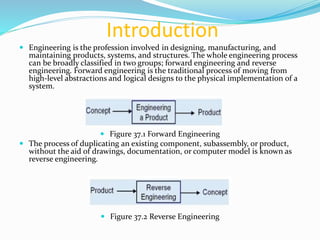
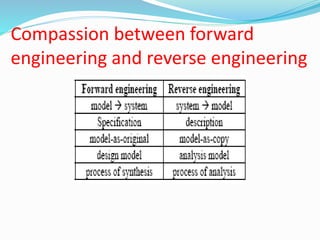
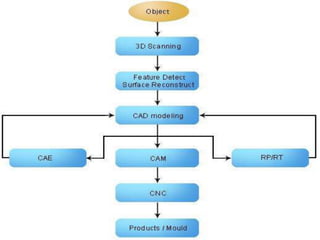
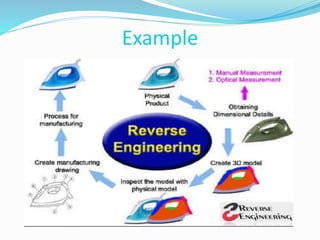
This document discusses reverse engineering and its importance. Reverse engineering is the process of analyzing a system to understand its components and recreate it without prior documentation. This allows reducing product development times for manufacturers. The methodology involves digitizing the object, creating a CAD model through discretization and data manipulation, and generating a functional part. Reverse engineering provides advantages like cost savings, quality improvements, and competitive advantages. Its applications include manufacturing, medical, and software fields.