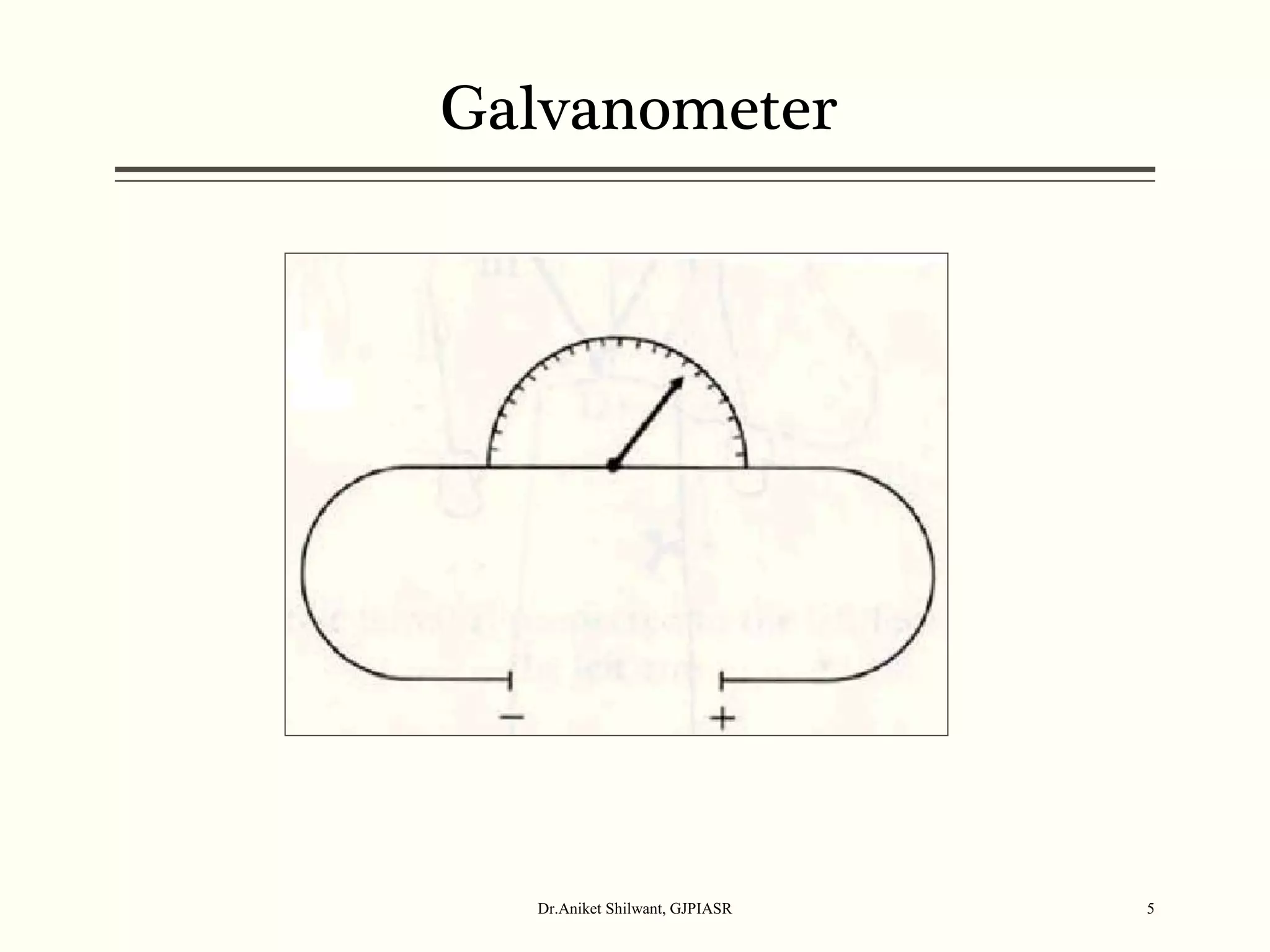
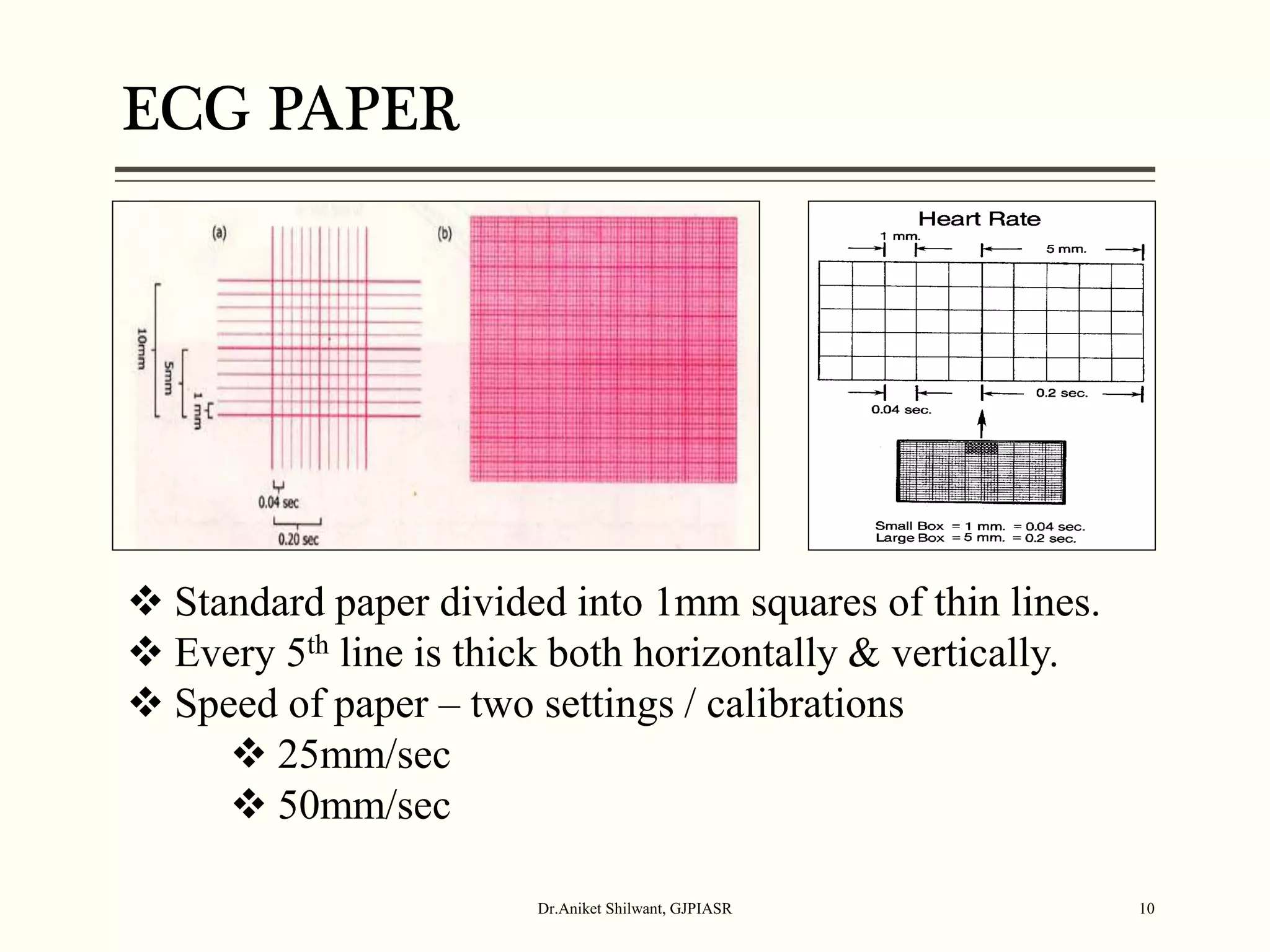
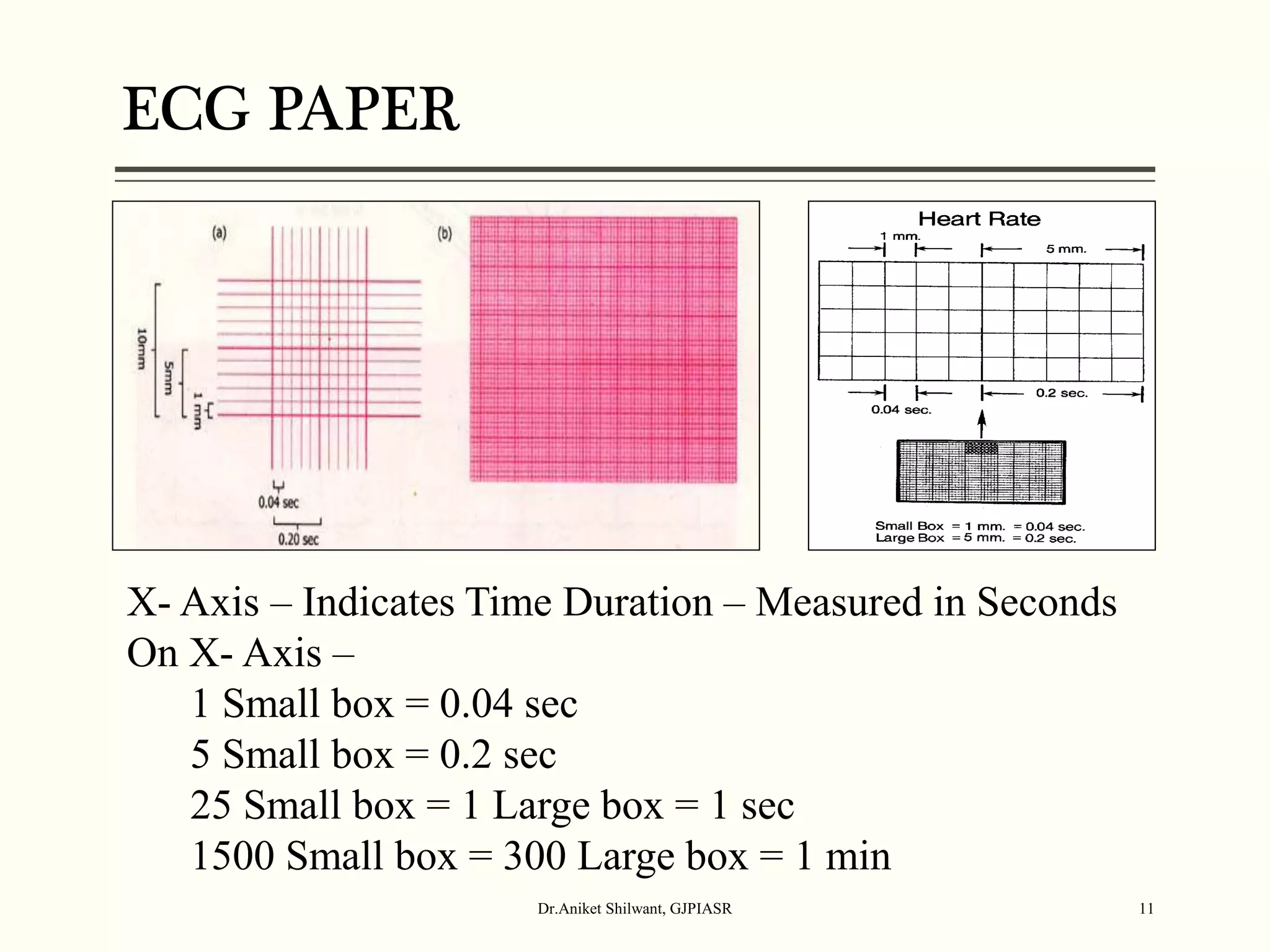
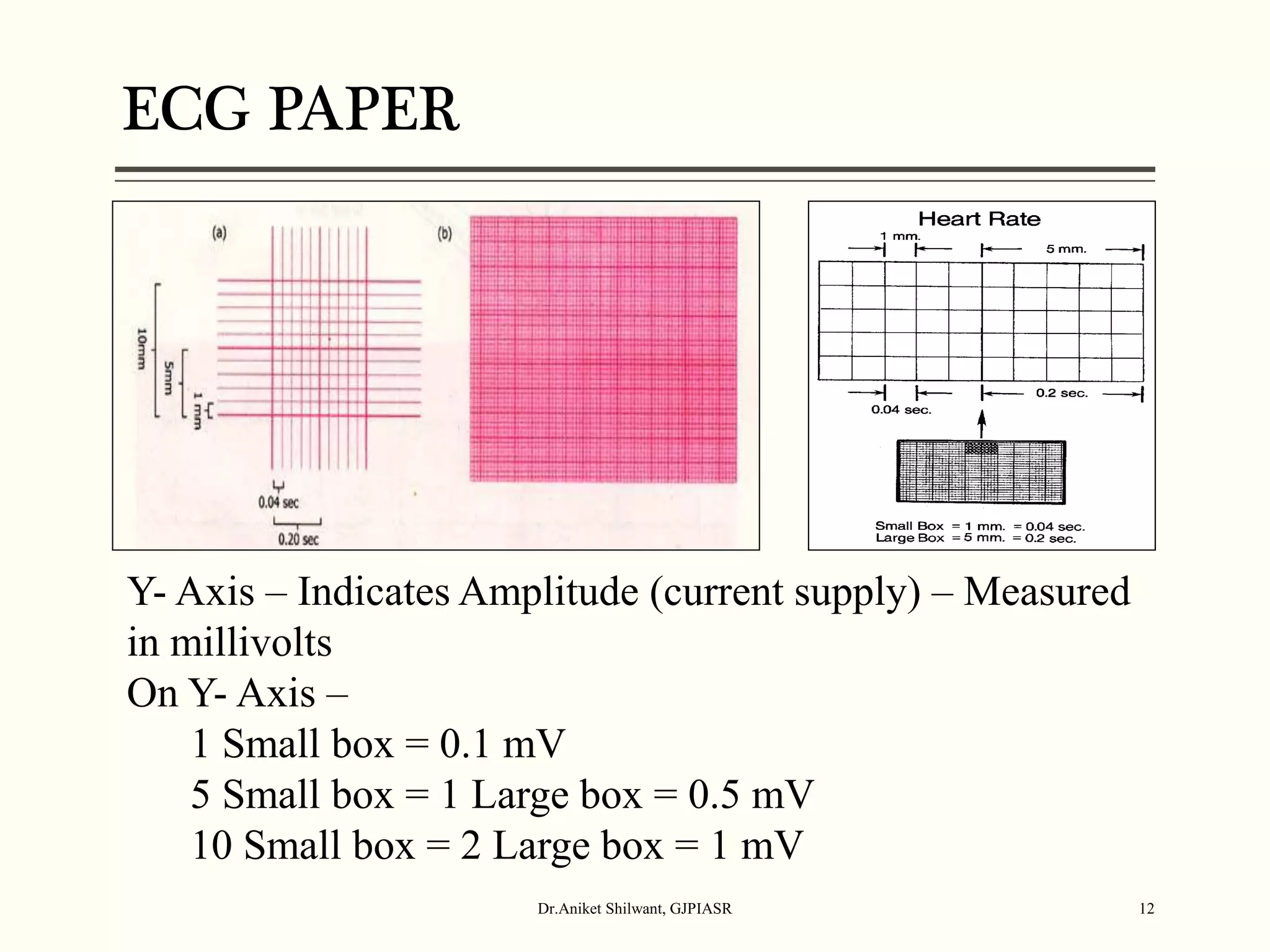
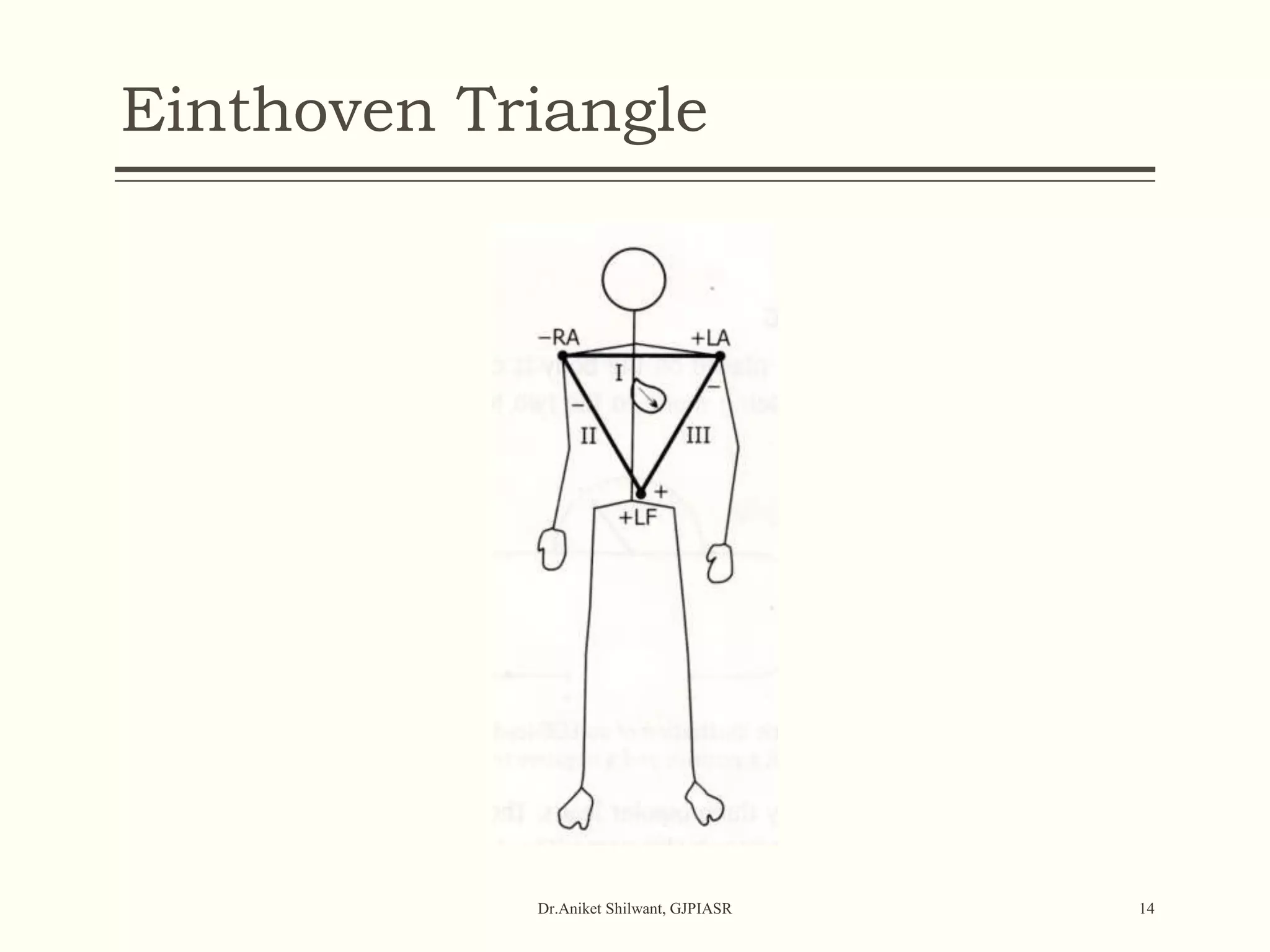
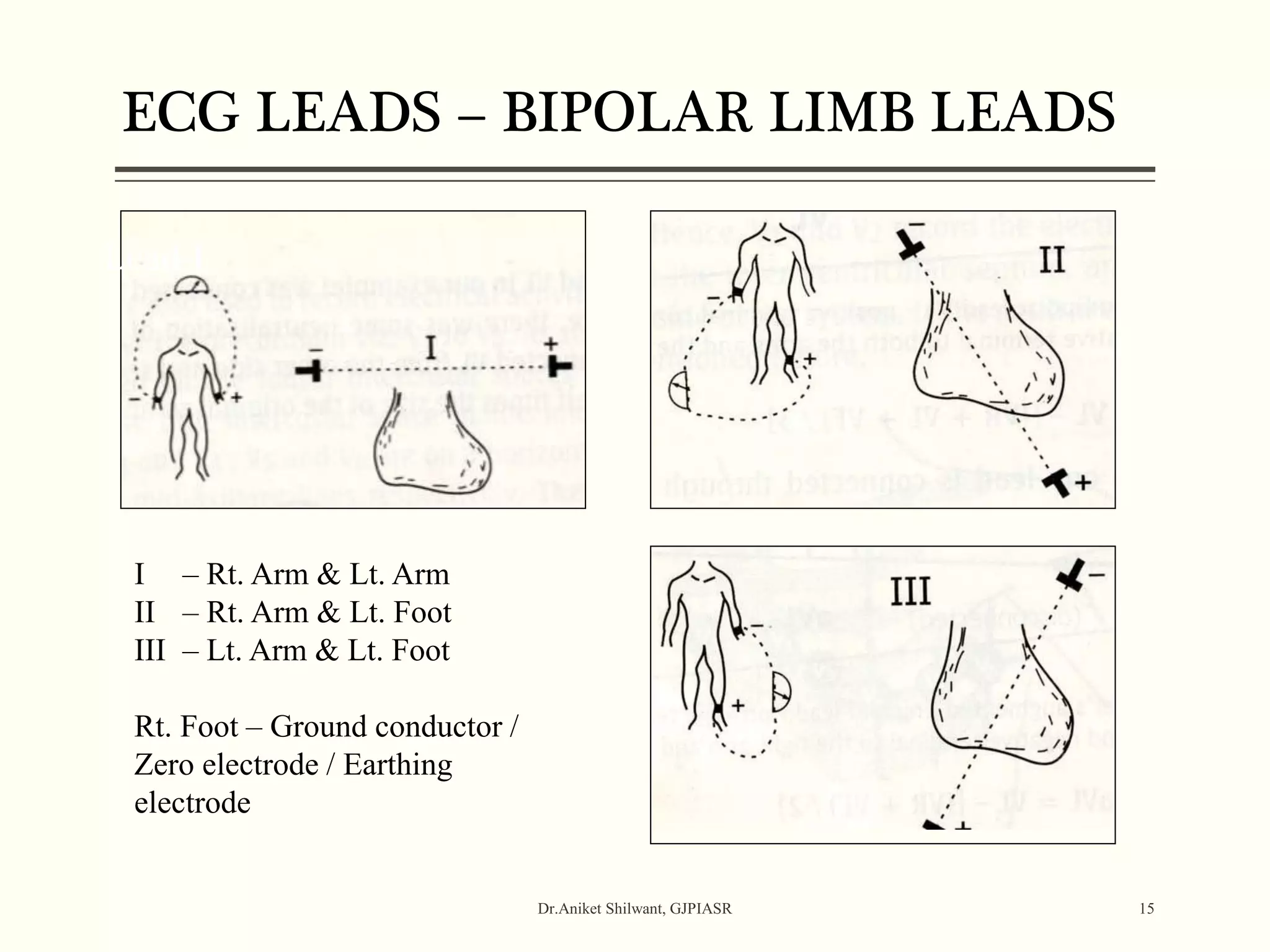
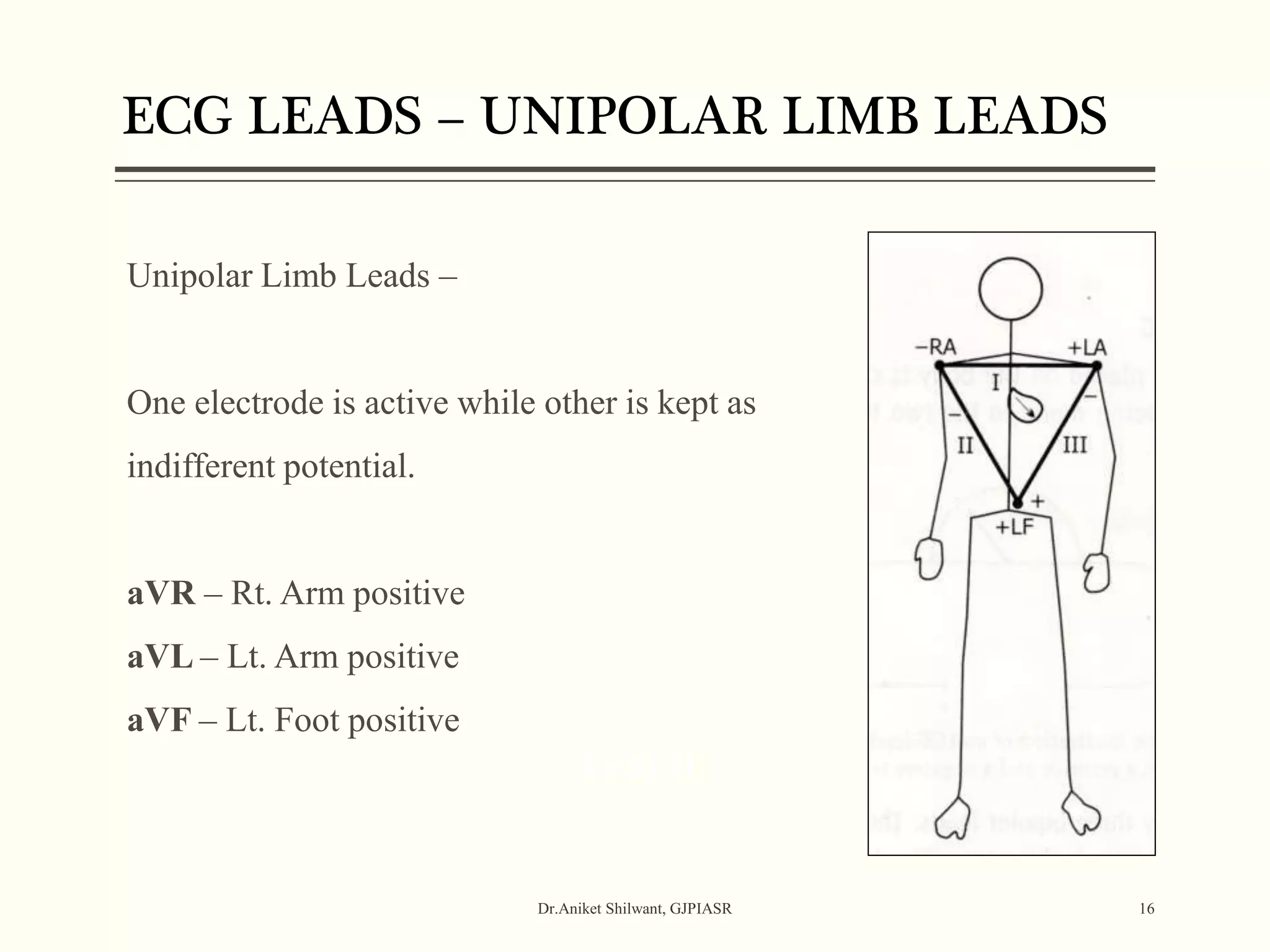
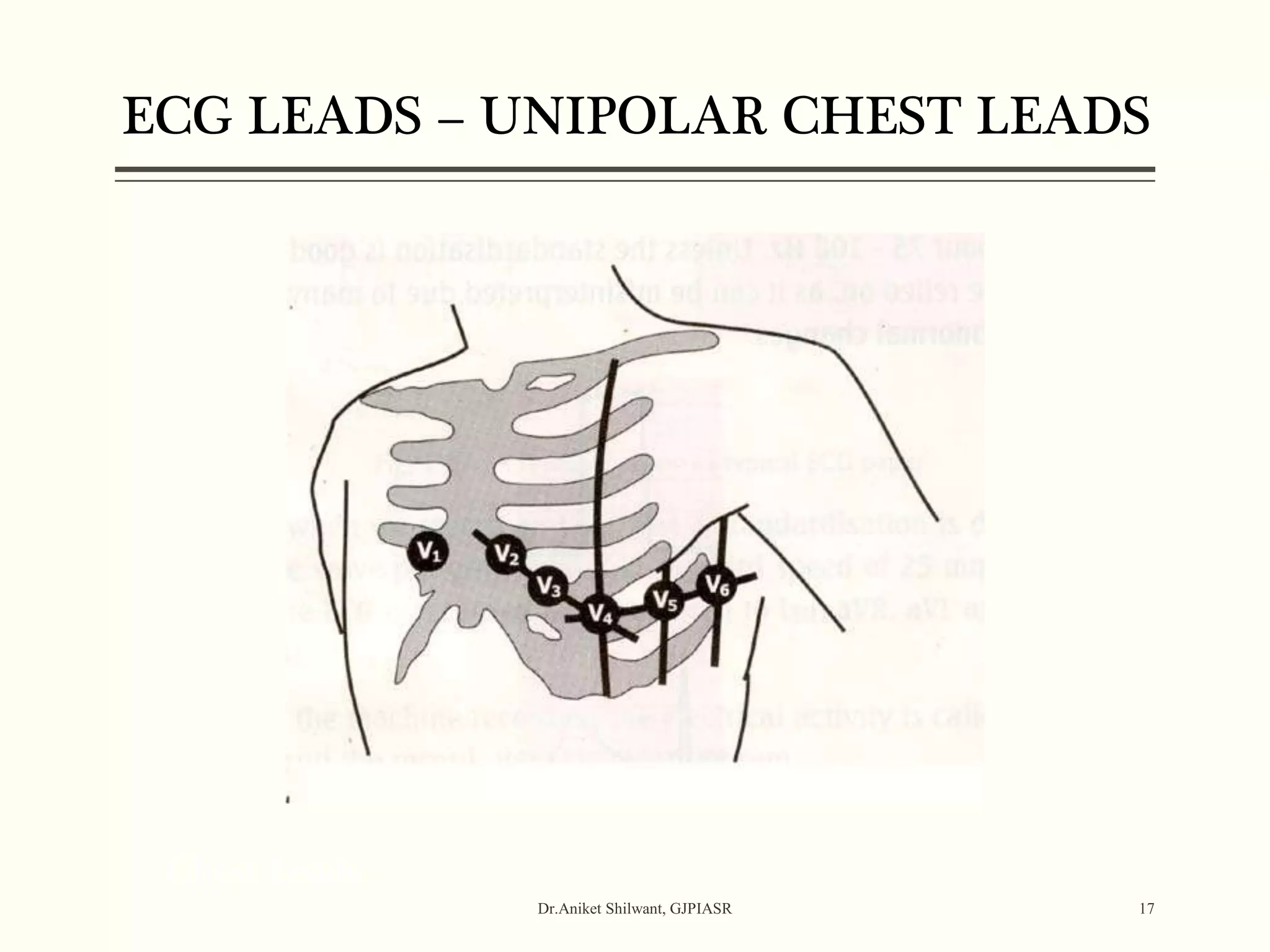
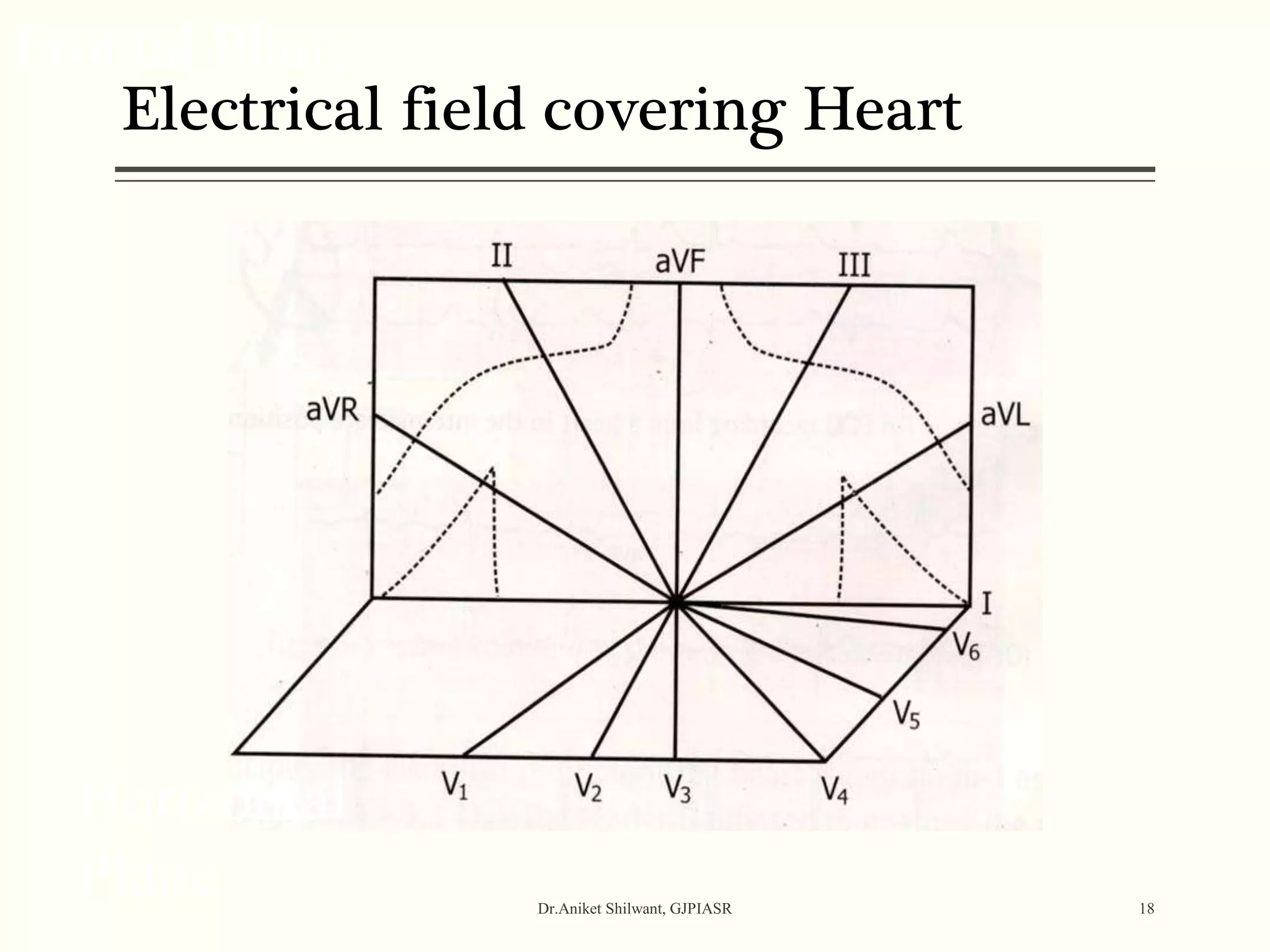
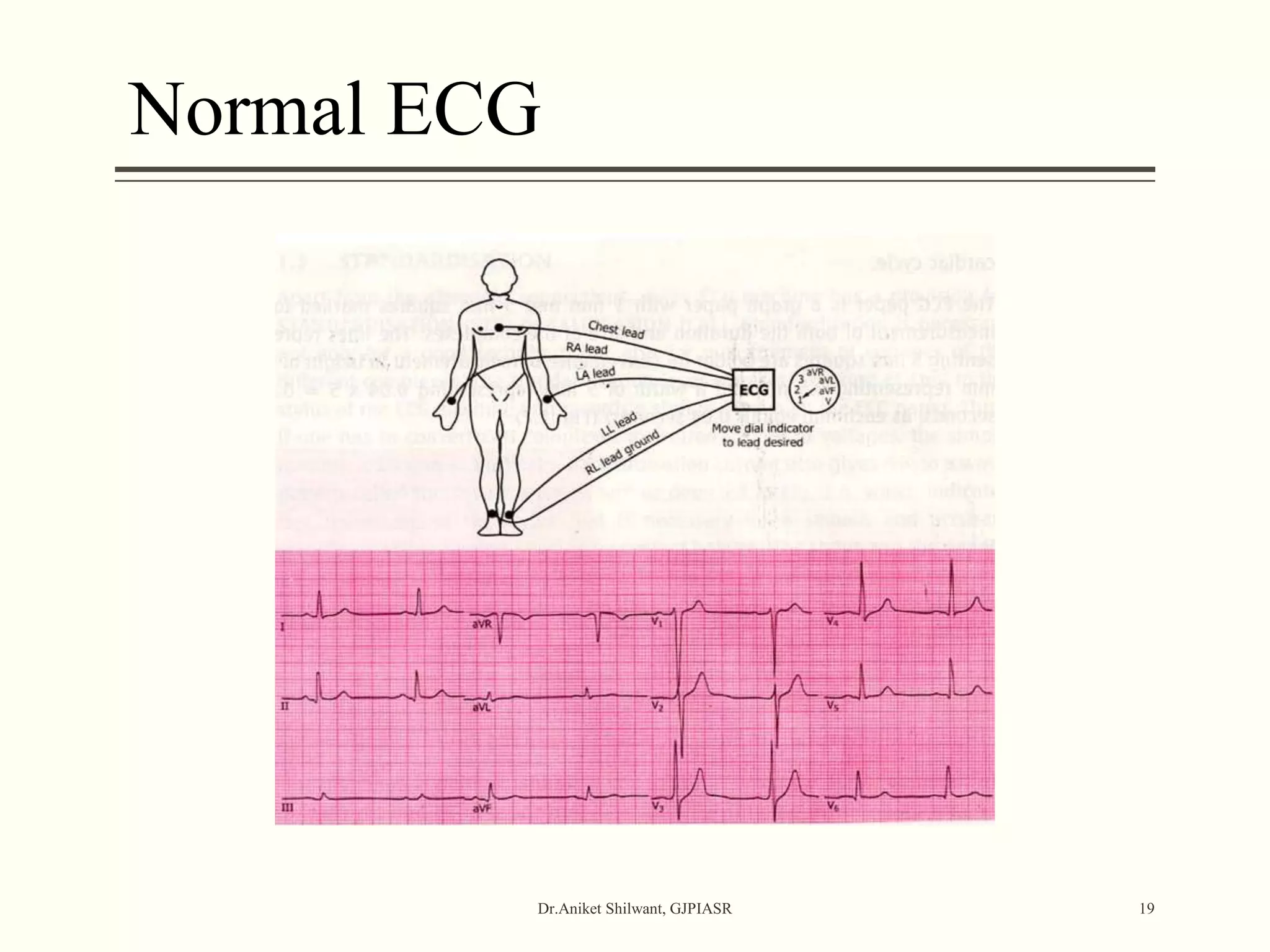
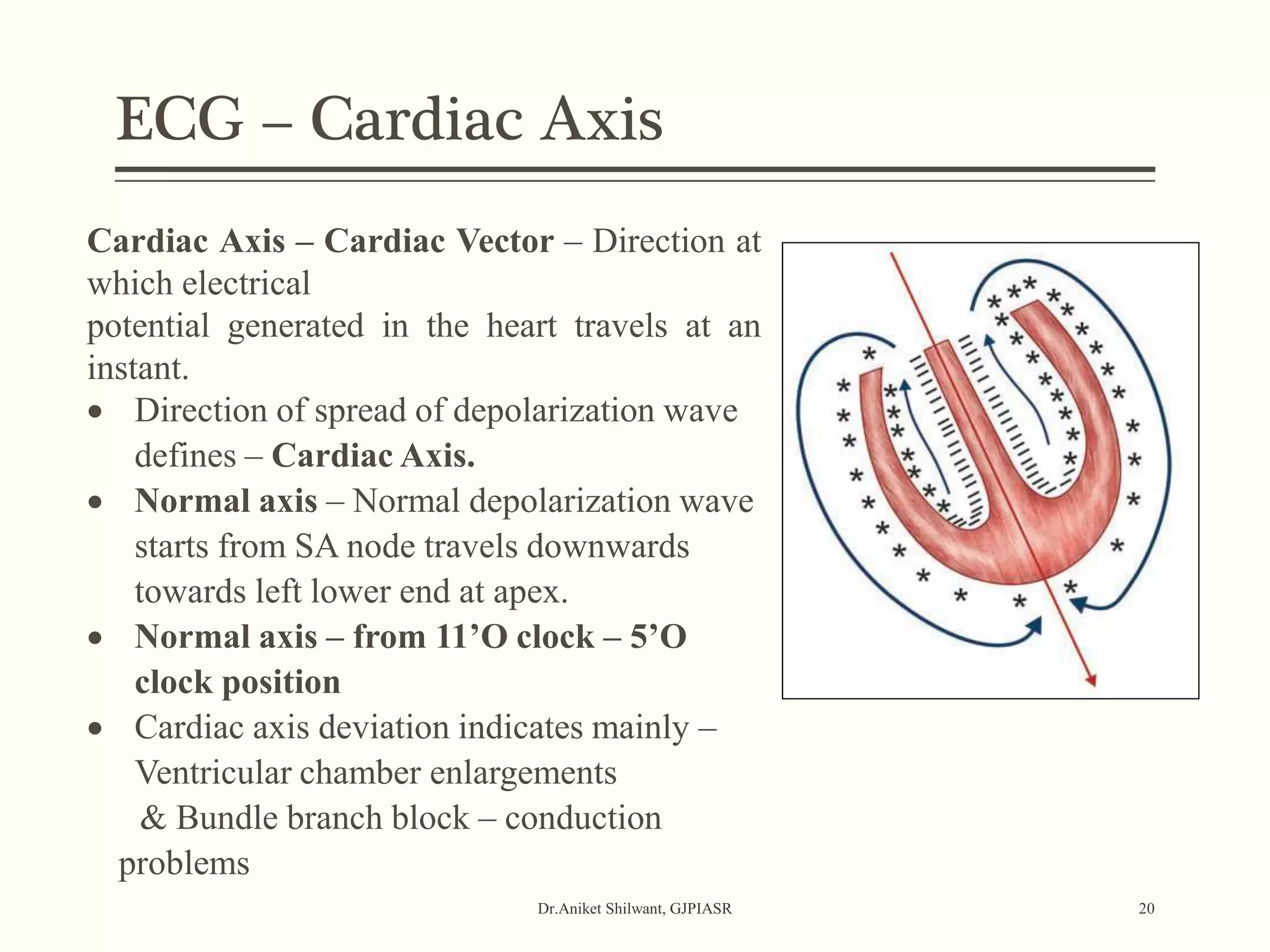
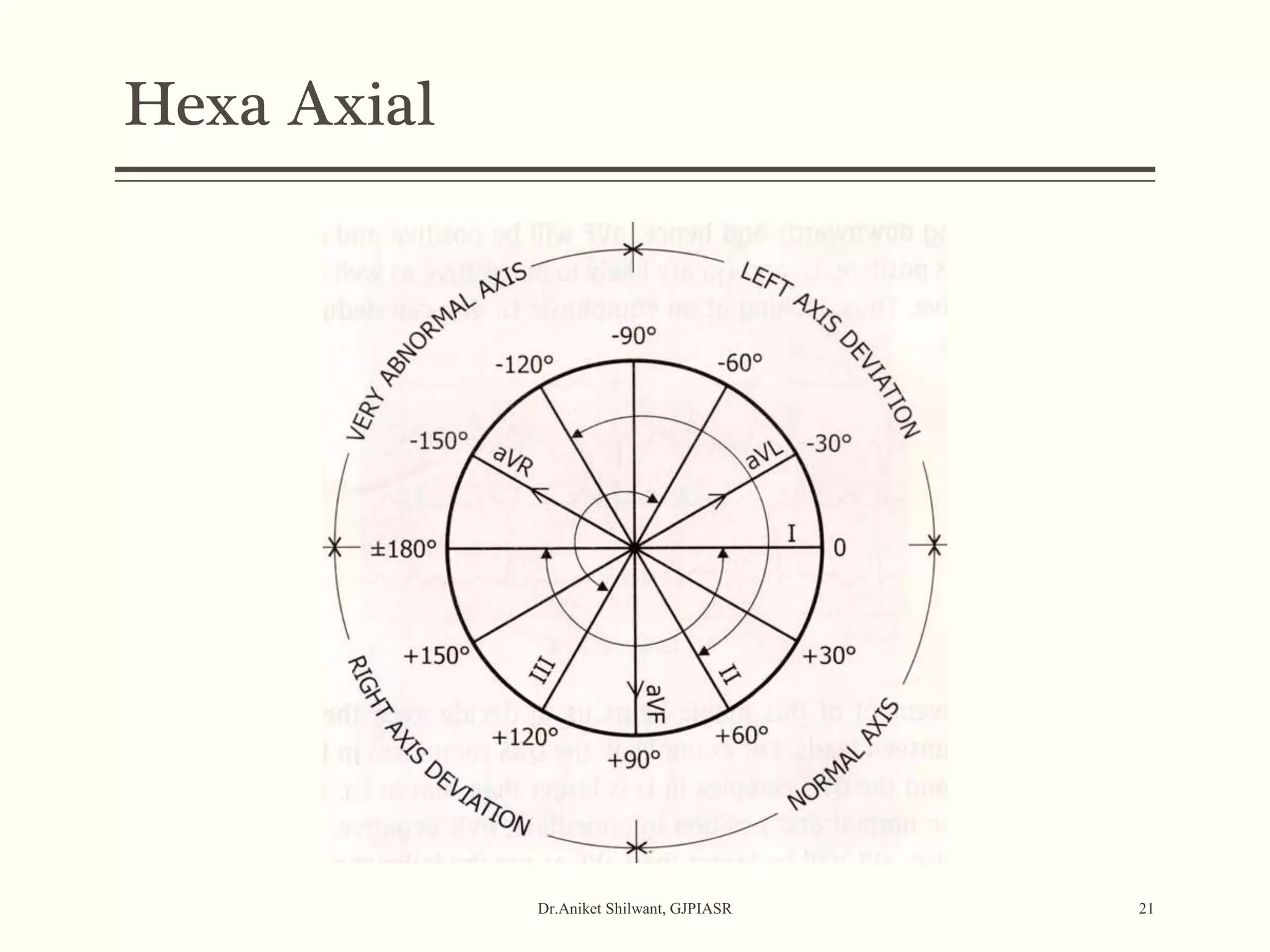
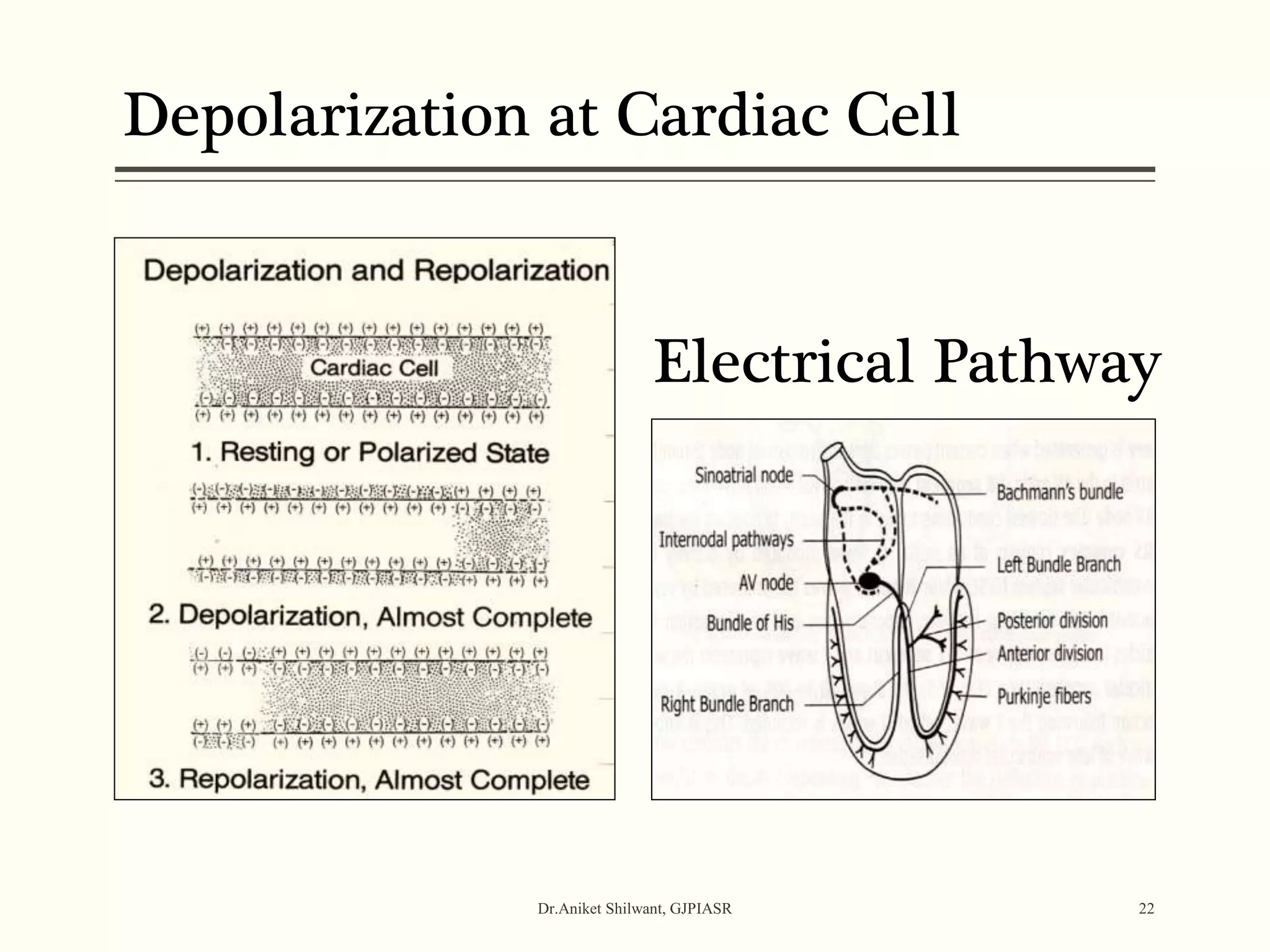
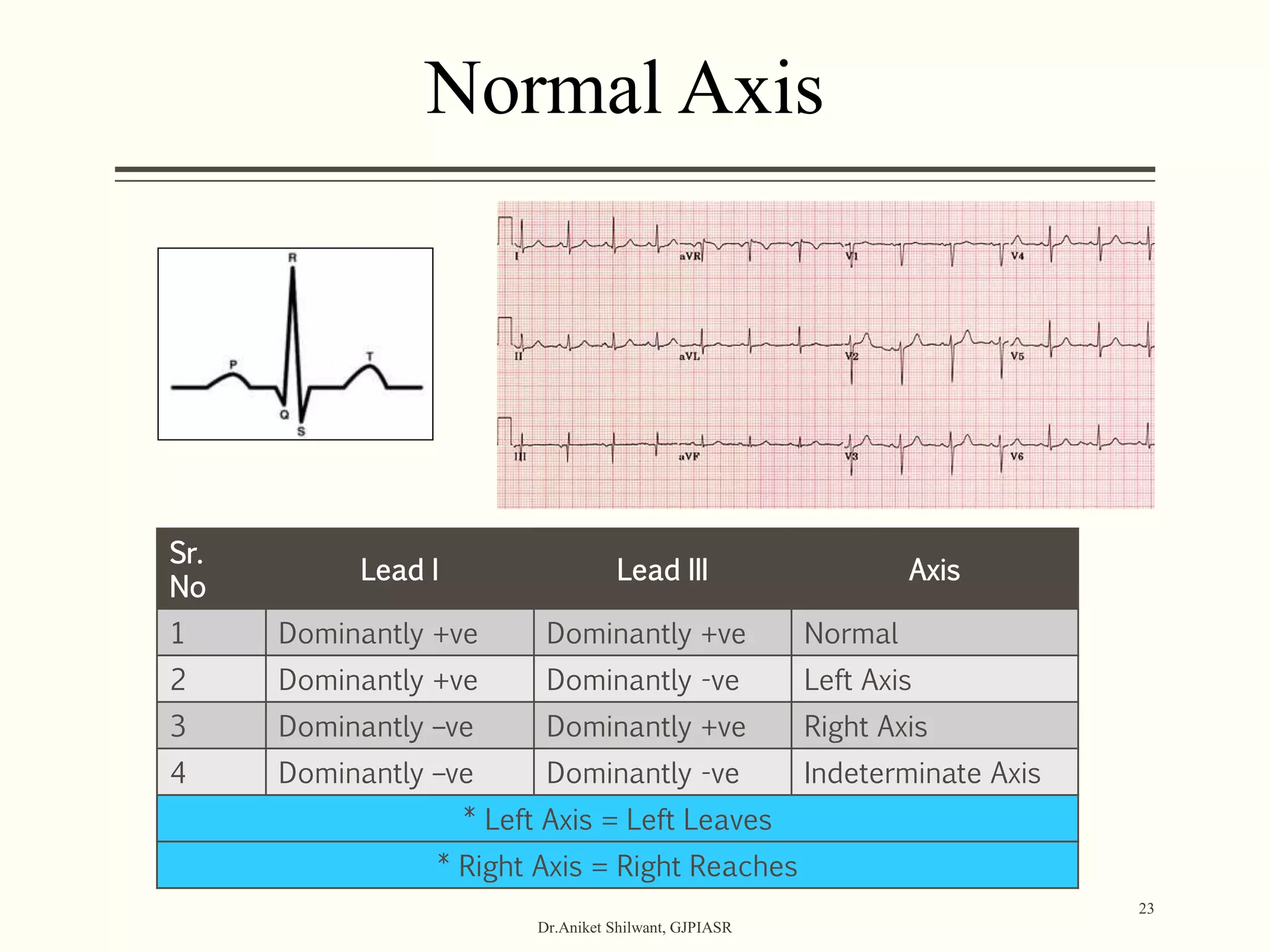
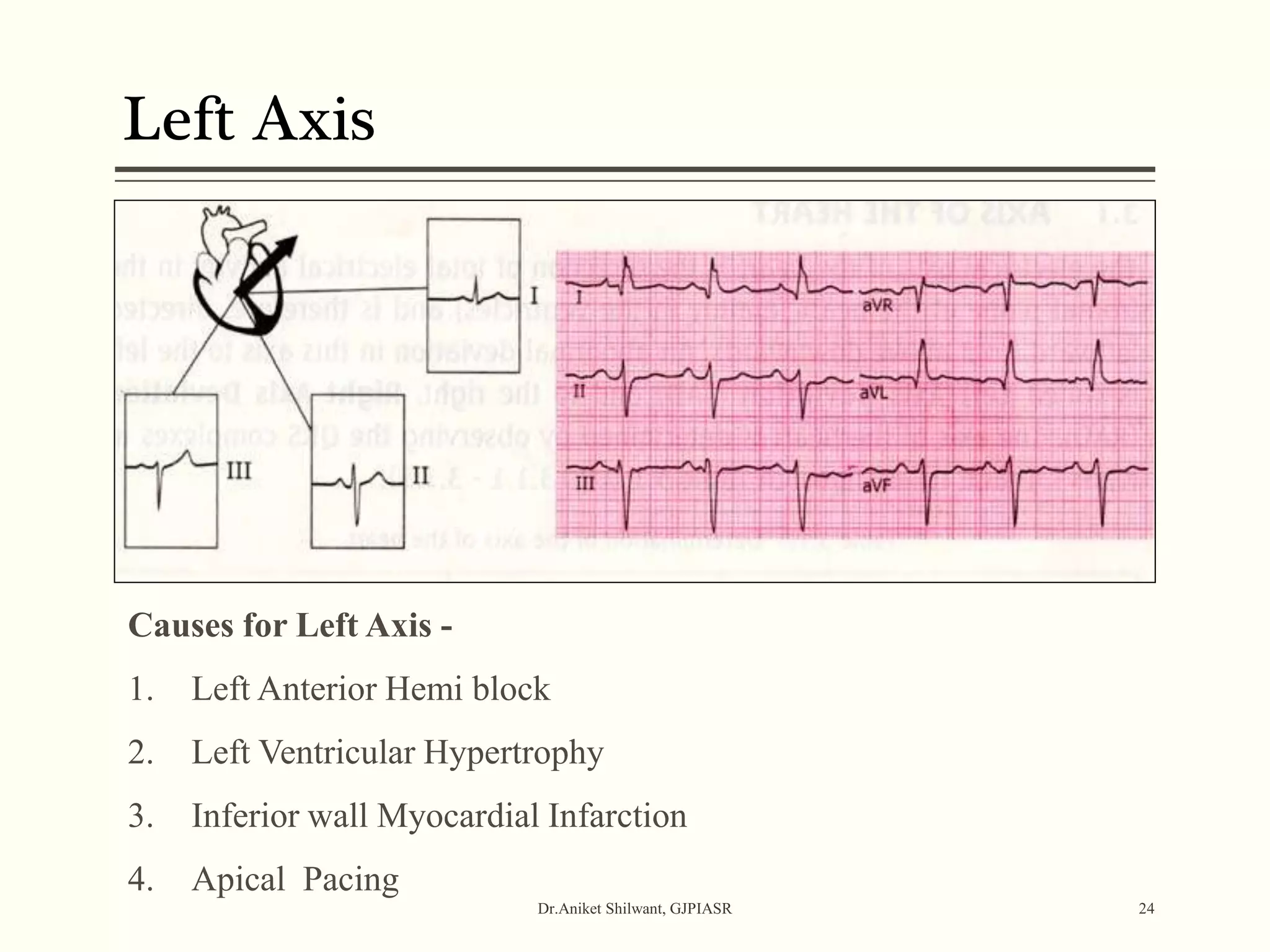
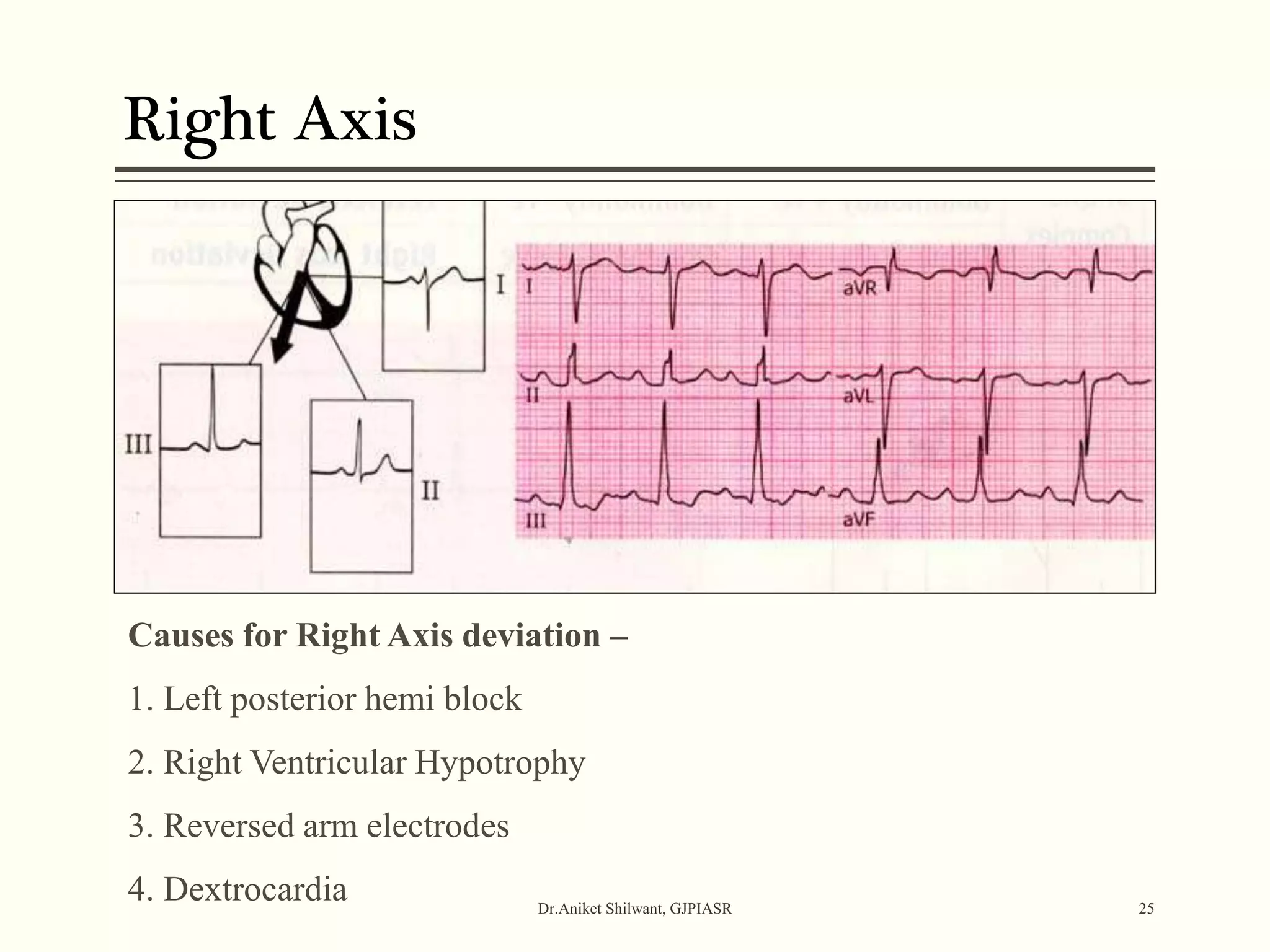
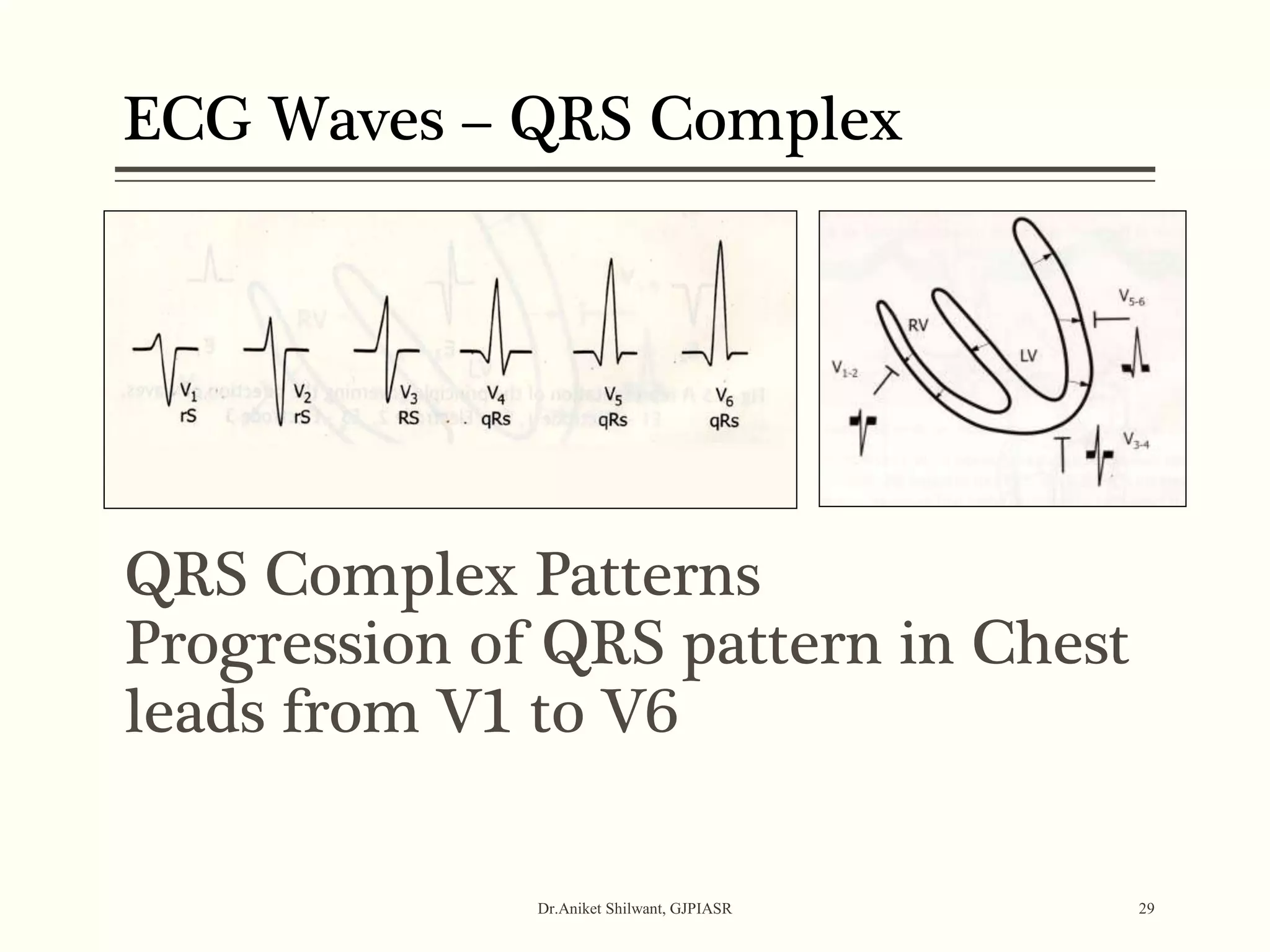
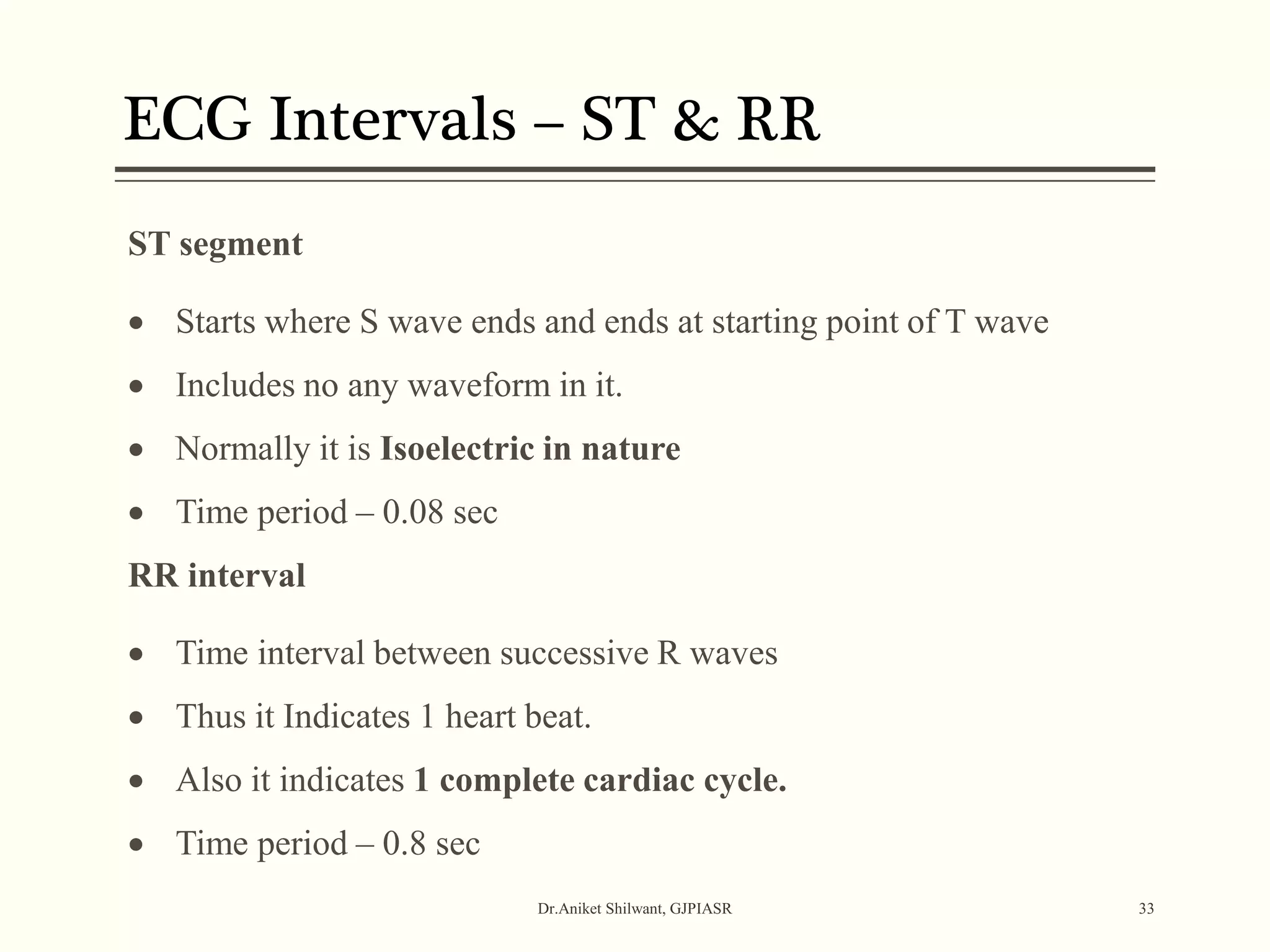
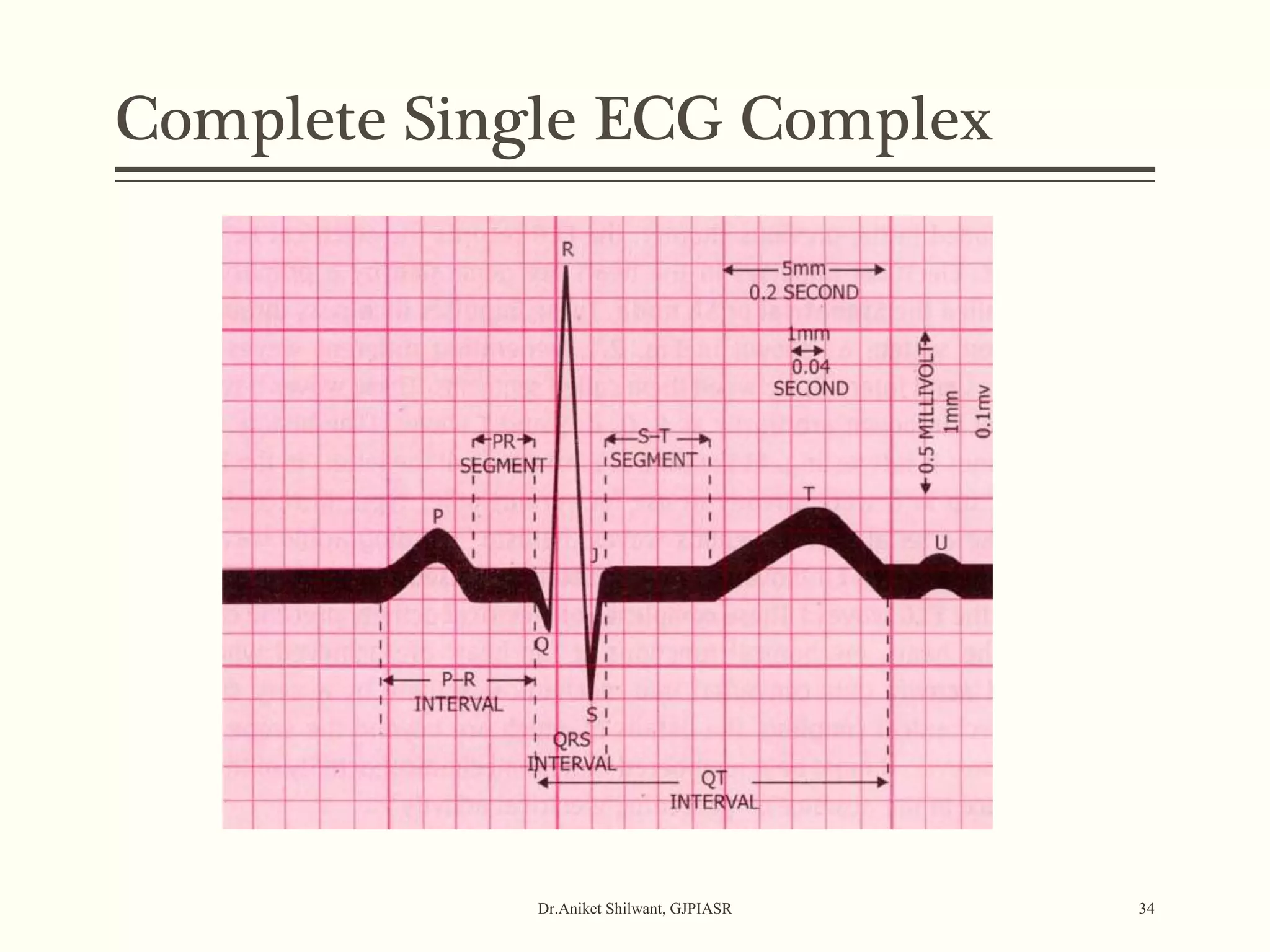
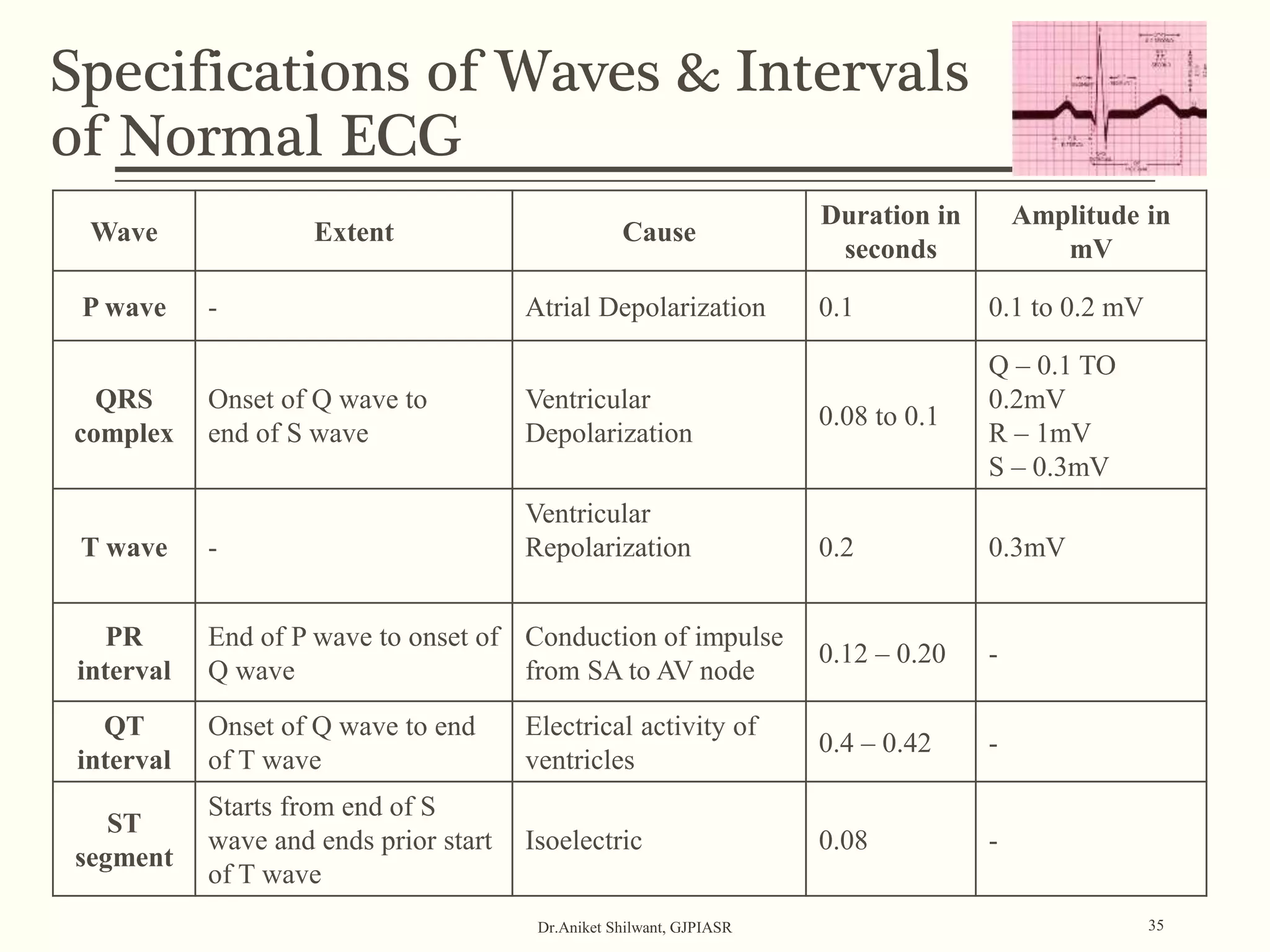
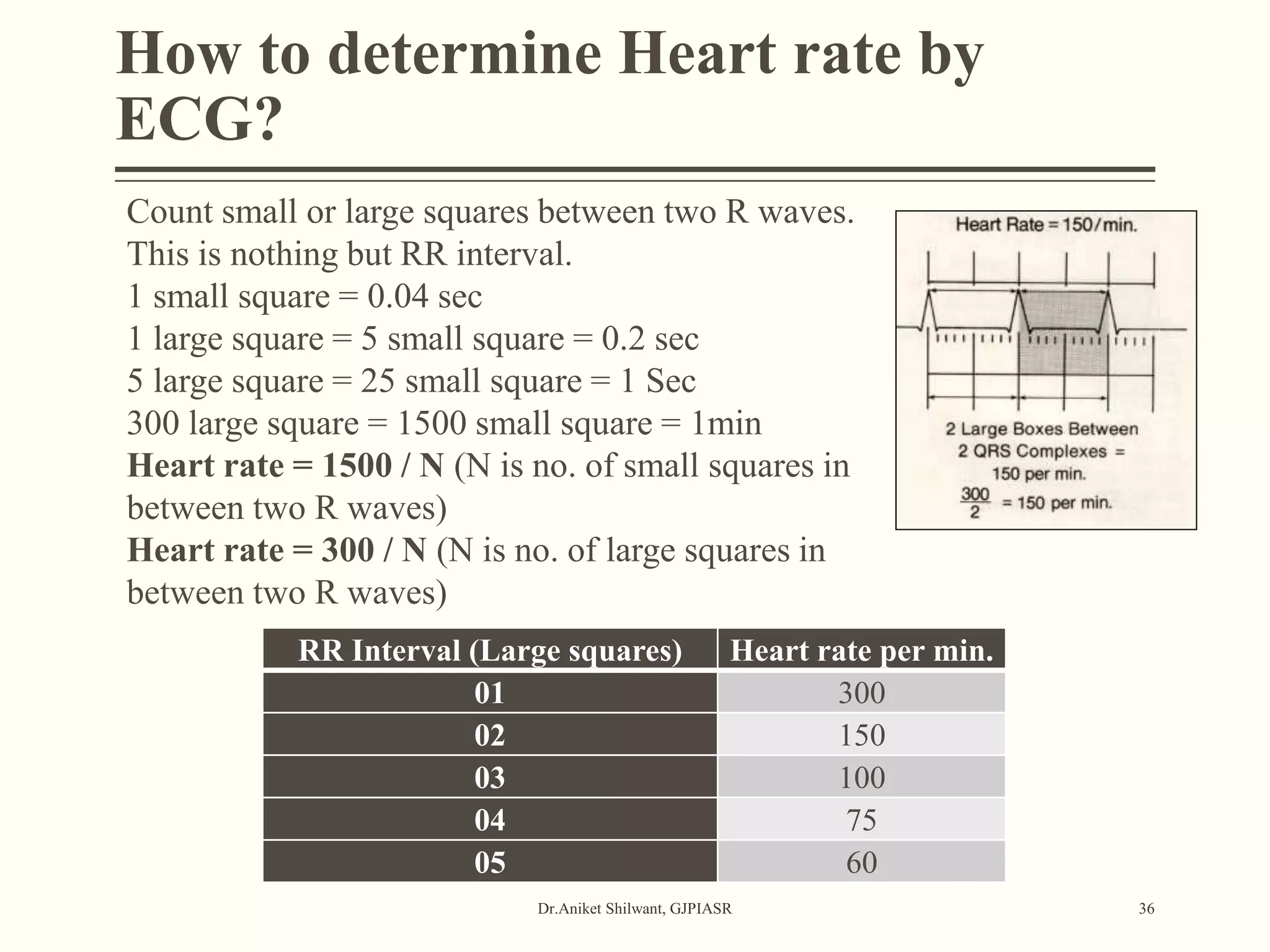
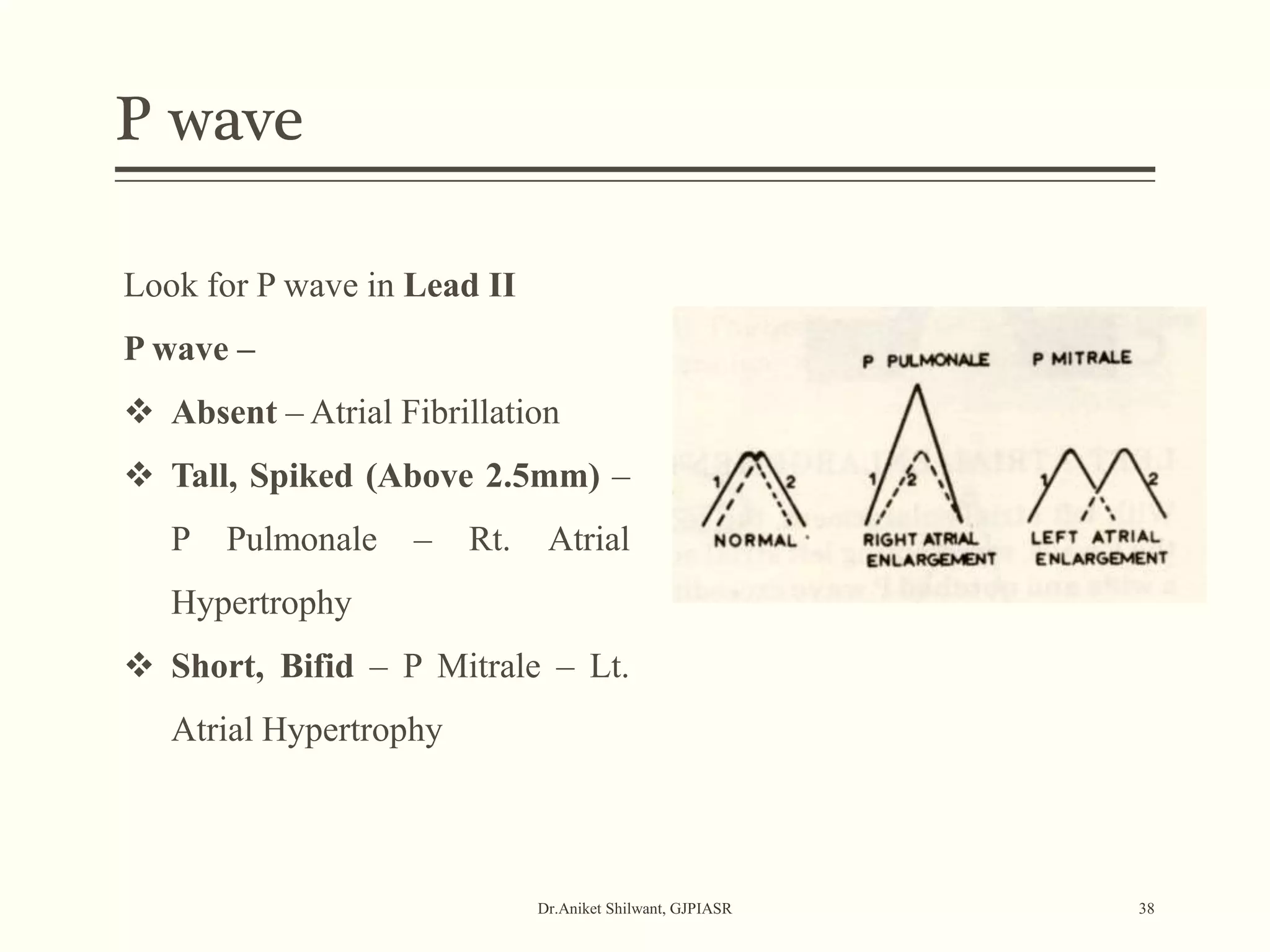
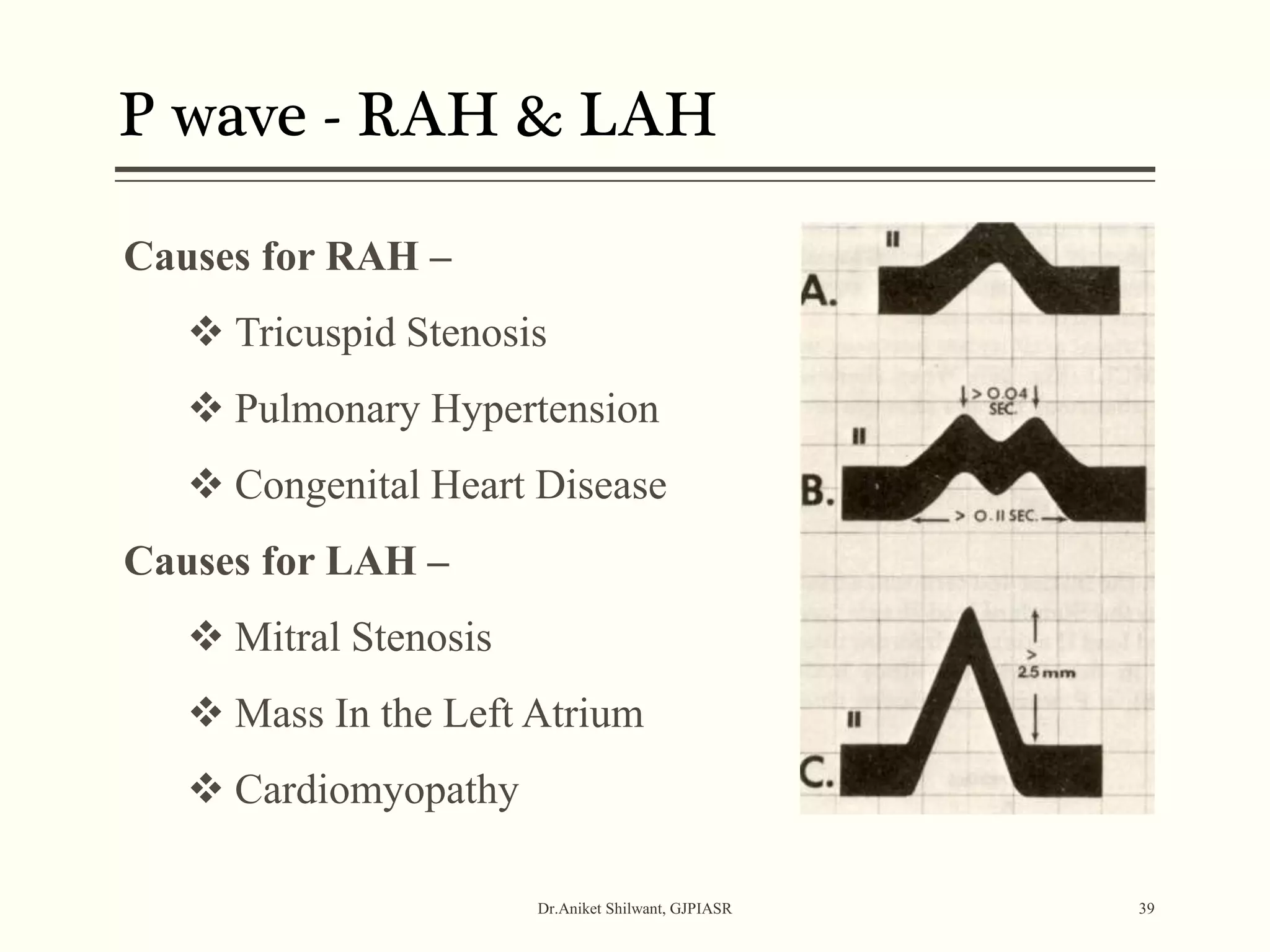
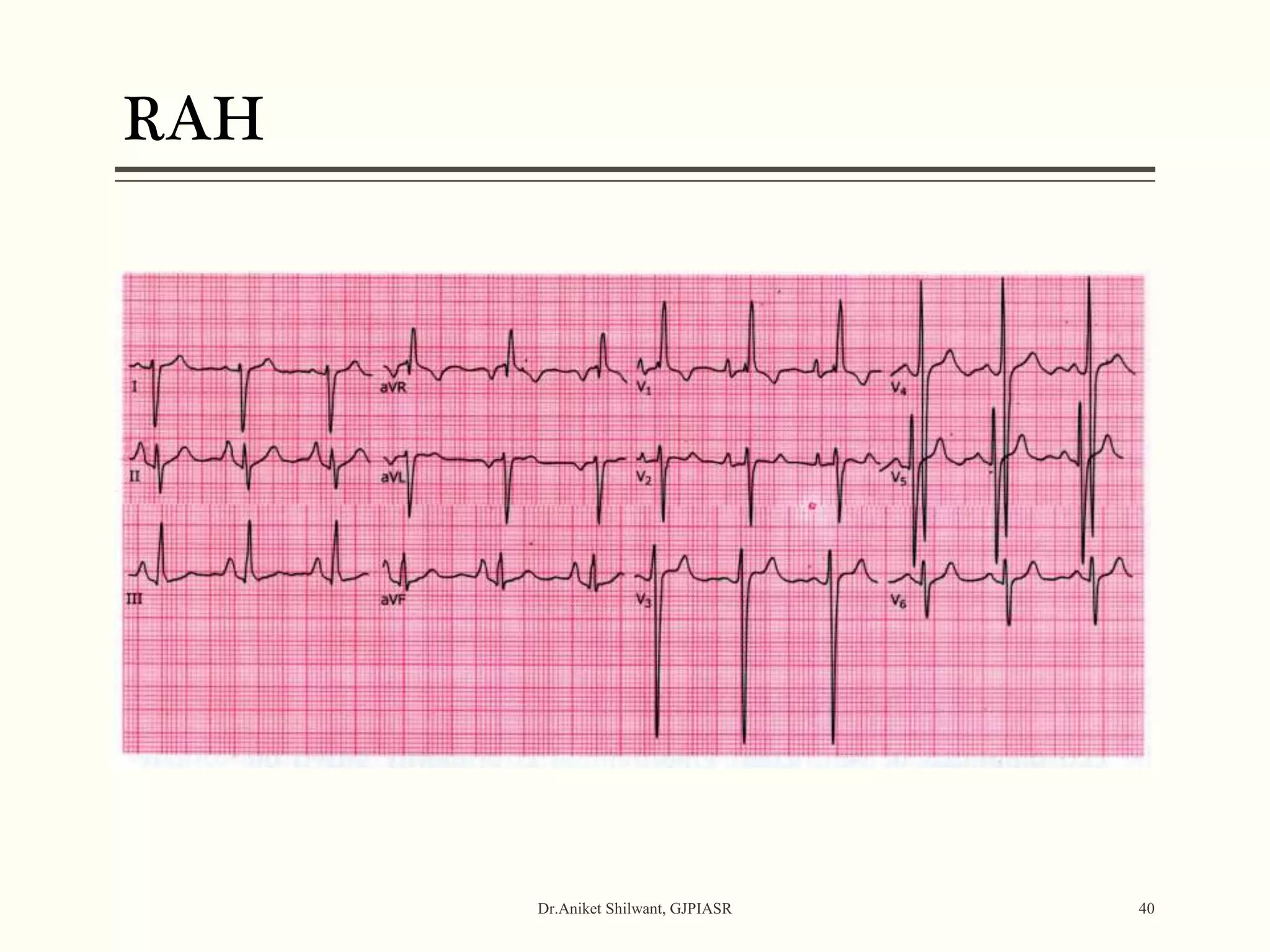
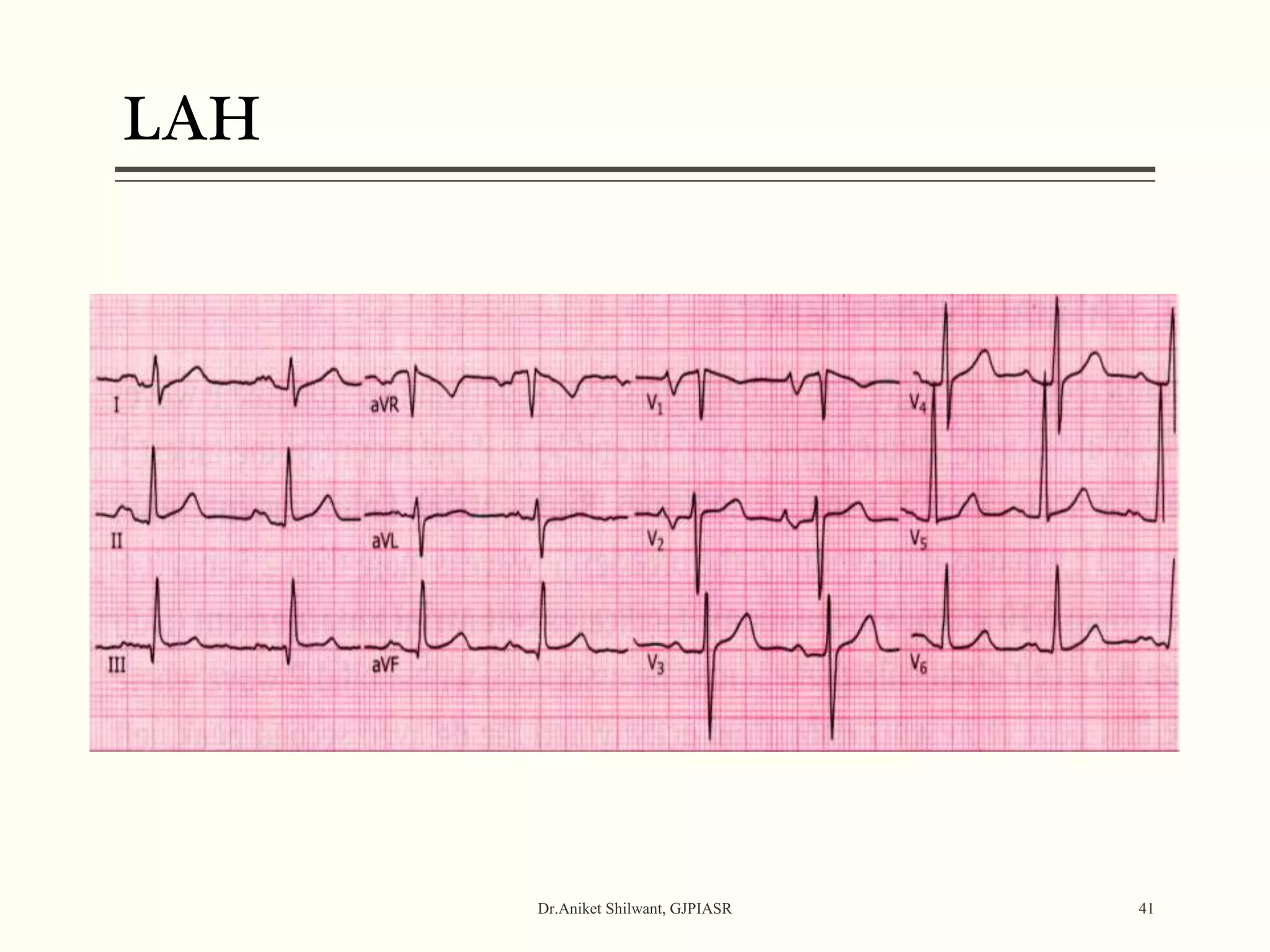
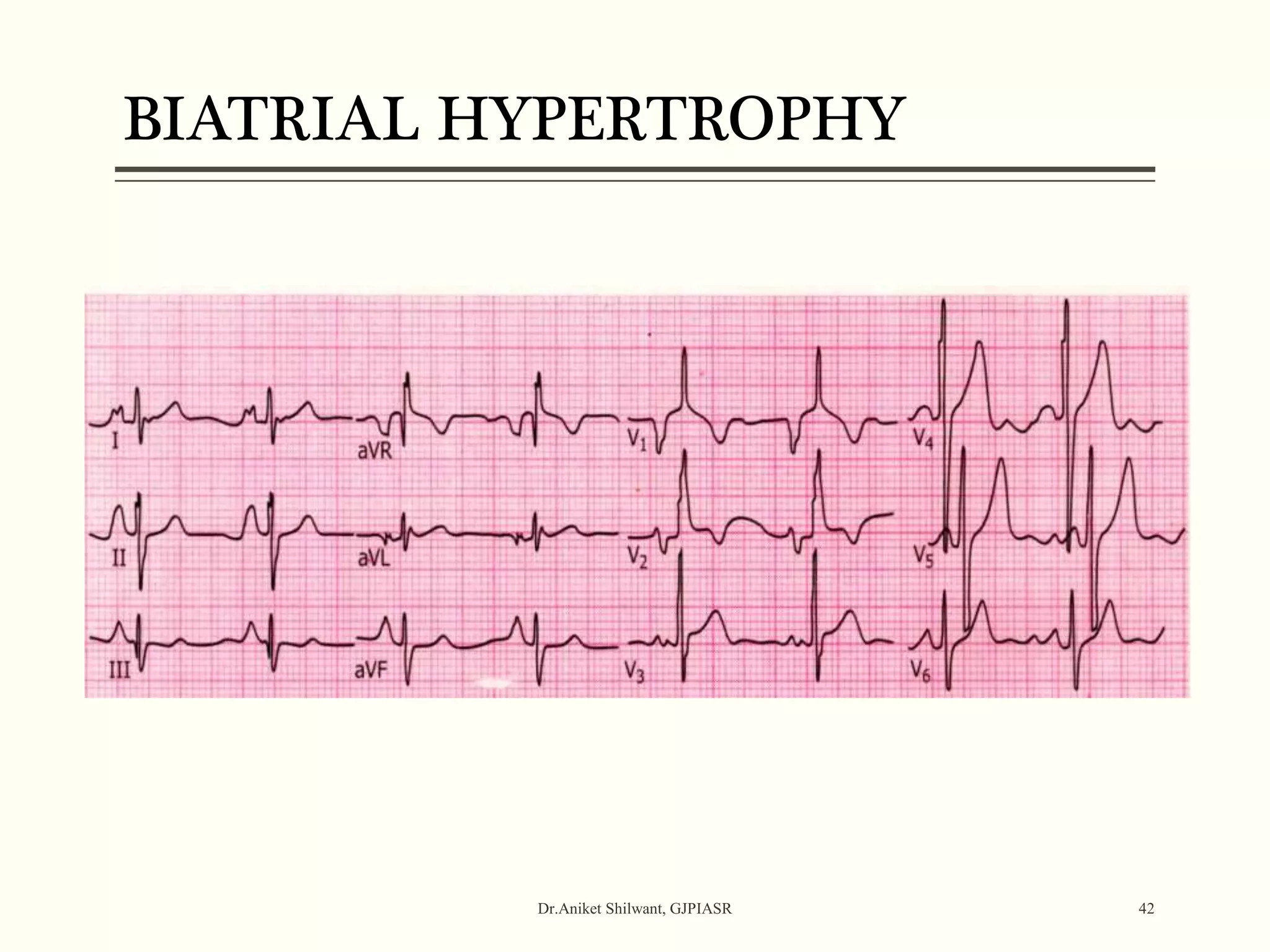
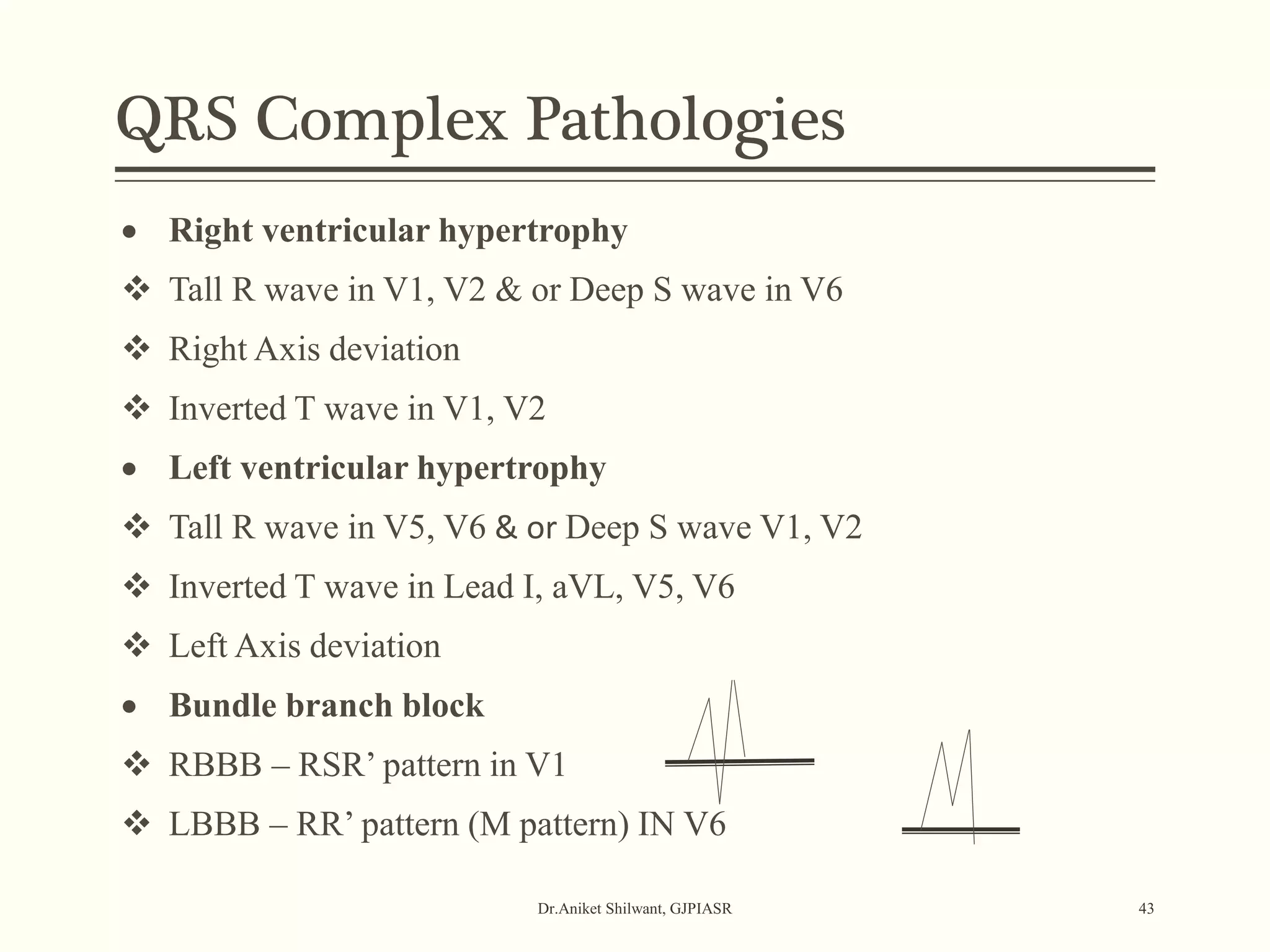
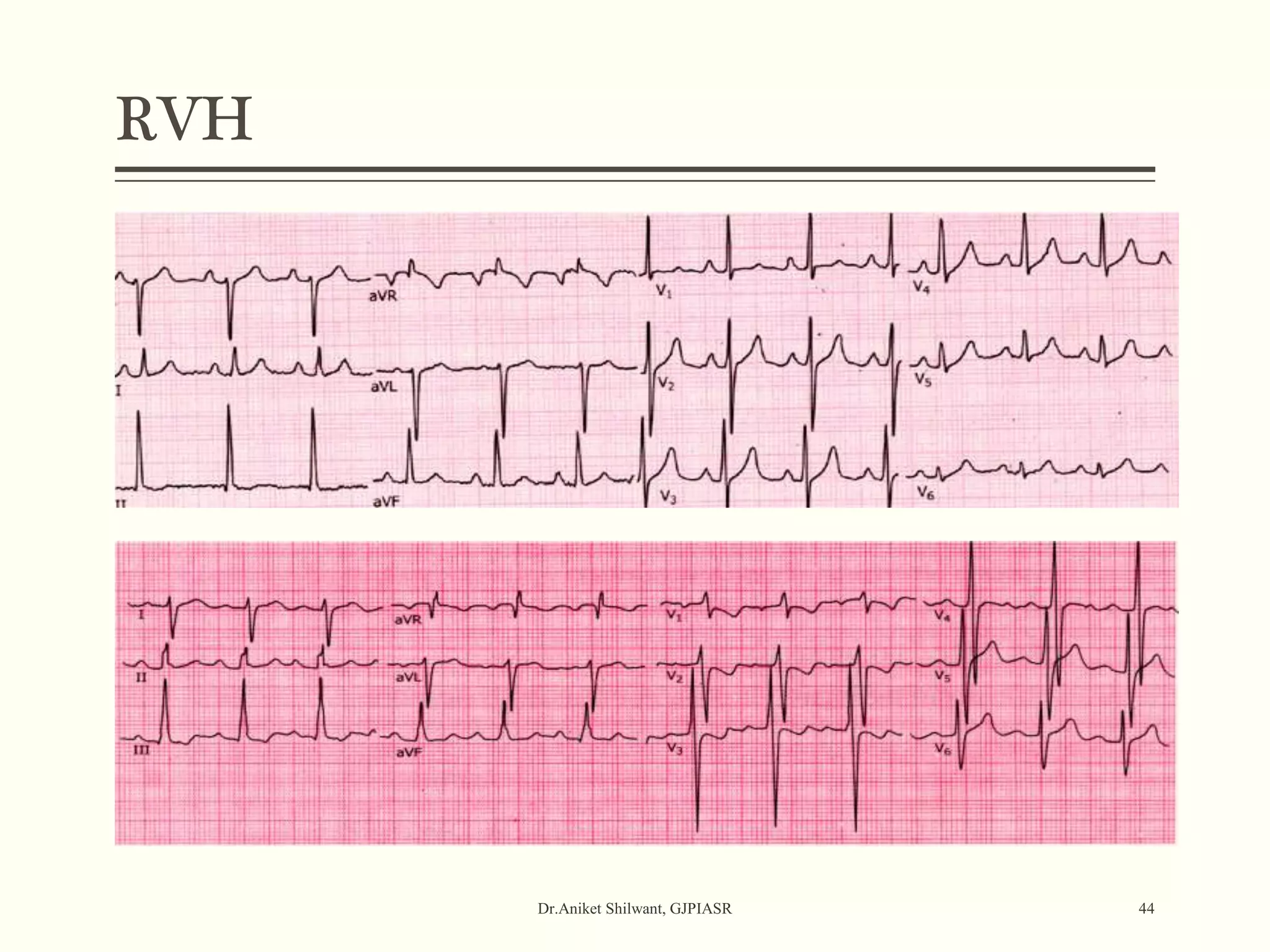
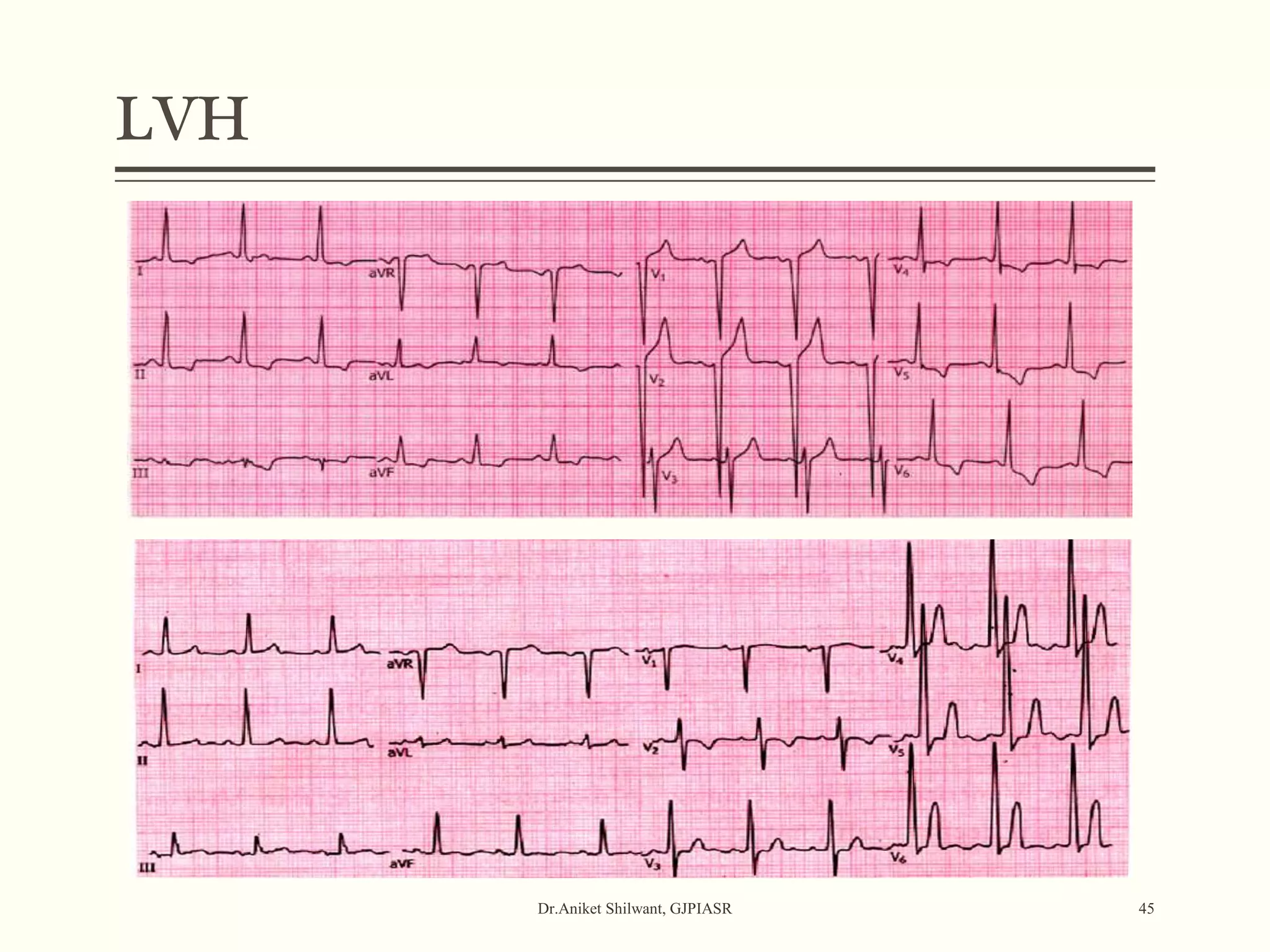
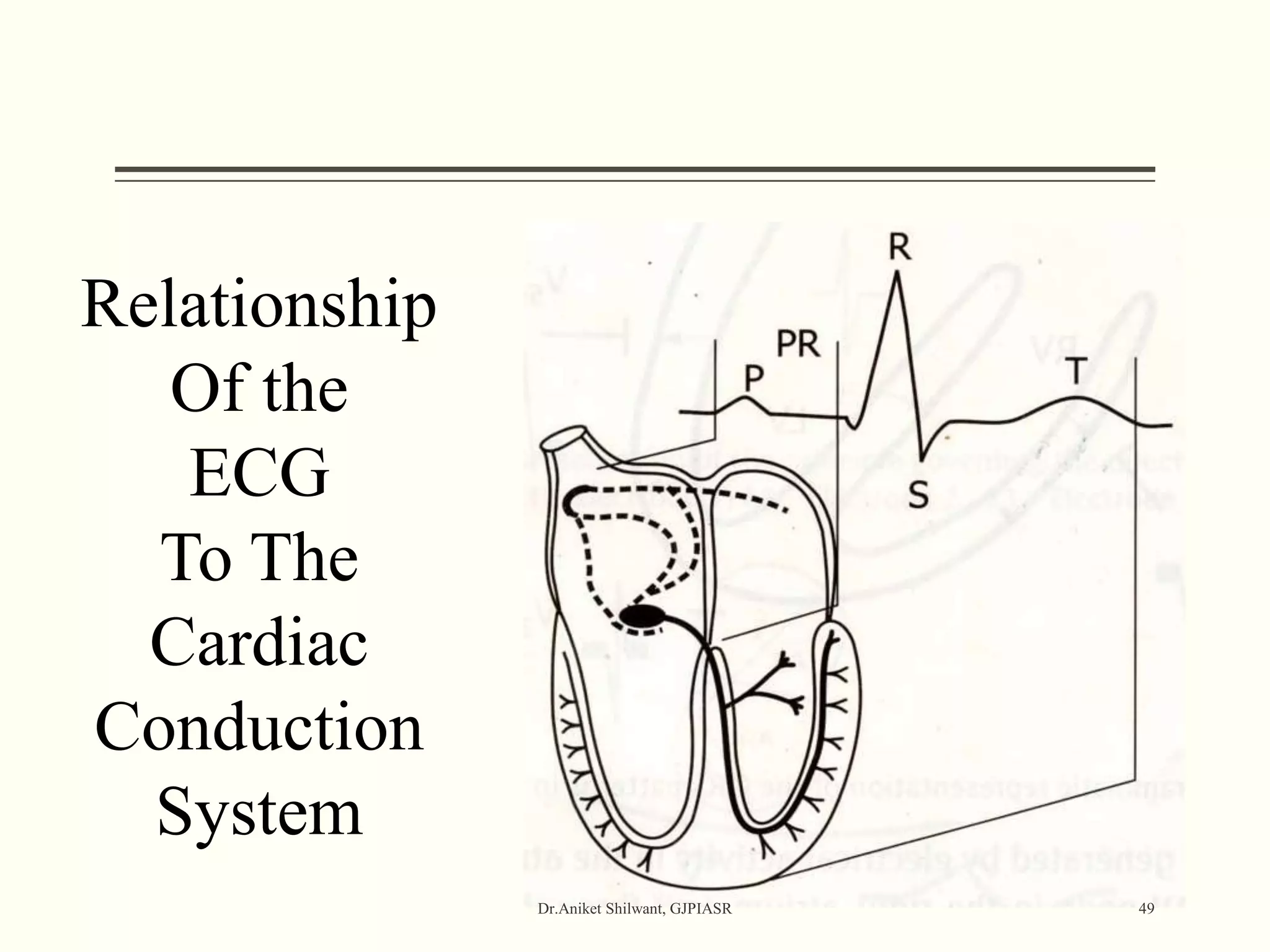
The document provides a comprehensive overview of electrocardiography (ECG), covering its fundamentals, including ECG paper, leads, waves, and intervals, as well as techniques for determining heart rate. It also discusses common pathologies associated with the ECG readings, such as atrial and ventricular hypertrophy, and the significance of various waveforms and intervals. Additionally, the document outlines how to interpret ECG results in relation to the cardiac conduction system.