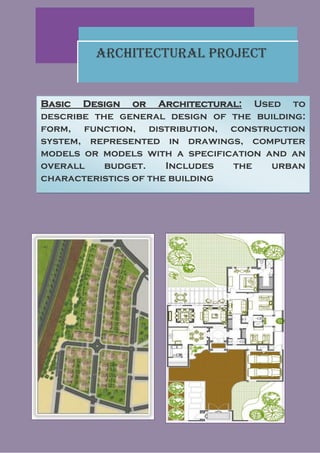
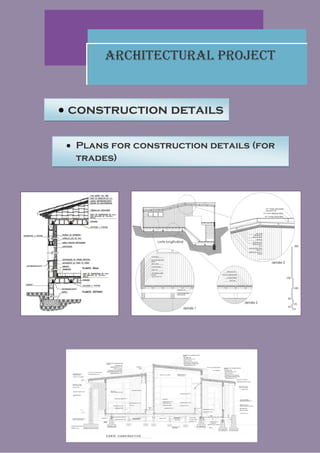
The document discusses the various stages of an architectural project from initial research and defining needs, to developing a program, basic design, draft plans, and finally execution plans. It explains key elements at each stage such as creating an architectural diagram, basic outline design, and draft drawings. The execution project stage involves creating detailed construction plans, specifications, and documents to guide the building process.