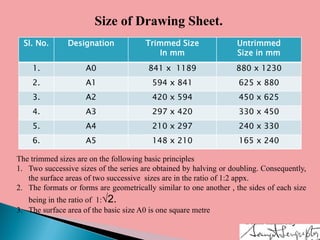
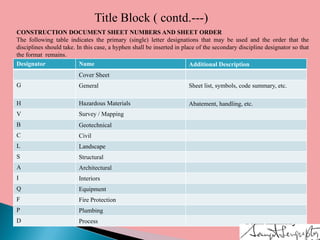
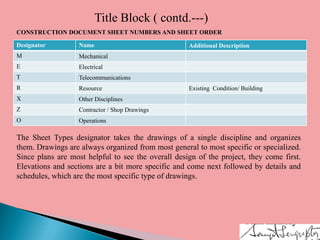
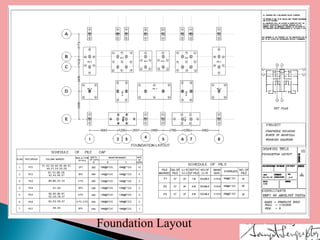
Architectural working drawings are technical drawings that provide all necessary information to construct a building project using graphical representations. They include plans, sections, elevations, schedules and specifications. The drawings are prepared according to conventions using appropriate scales, symbols and dimensions. They serve to communicate design details to construction teams, guide contractors, and obtain necessary approvals from authorities. Key components of working drawings include title blocks, site plans, floor plans, sections, elevations, structural details and specifications of finishes.