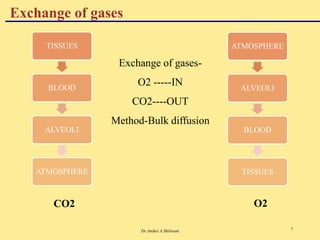
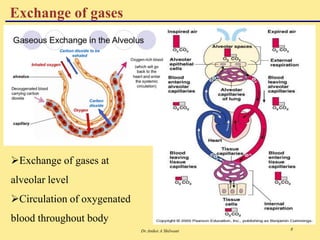
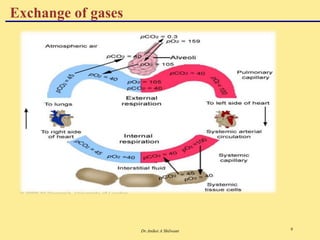
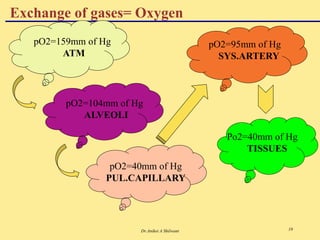
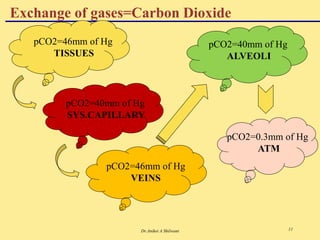
The document discusses the mechanics of respiration, including the roles of primary and accessory muscles in the respiratory process. It explains gas exchange in the lungs, detailing how oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported between the atmosphere, alveoli, blood, and tissues. Additionally, the document covers various forms of gases as they are carried in the blood, emphasizing the significance of hemoglobin.