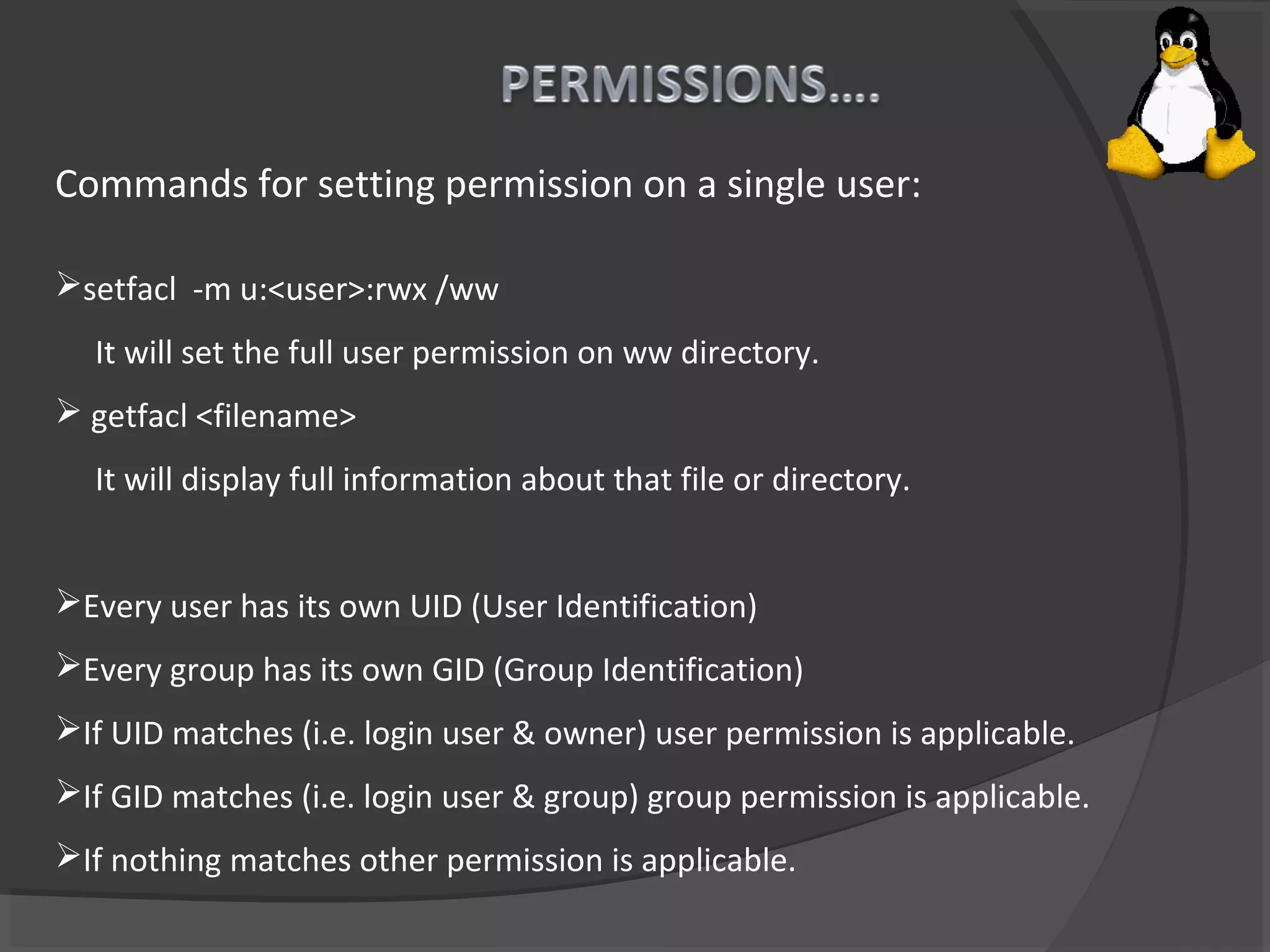
This document summarizes the history and development of Unix and Linux operating systems. It describes how Unix was created in 1969 at Bell Labs by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie and others. Brian Kernighan named the program Unix in 1970. The operating system was later rewritten in C language by Dennis Ritchie. Linux was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 based on Unix. The document also provides system requirements and descriptions of common Linux commands and file system structure.