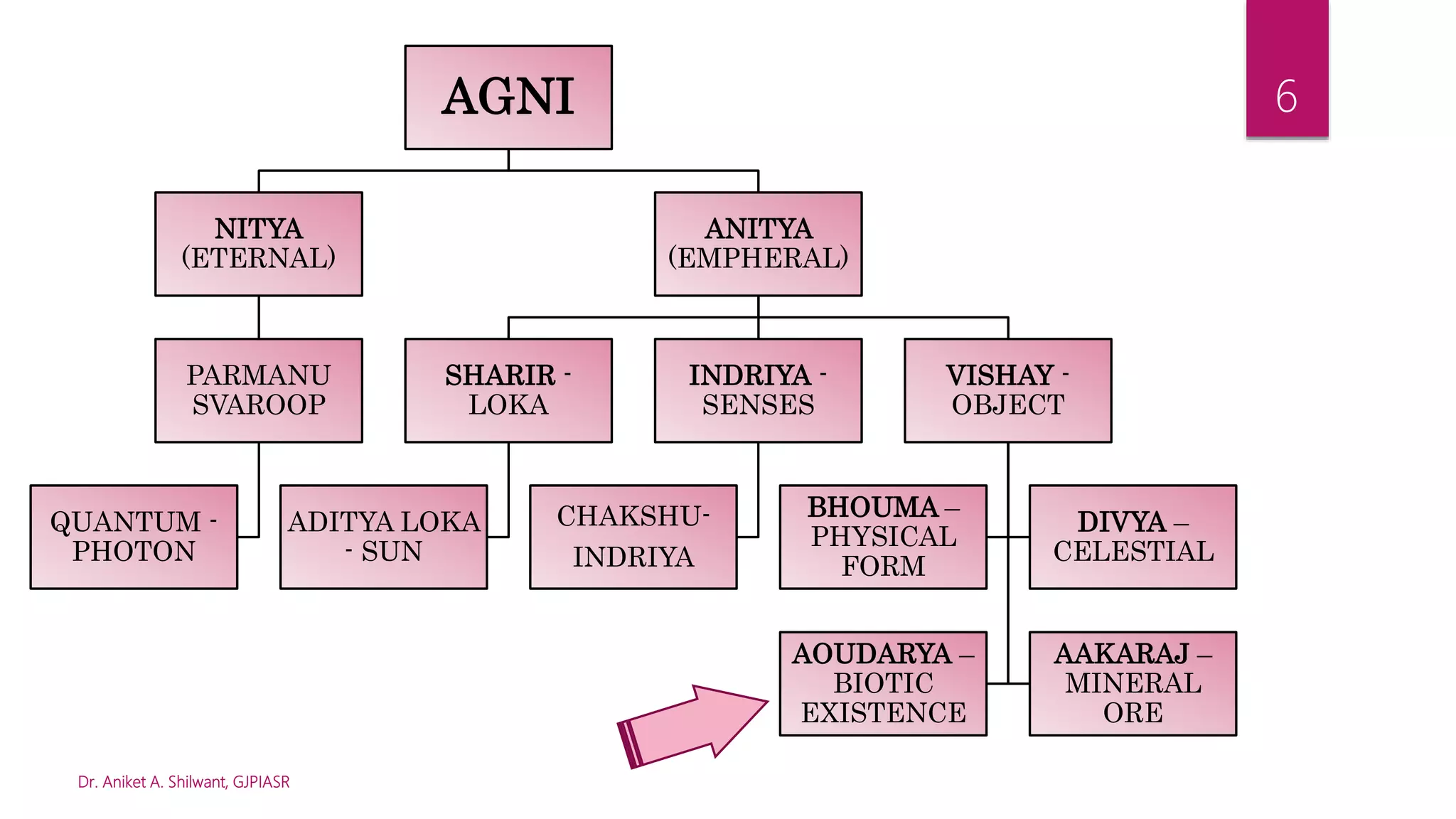
The document explains the concept of 'Agni' in Ayurvedic medicine, detailing its etymology, definitions, and various types including Jatharagni, Panchbhautikagni, and Dhatwagni. It highlights the significance of Agni in metabolic processes, digestion, and overall health, emphasizing its essential role in the body. Furthermore, the document explores the clinical implications of Agni, noting its importance in treatment protocols for various health issues.