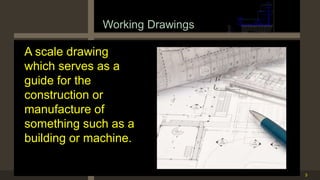
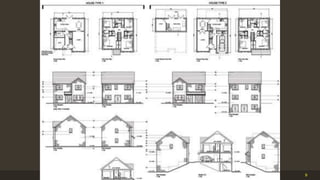
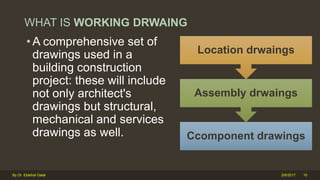
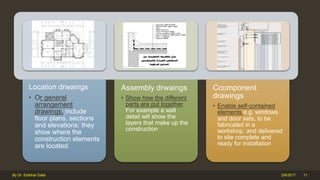
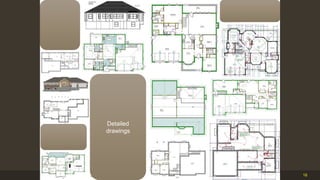
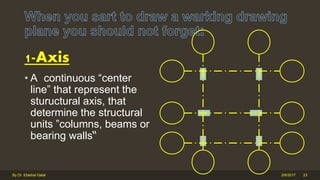
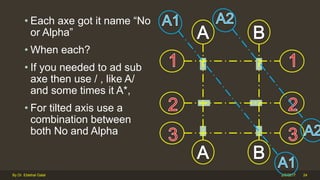
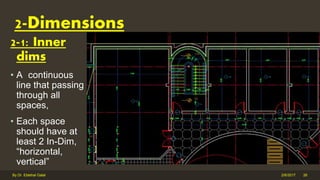
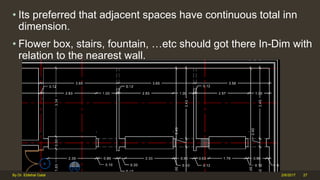
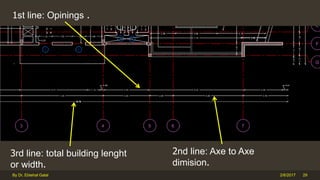
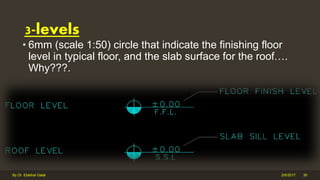
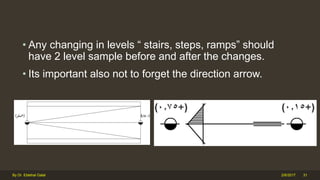
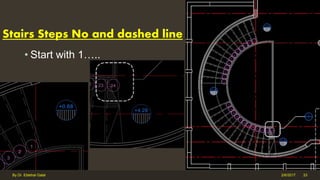
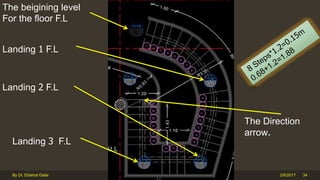
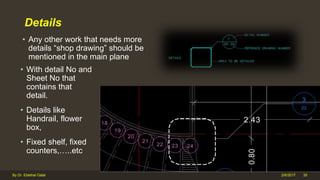
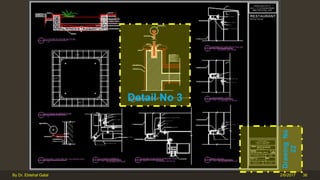
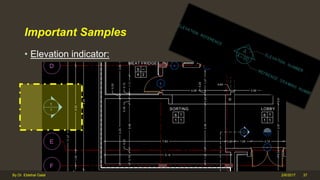
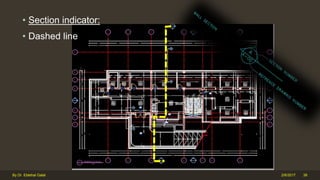
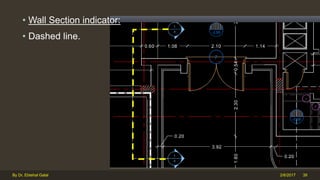
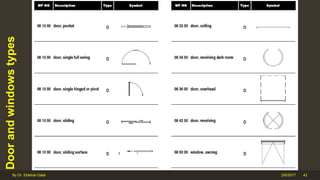
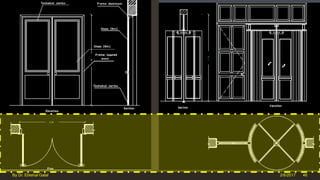
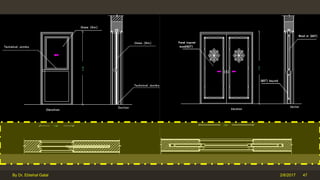
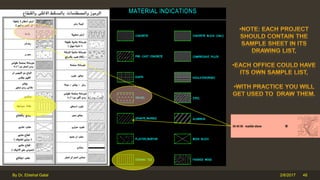
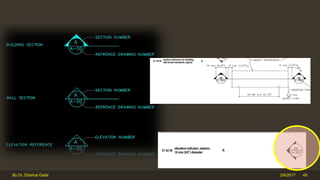
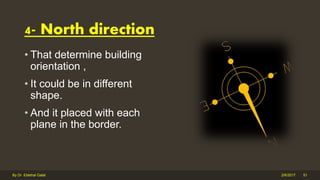
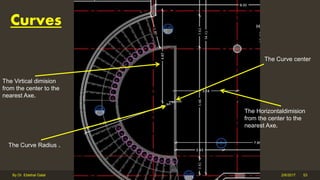
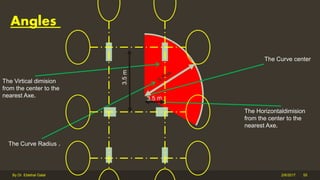
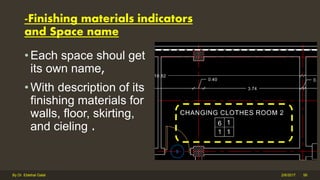
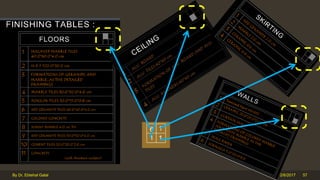
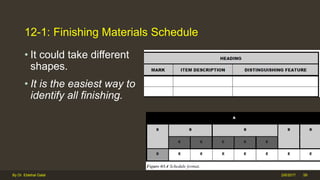
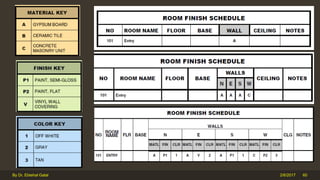
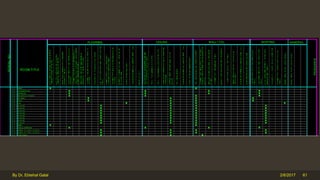
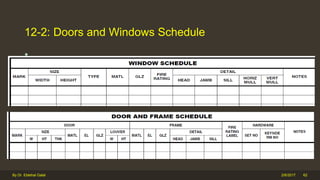
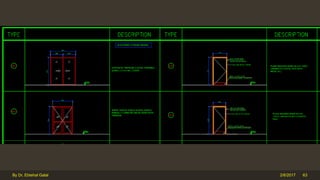
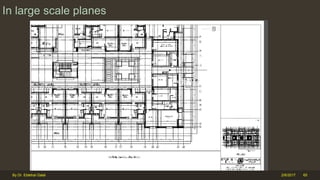
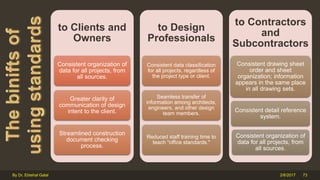
The document outlines the importance and components of working drawings in architectural and construction projects, which include various types of drawings such as location, assembly, and component drawings. It emphasizes the necessity of comprehensive documentation to guide construction processes, ensuring accurate representation of designs and adherence to specifications. Additionally, it discusses the significance of standards for CAD systems to promote consistency in drawing presentation and data communication across different stakeholders in a project.