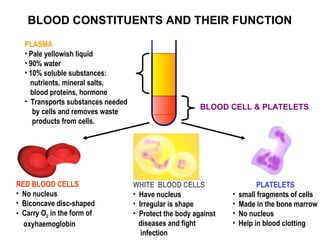
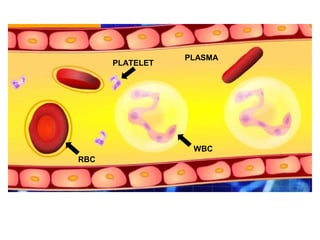
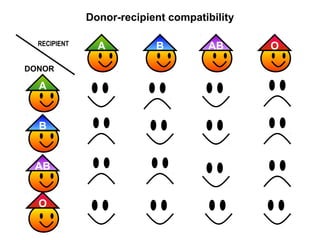
Blood is composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Plasma transports substances through the body and removes waste, while red blood cells carry oxygen through hemoglobin. White blood cells protect the body against infection and disease. Platelets help the blood to clot. There are four main blood groups - A, B, AB, and O - and compatibility between donor and recipient blood is important to avoid clotting. People with type O blood are universal donors and can donate to all groups, while those with type AB blood are universal recipients. Blood donation is important as blood cannot be manufactured and is needed for medical procedures, accidents, childbirth, and other illnesses. Donated blood is tested,