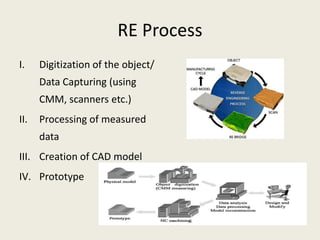
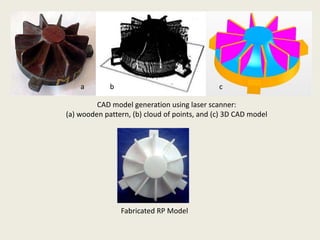
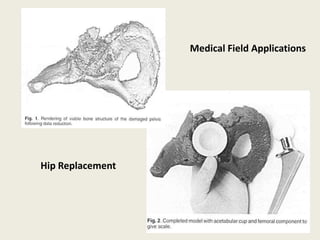
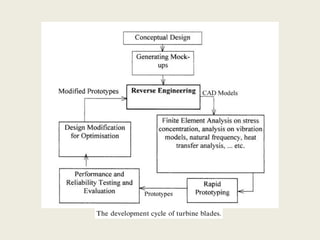
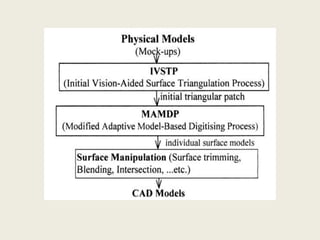
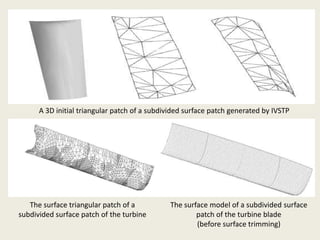
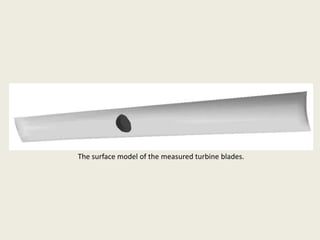
Reverse engineering is the process of systematically evaluating a product to replicate or redesign it. It is an important step in product development that allows optimization of resources and reduction in development time and costs. The reverse engineering process involves digitizing an existing object through scanning or other methods, processing the captured data to create a CAD model, and then using that model to develop prototypes or redesign parts as needed. It has various applications in fields like manufacturing, software, chemicals, entertainment, and medicine. A case study described how reverse engineering and rapid prototyping were used together to redesign turbine blades by capturing high-quality surface data and iteratively digitizing to create accurate CAD models.