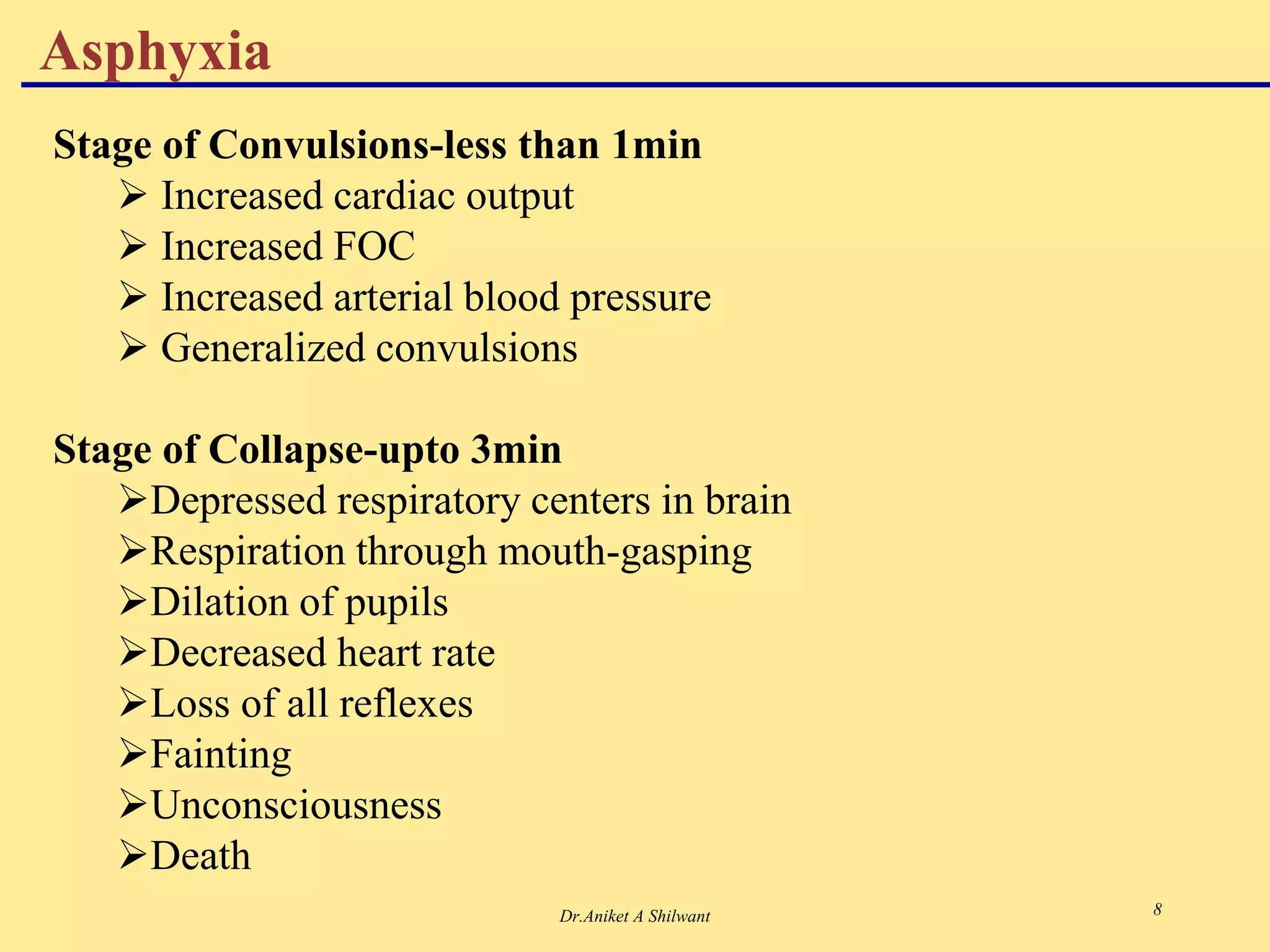
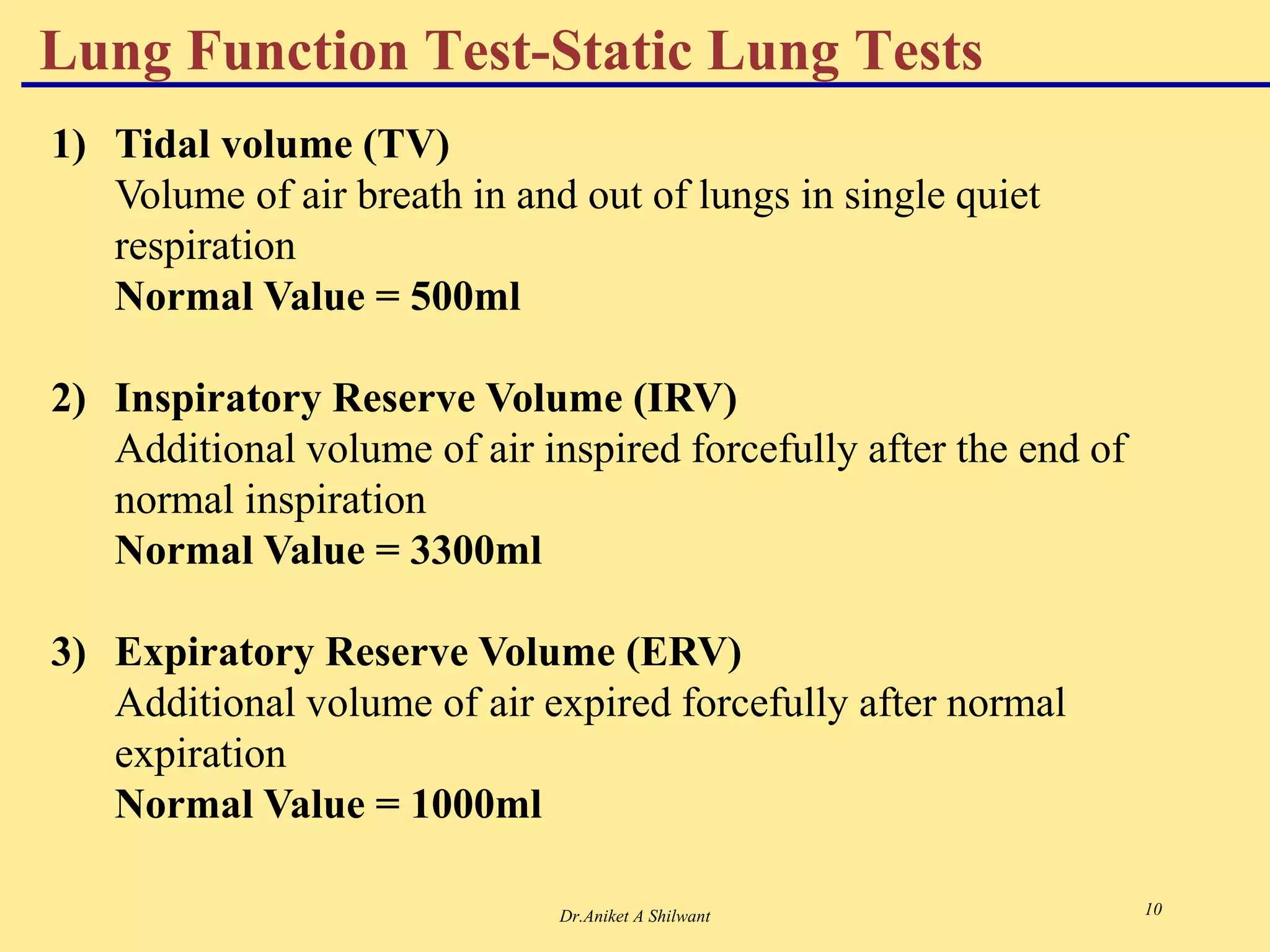
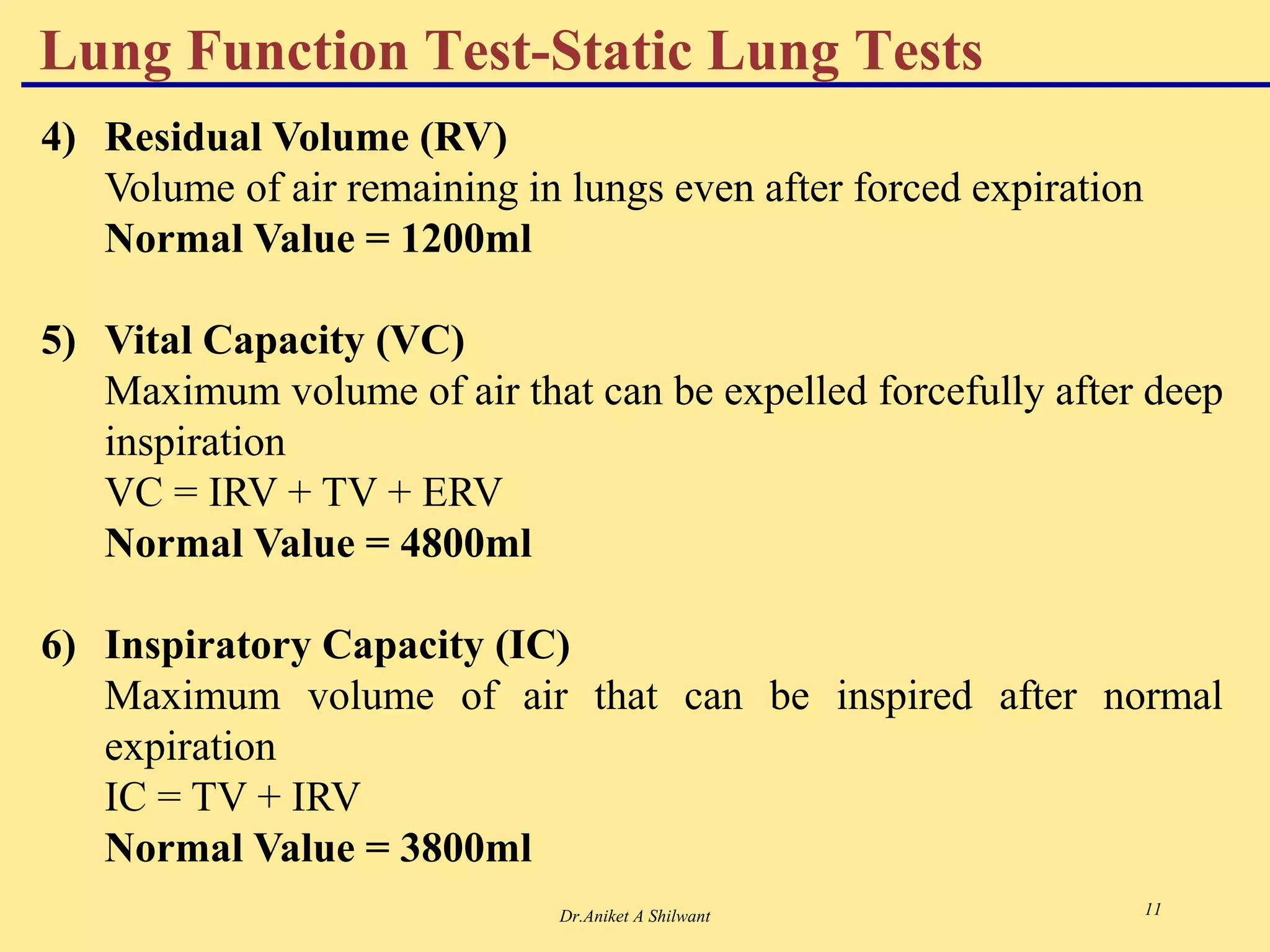
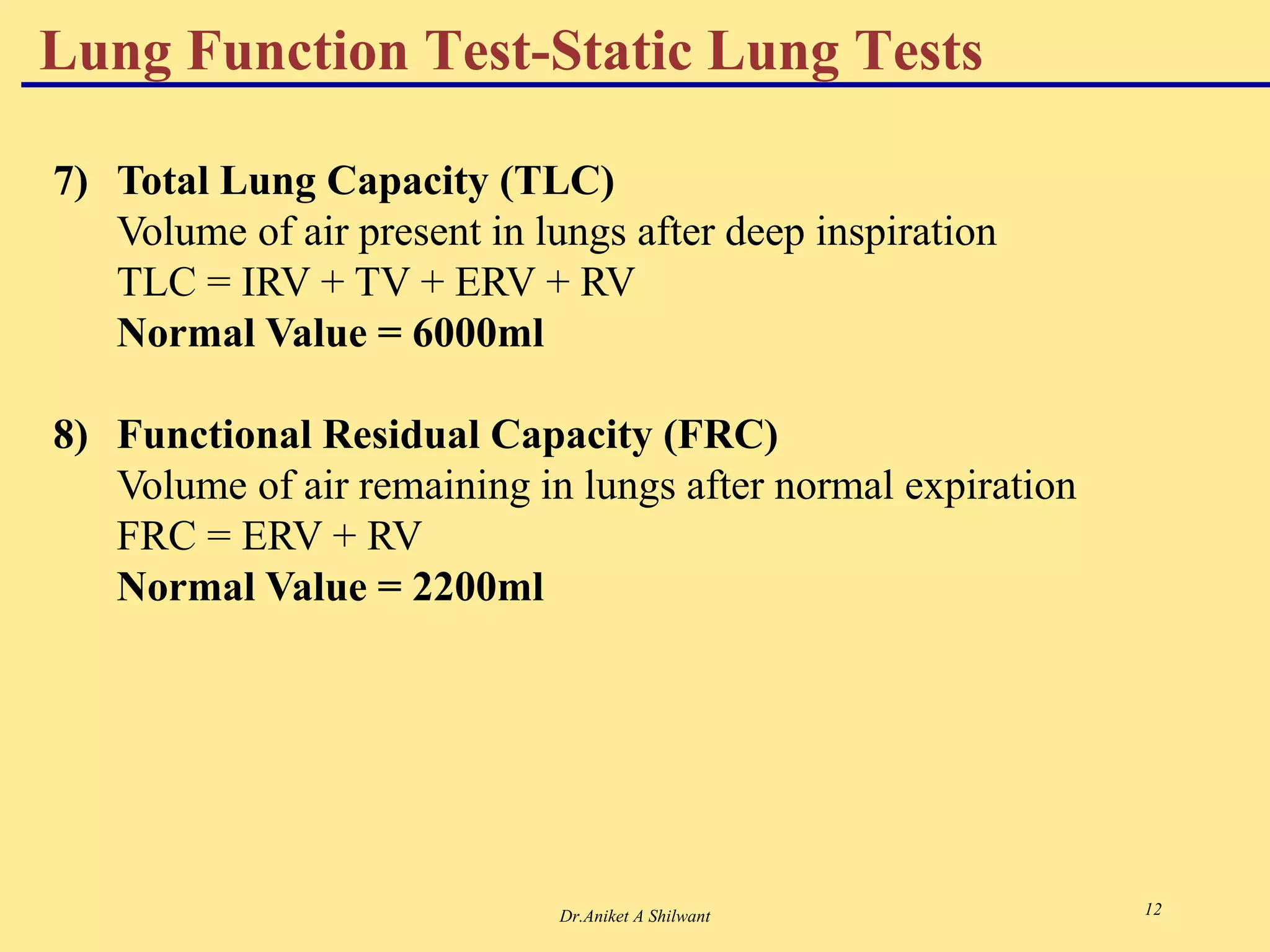
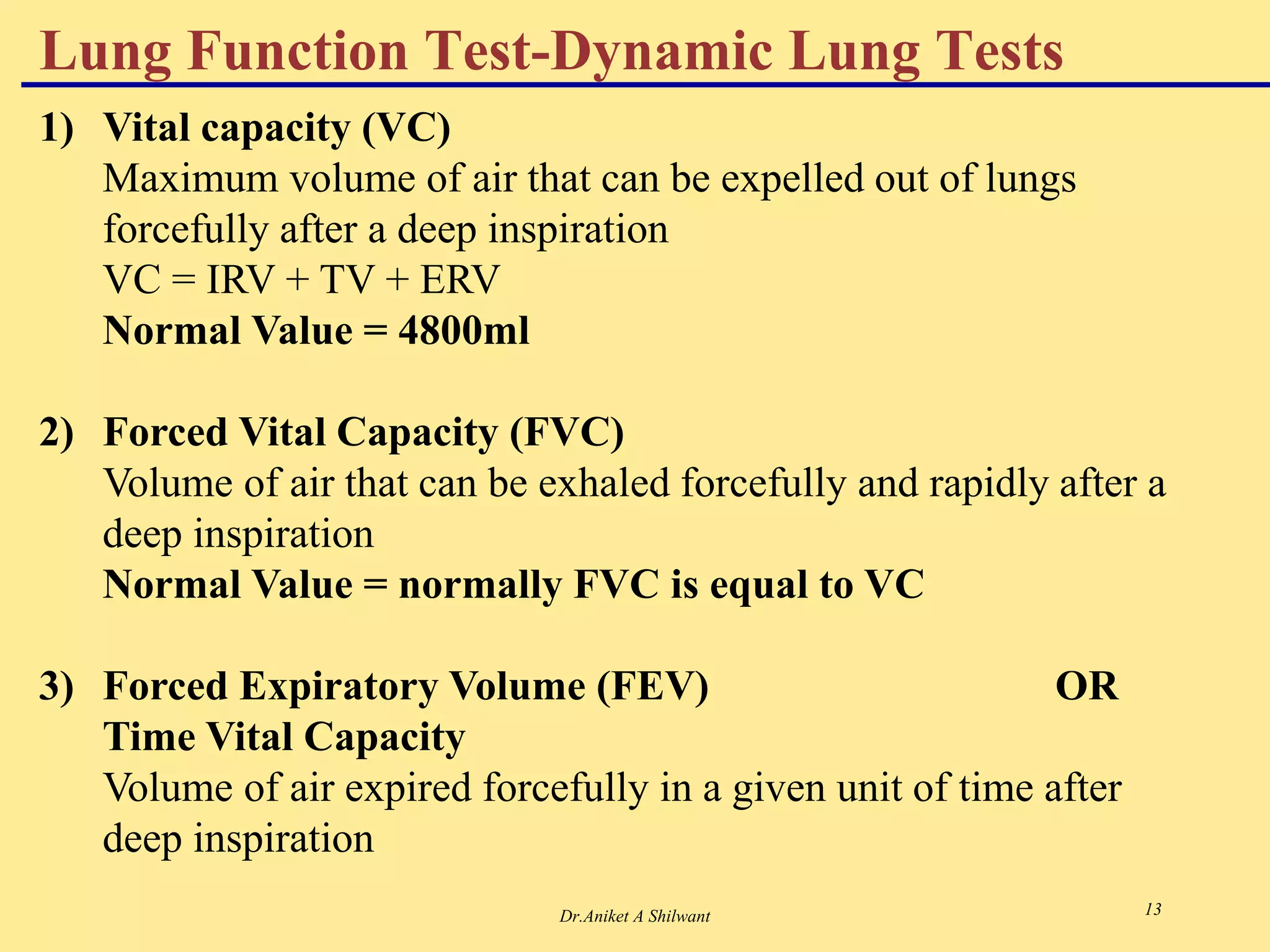
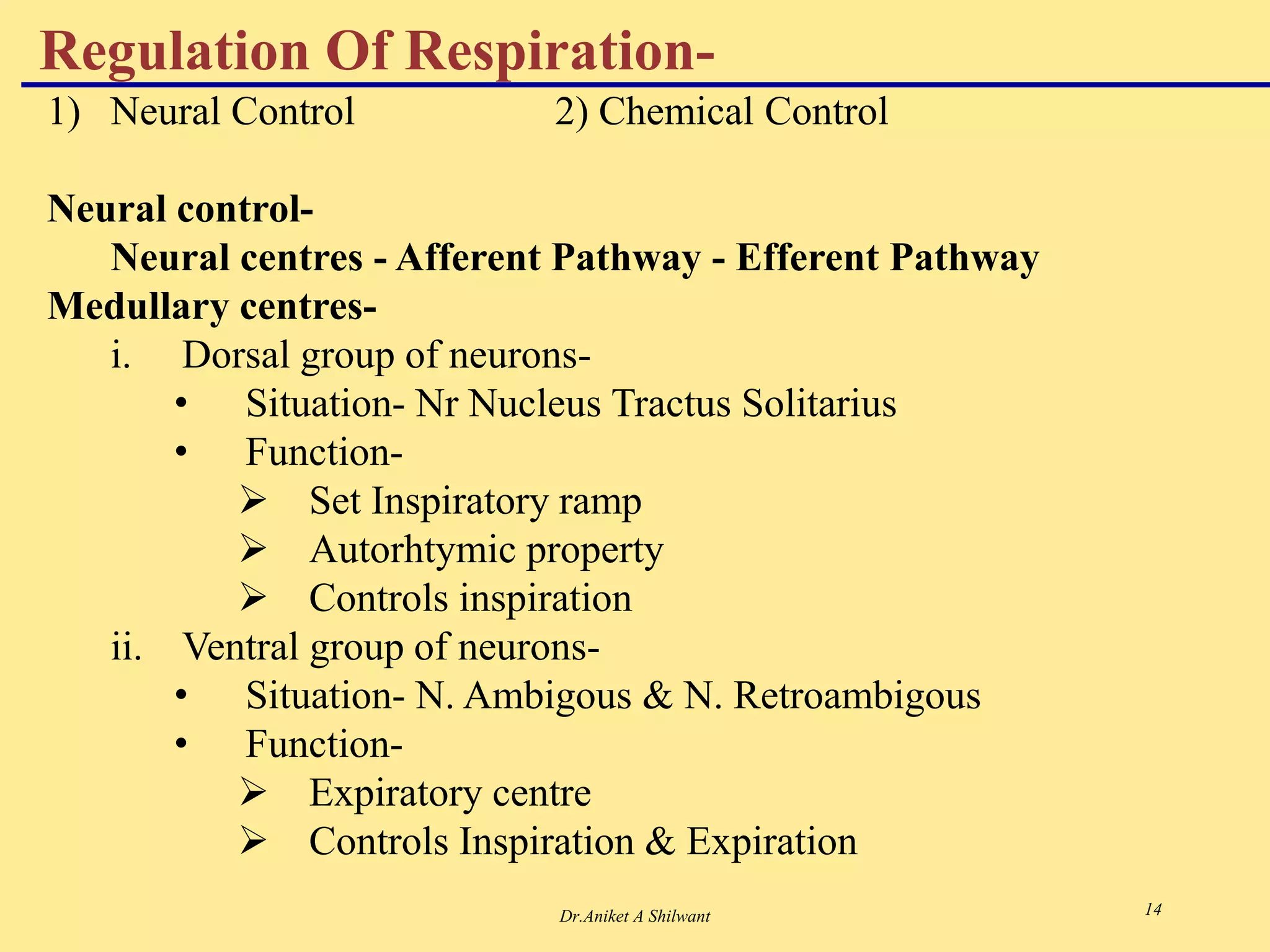
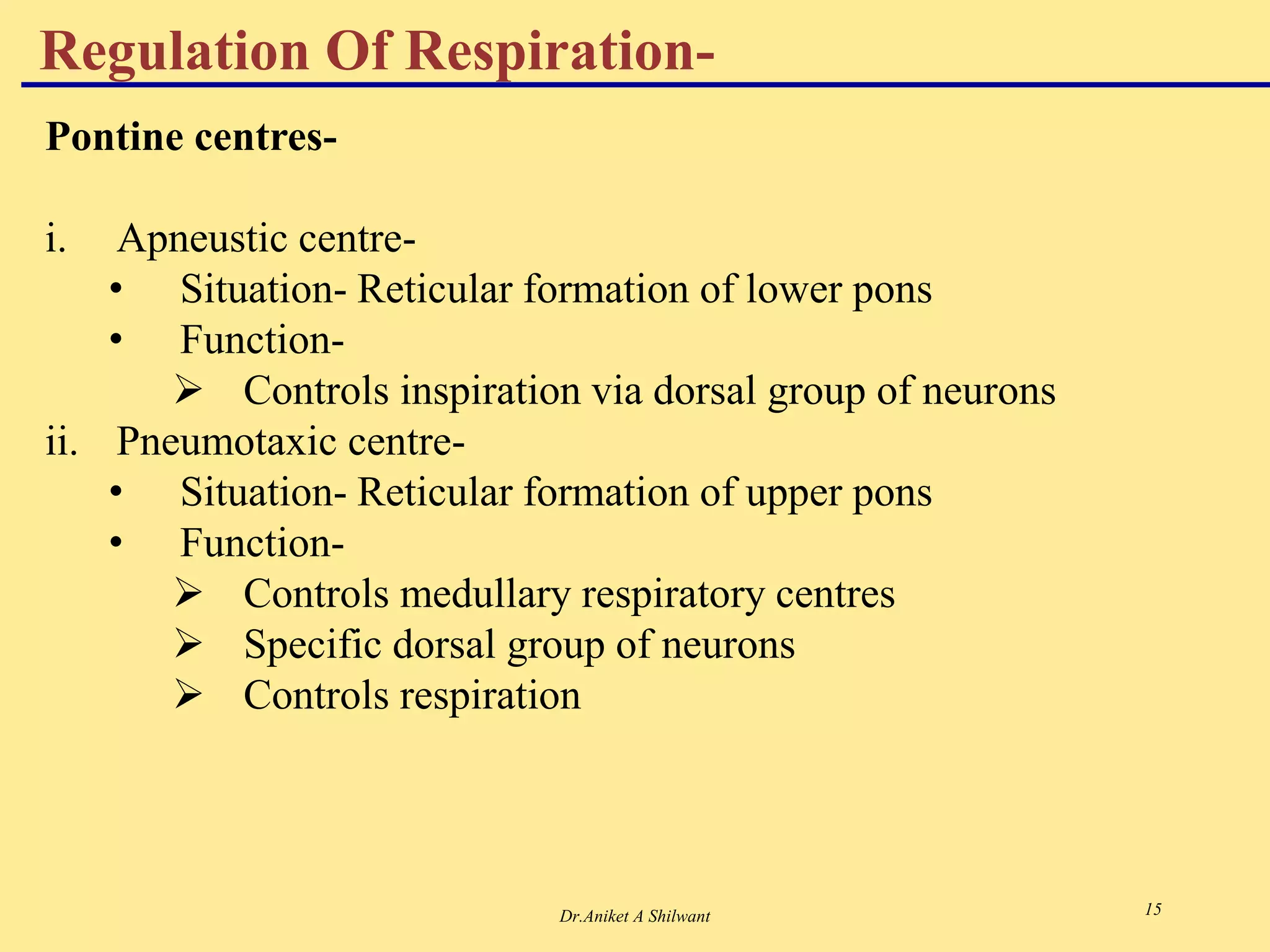
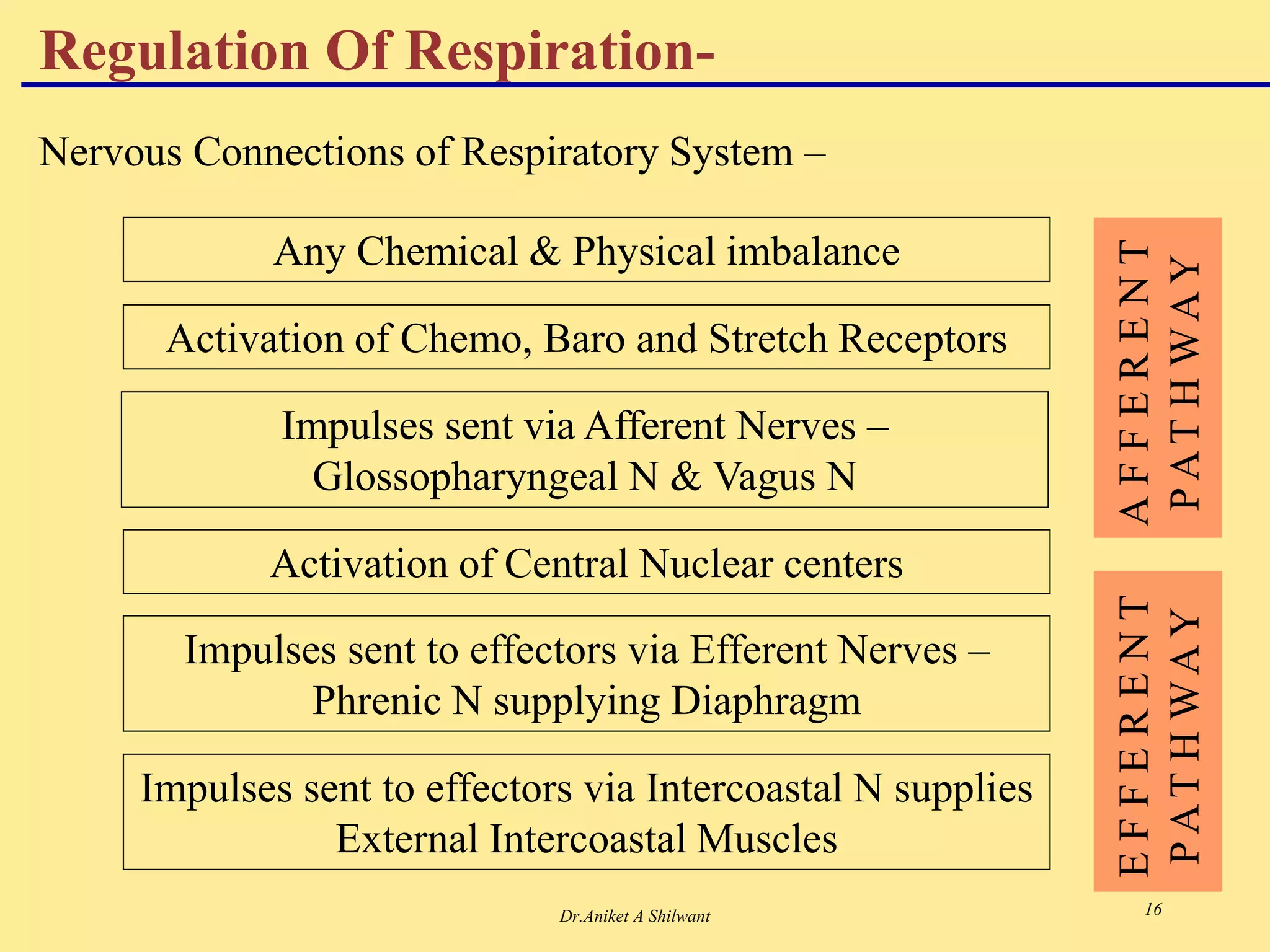
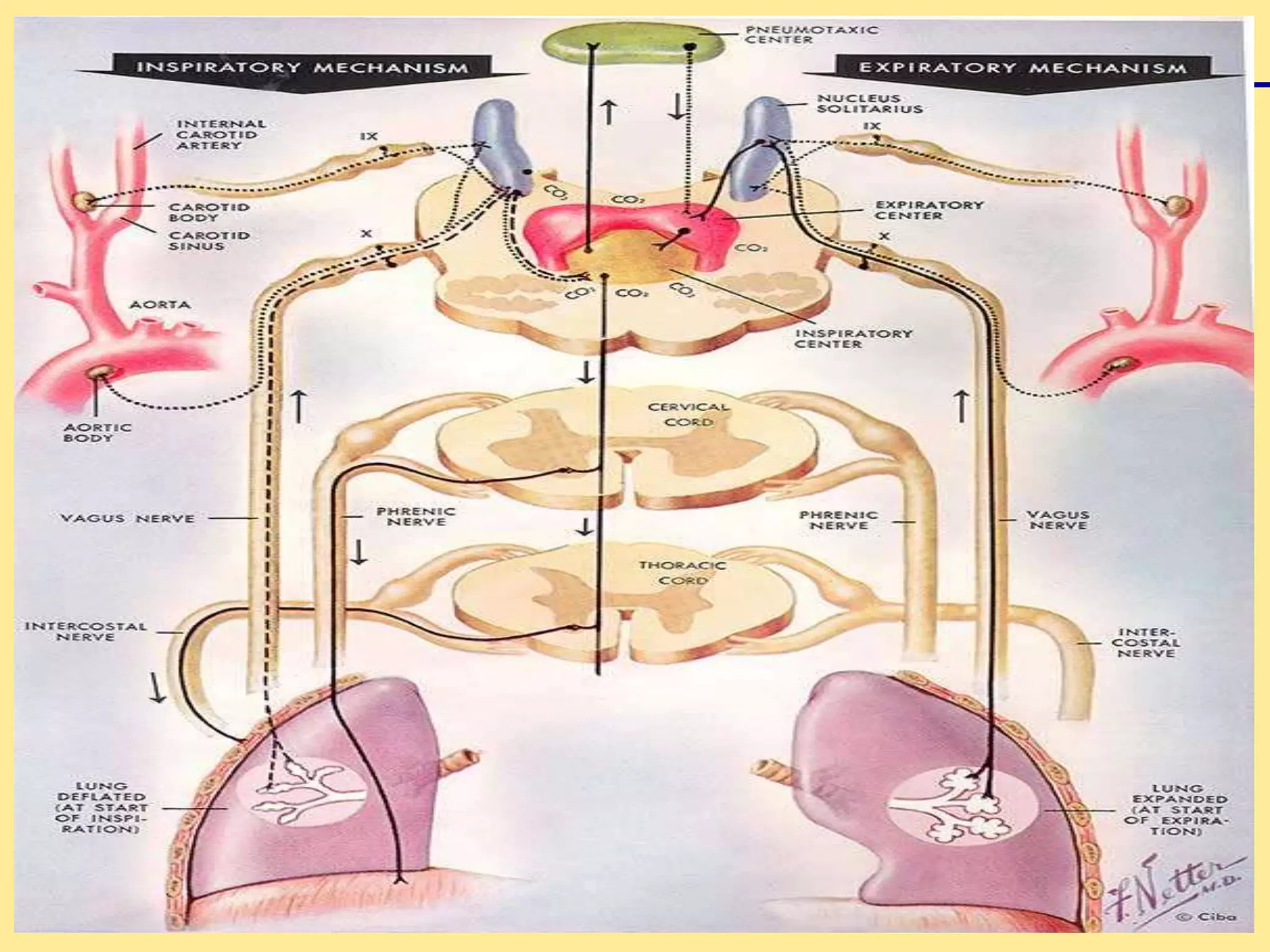
The document presents an overview of the respiratory system, focusing on hypoxia and asphyxia, along with various lung function tests used to assess respiratory health. It categorizes hypoxia into four types based on the underlying causes and describes the stages of asphyxia and lung function measurements. Additionally, the regulation of respiration is explained, involving neural and chemical controls that impact respiratory function.