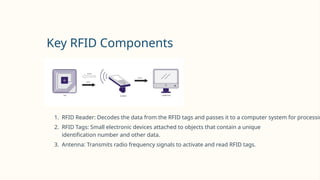
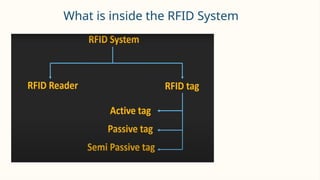
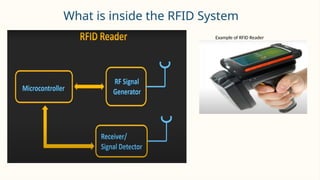
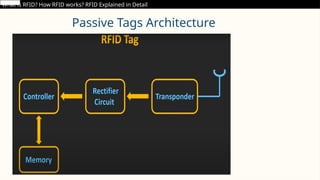
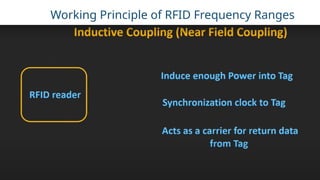
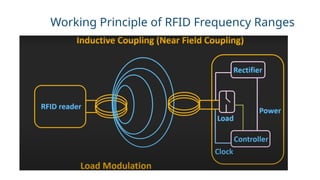
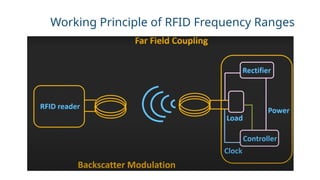
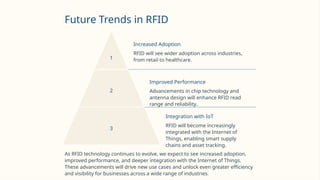
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a wireless technology that enables contactless identification and tracking of objects through embedded tags, antennas, and readers. Its applications span multiple sectors including supply chain management, access control, and inventory tracking, providing benefits such as improved efficiency and enhanced security. However, concerns regarding security breaches and privacy must be addressed as RFID technology continues to evolve and integrate with other technologies like IoT.