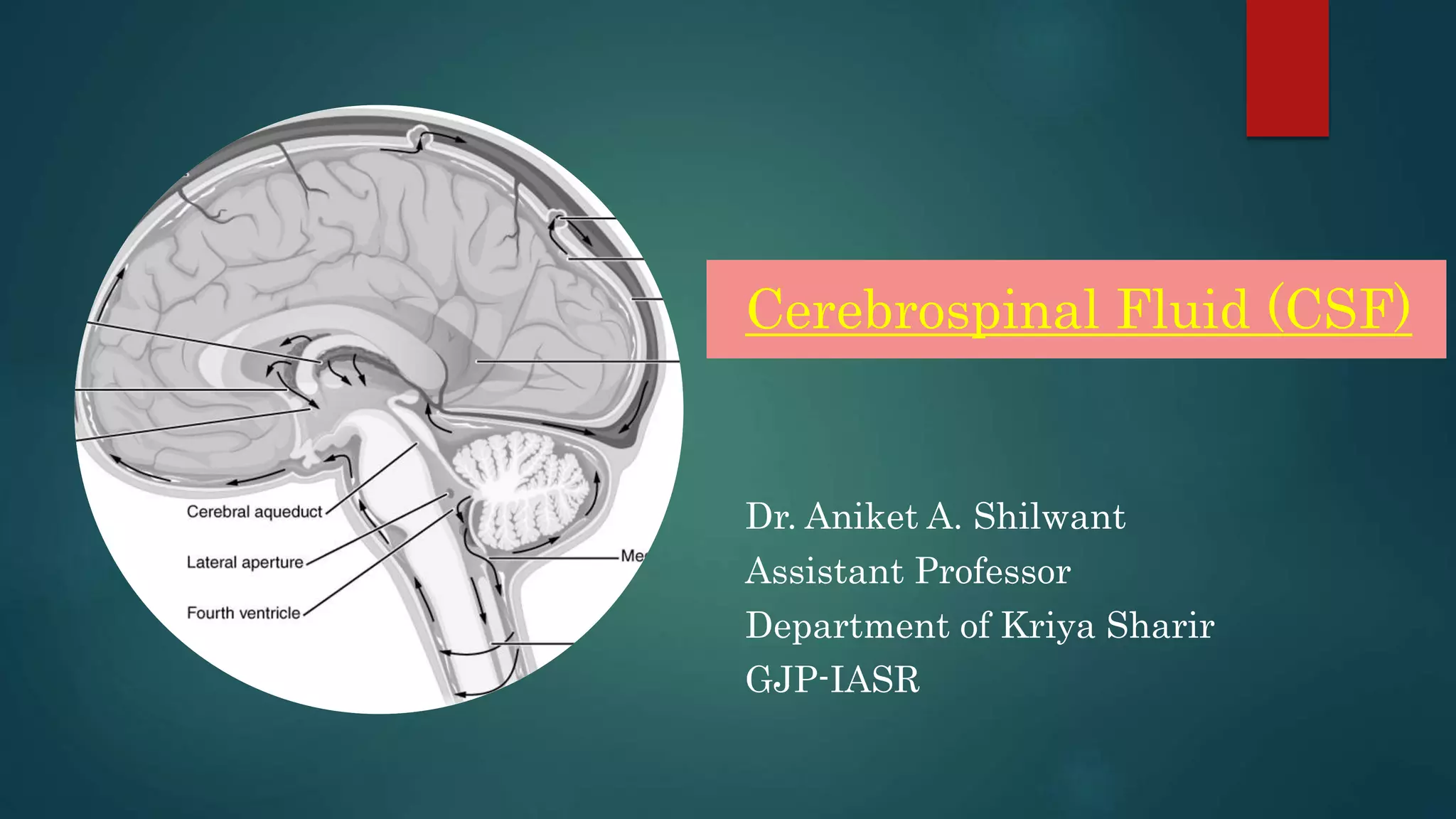
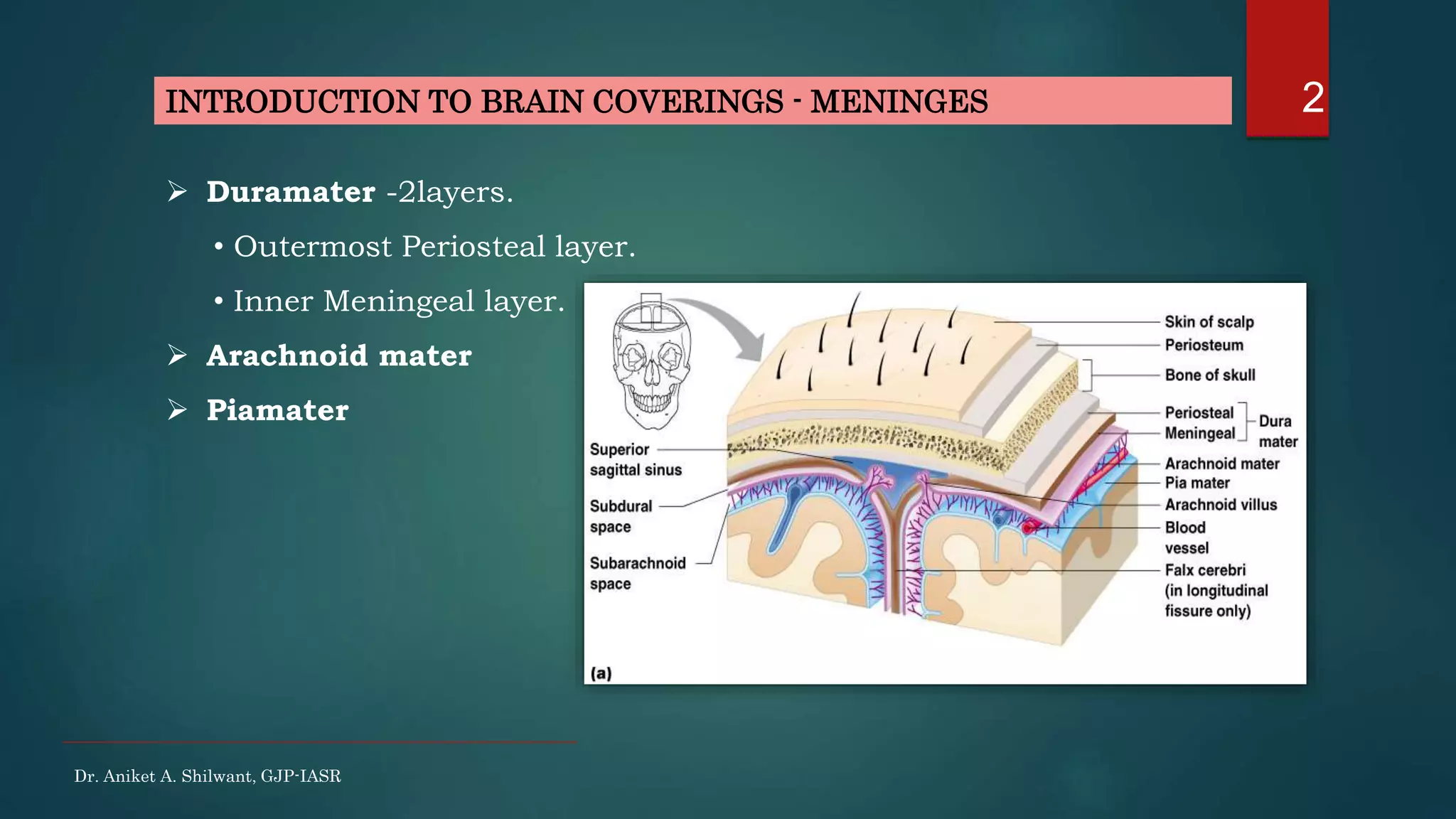
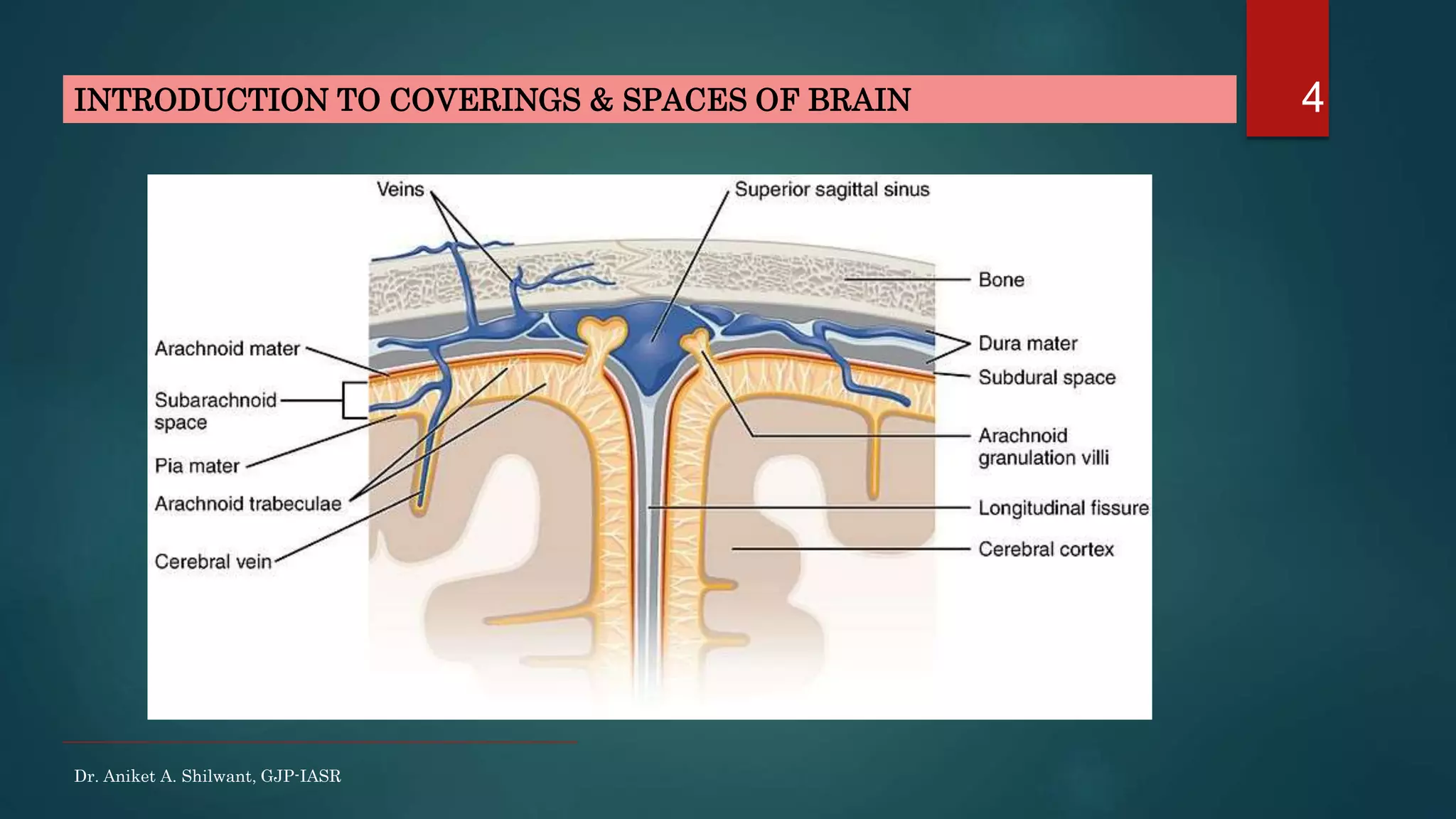
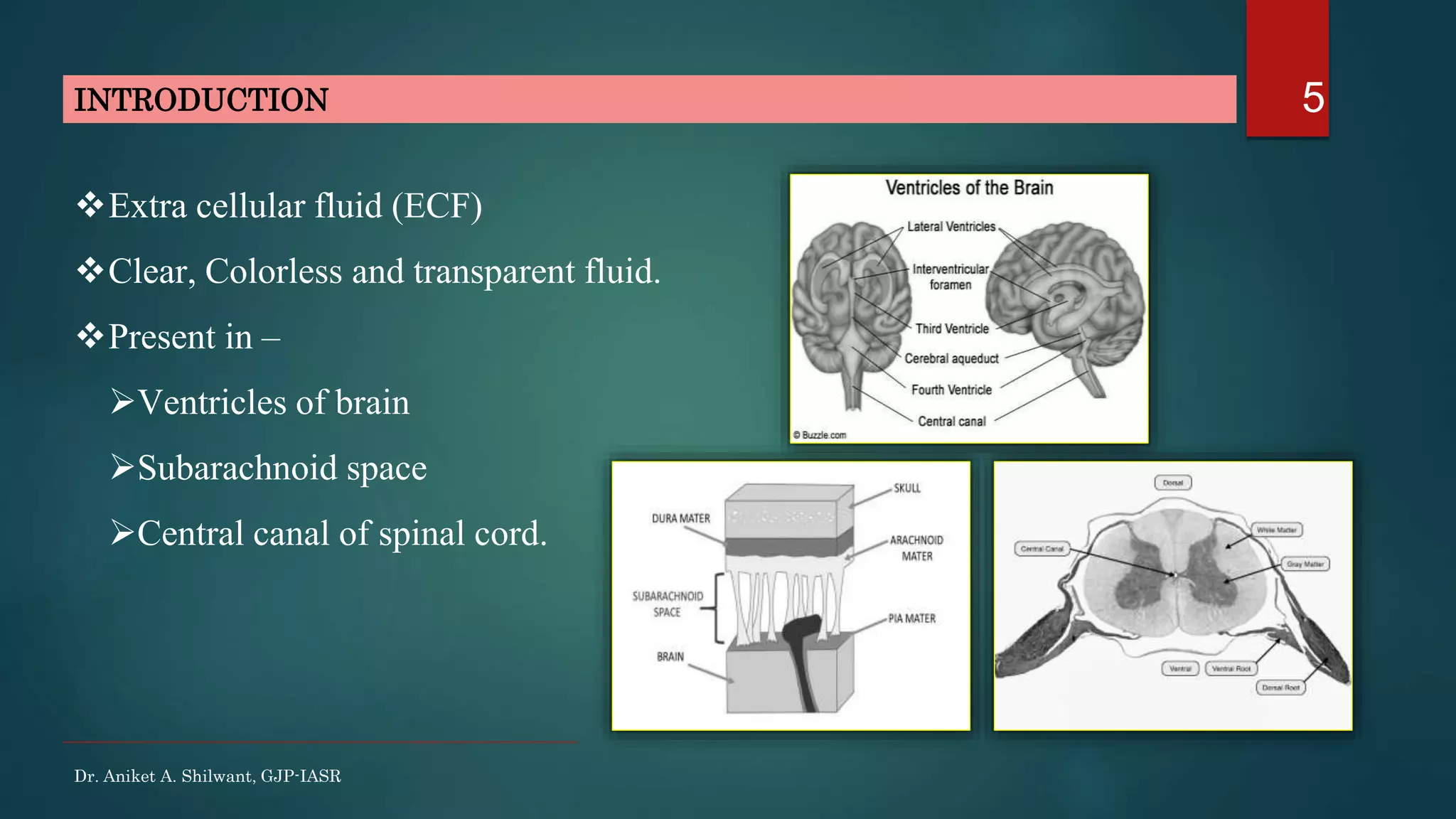
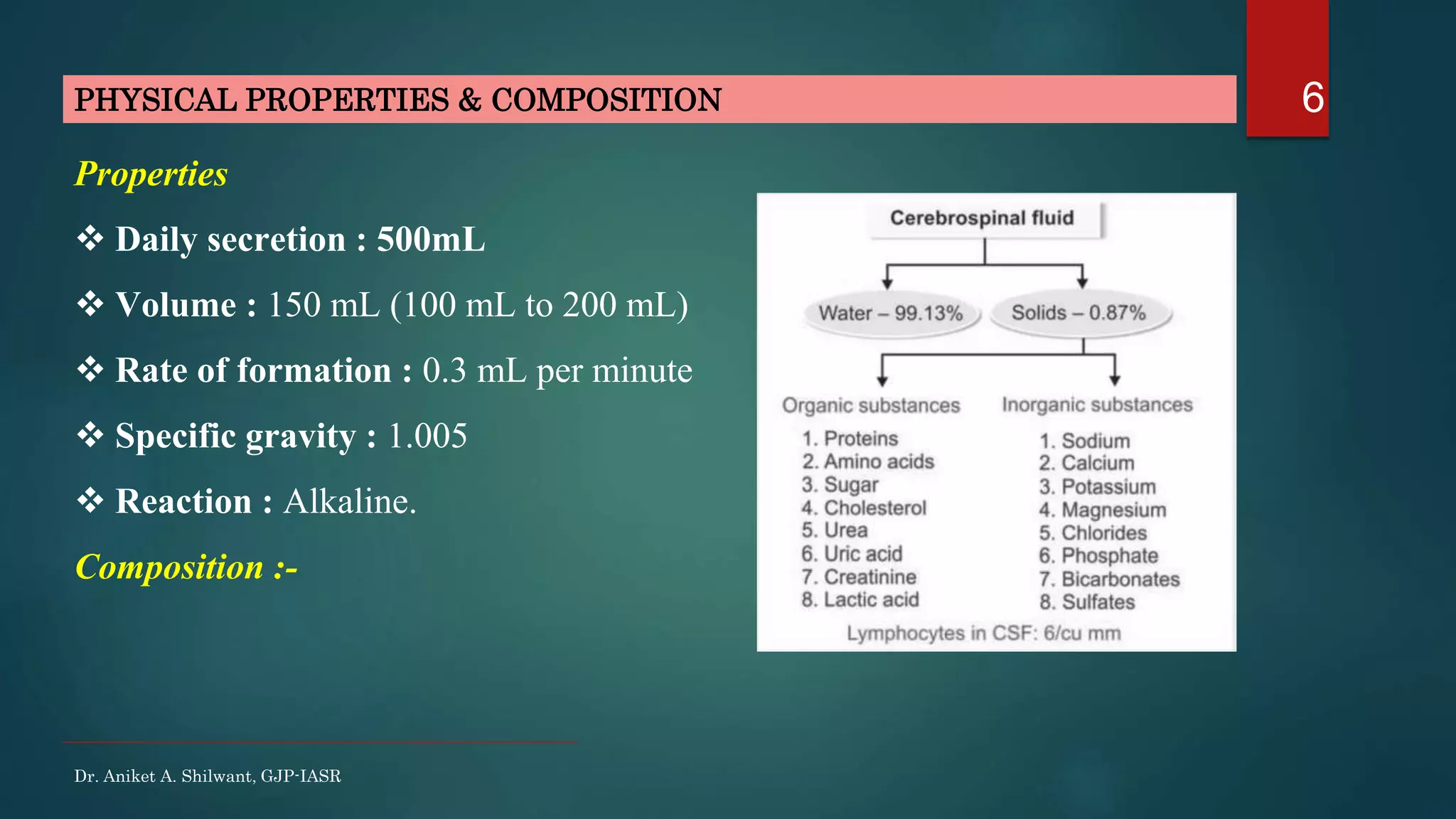
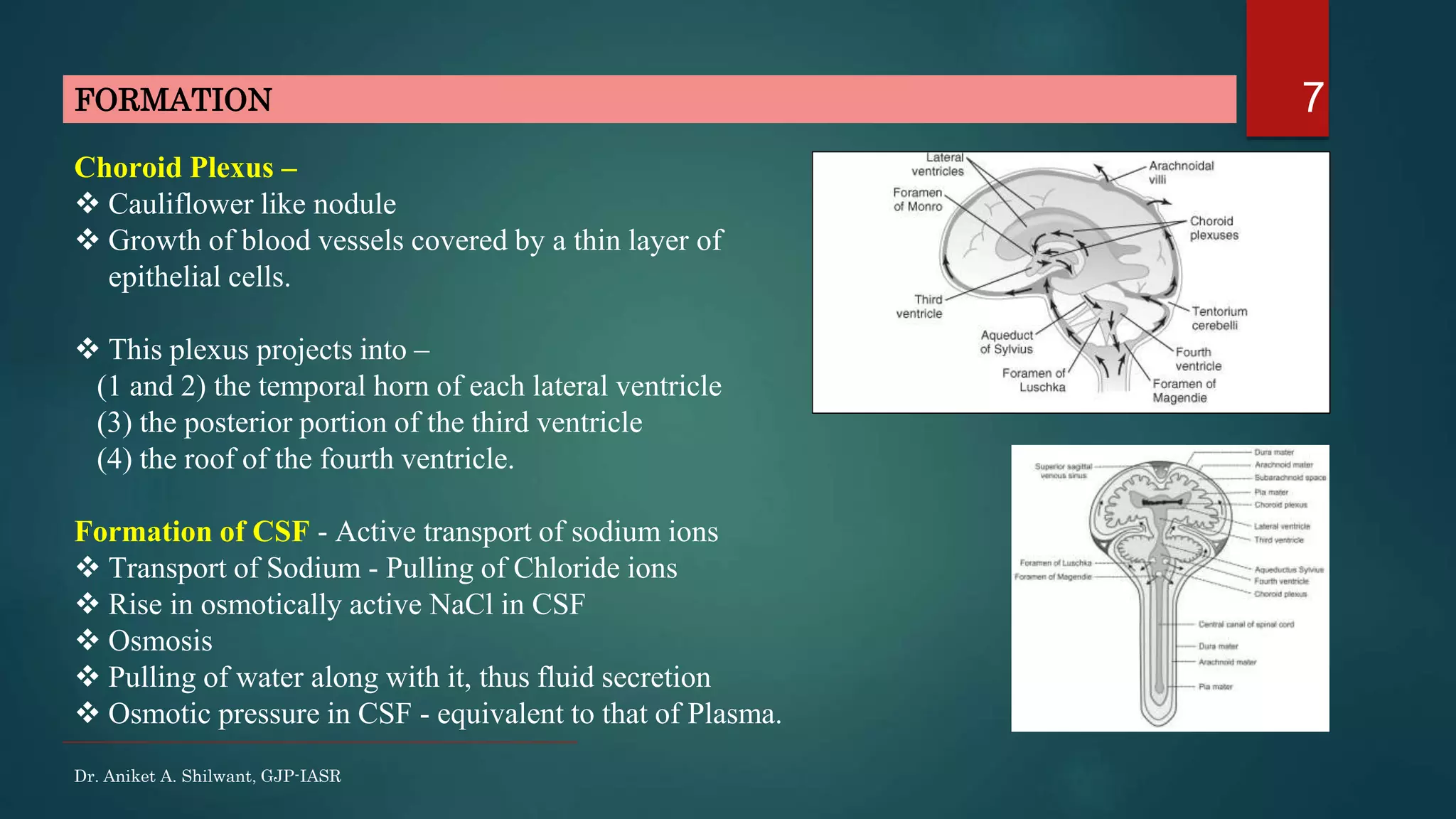
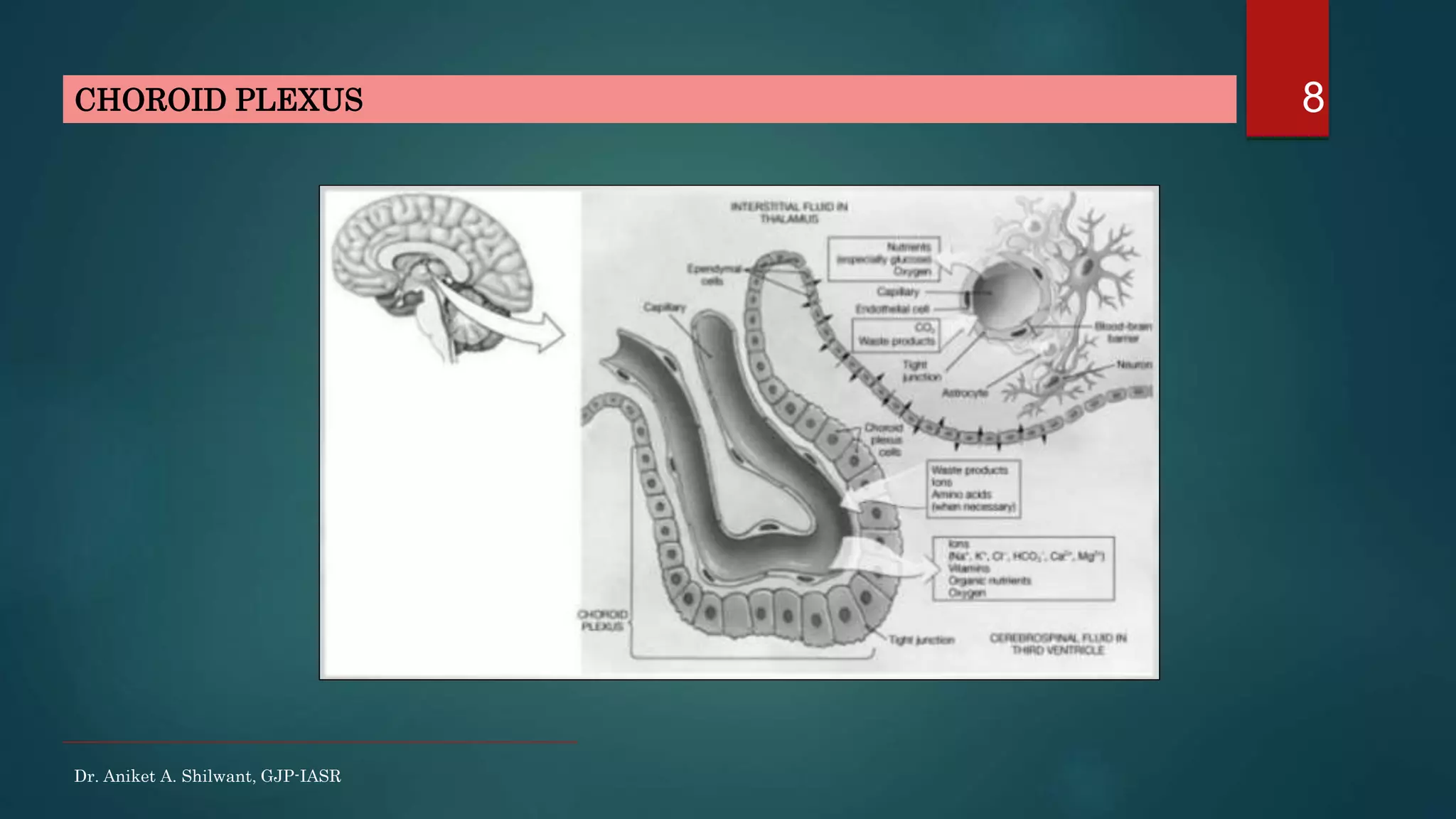
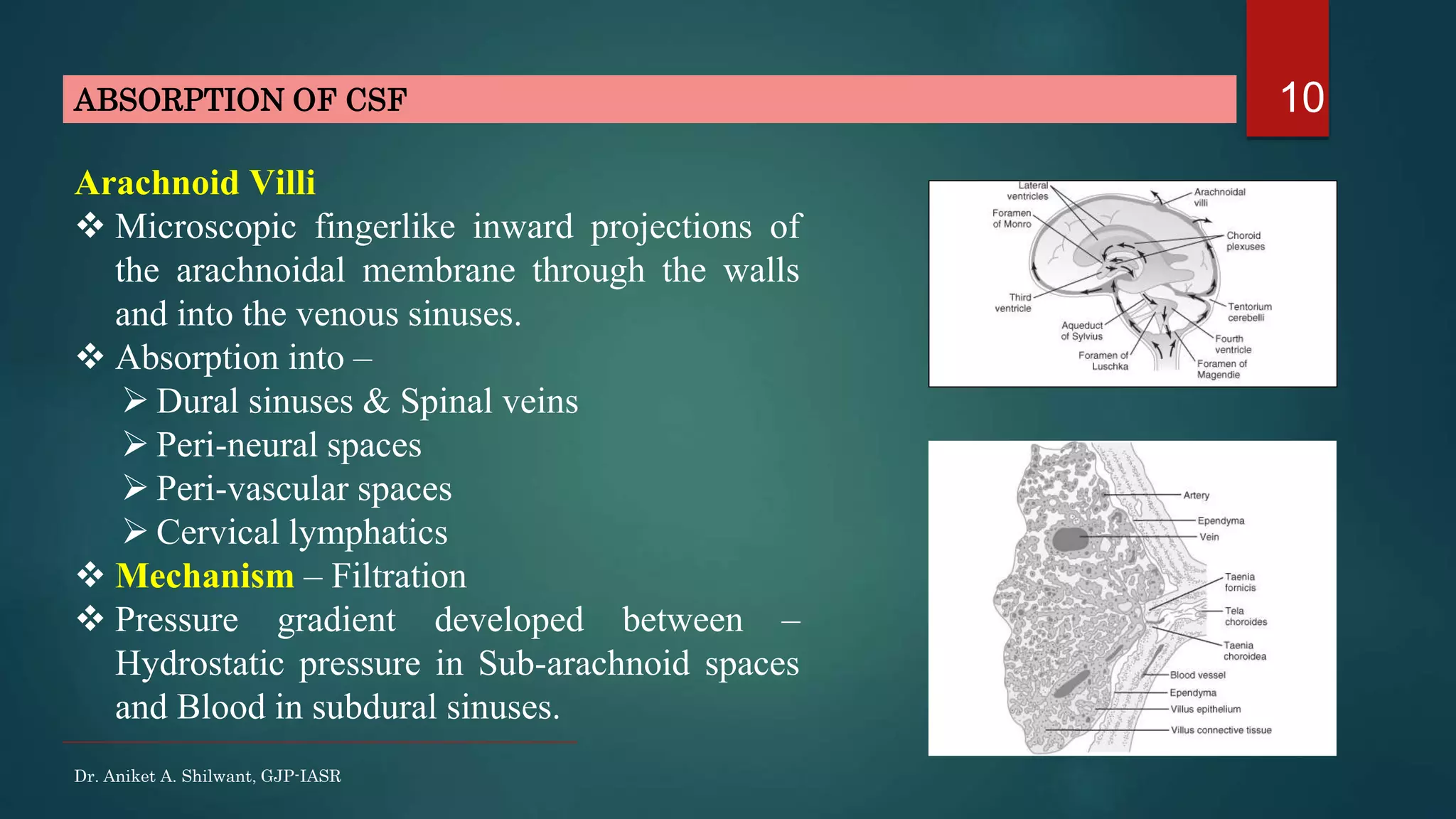
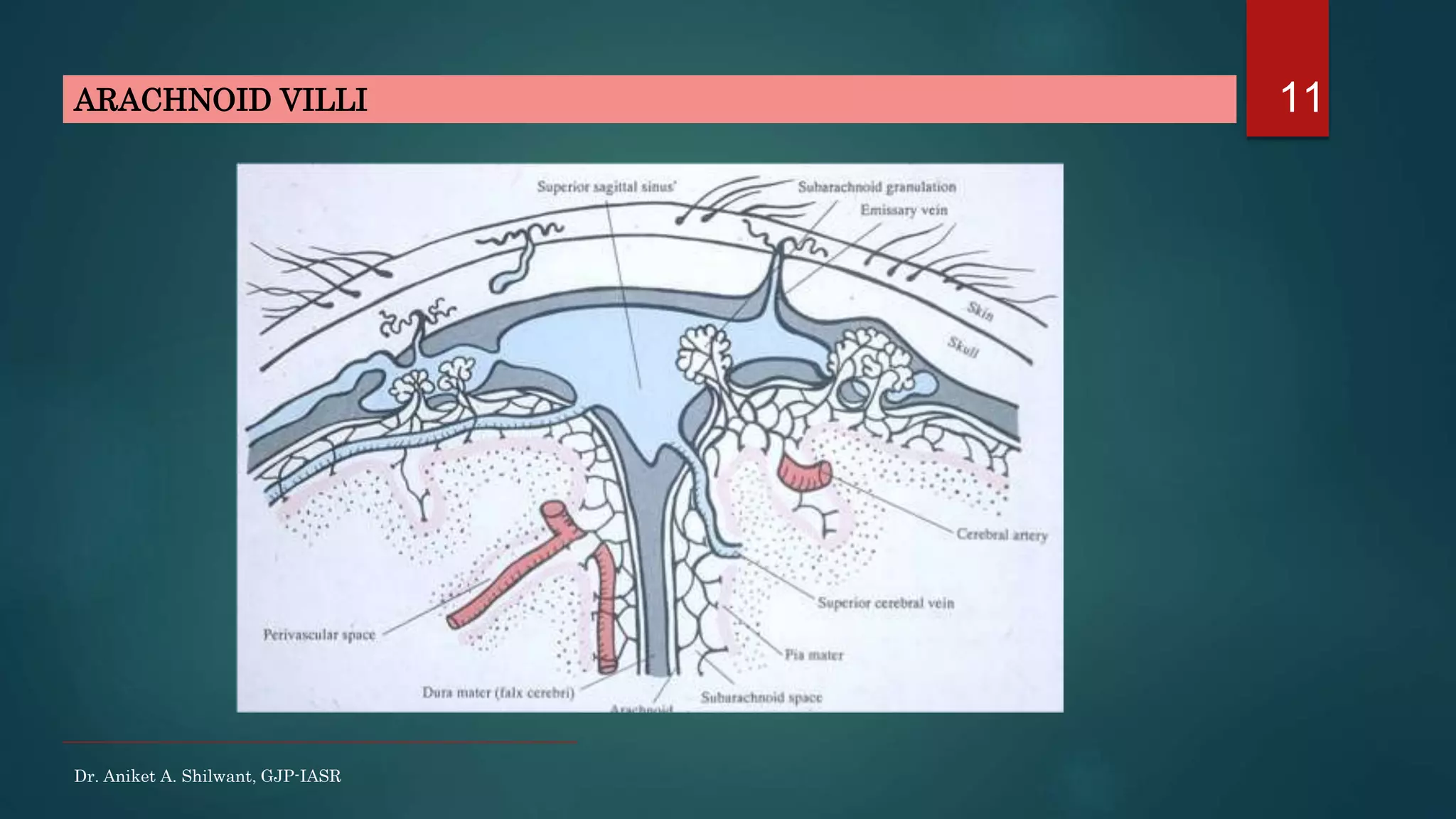
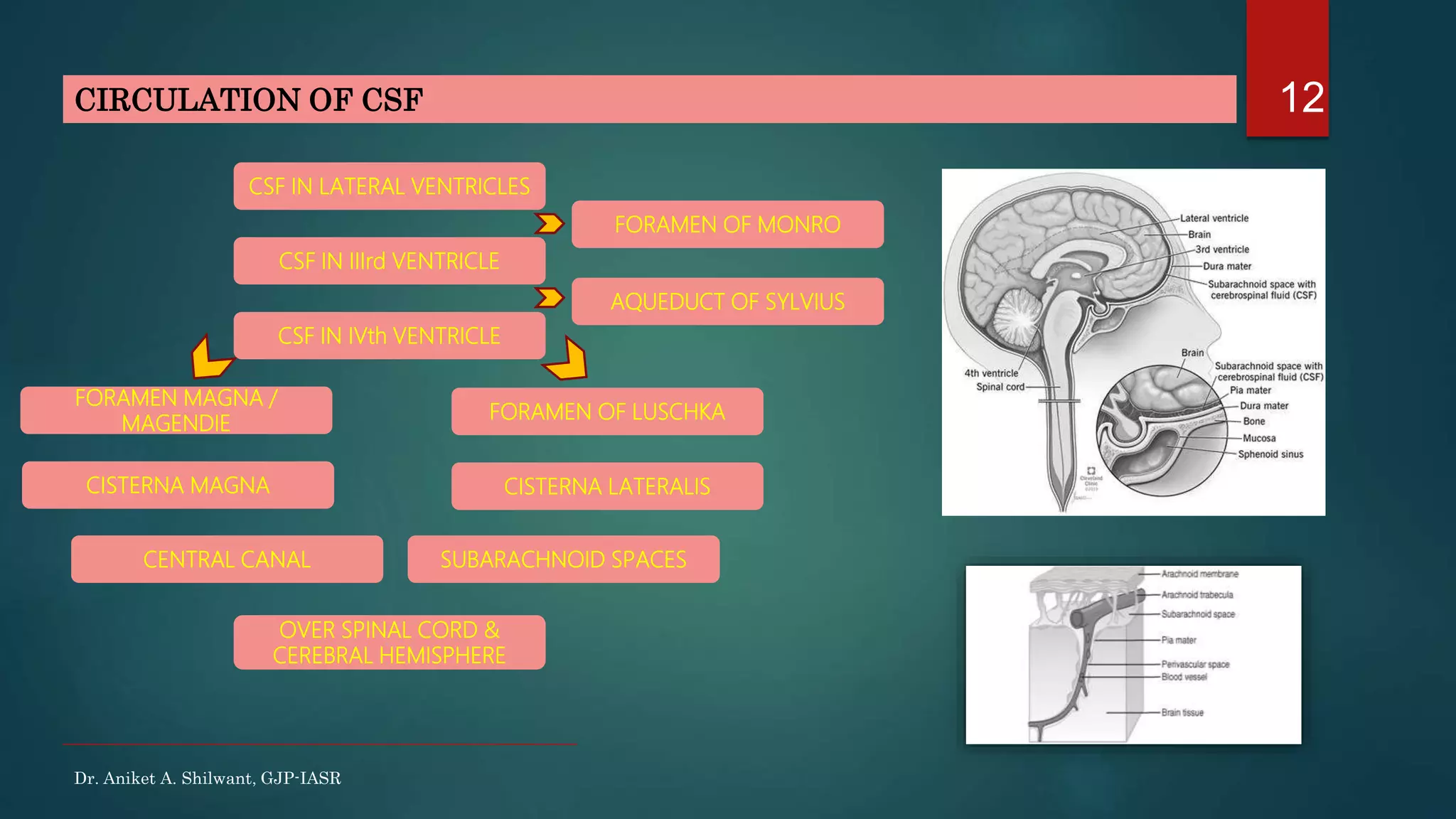
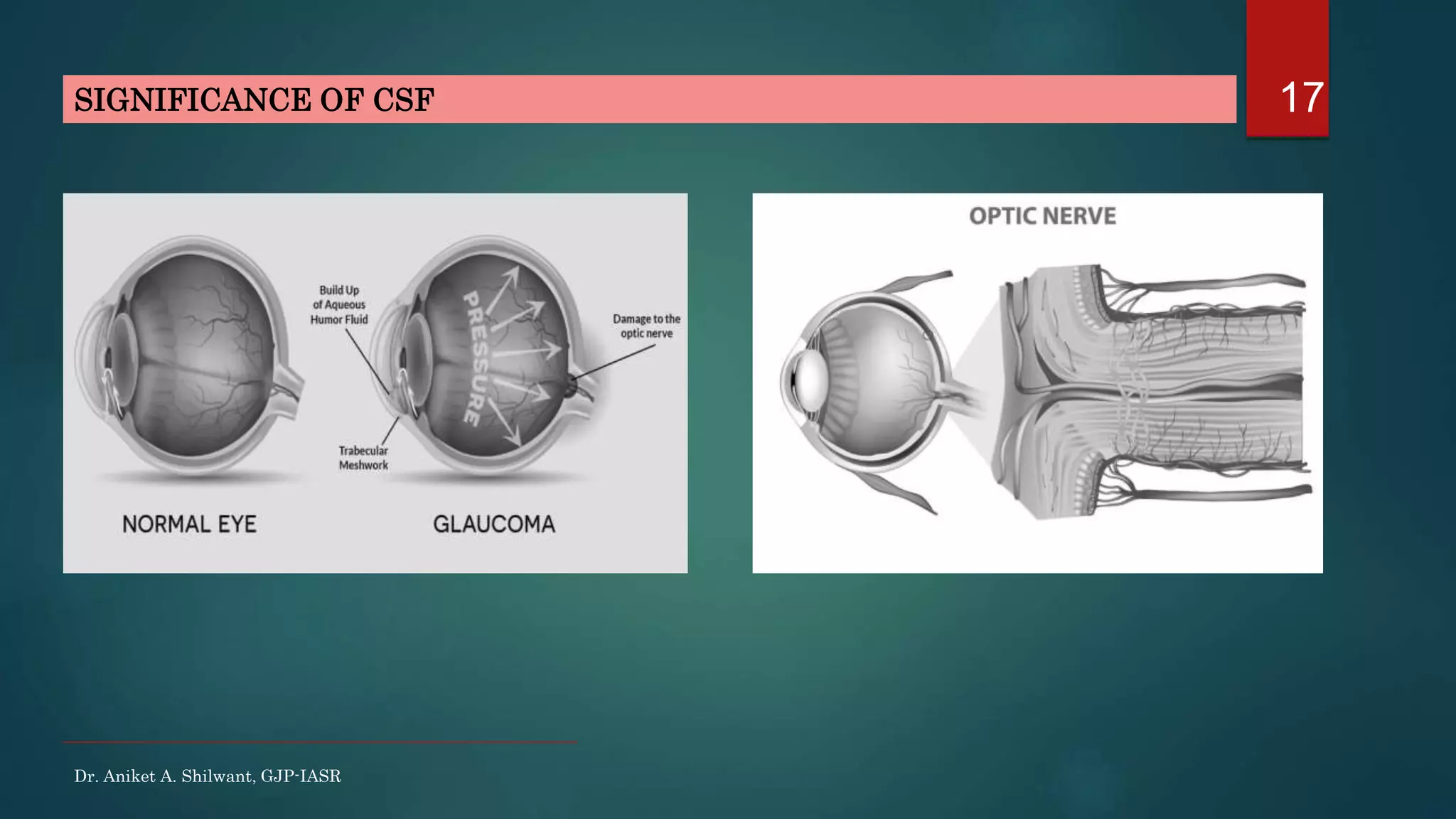
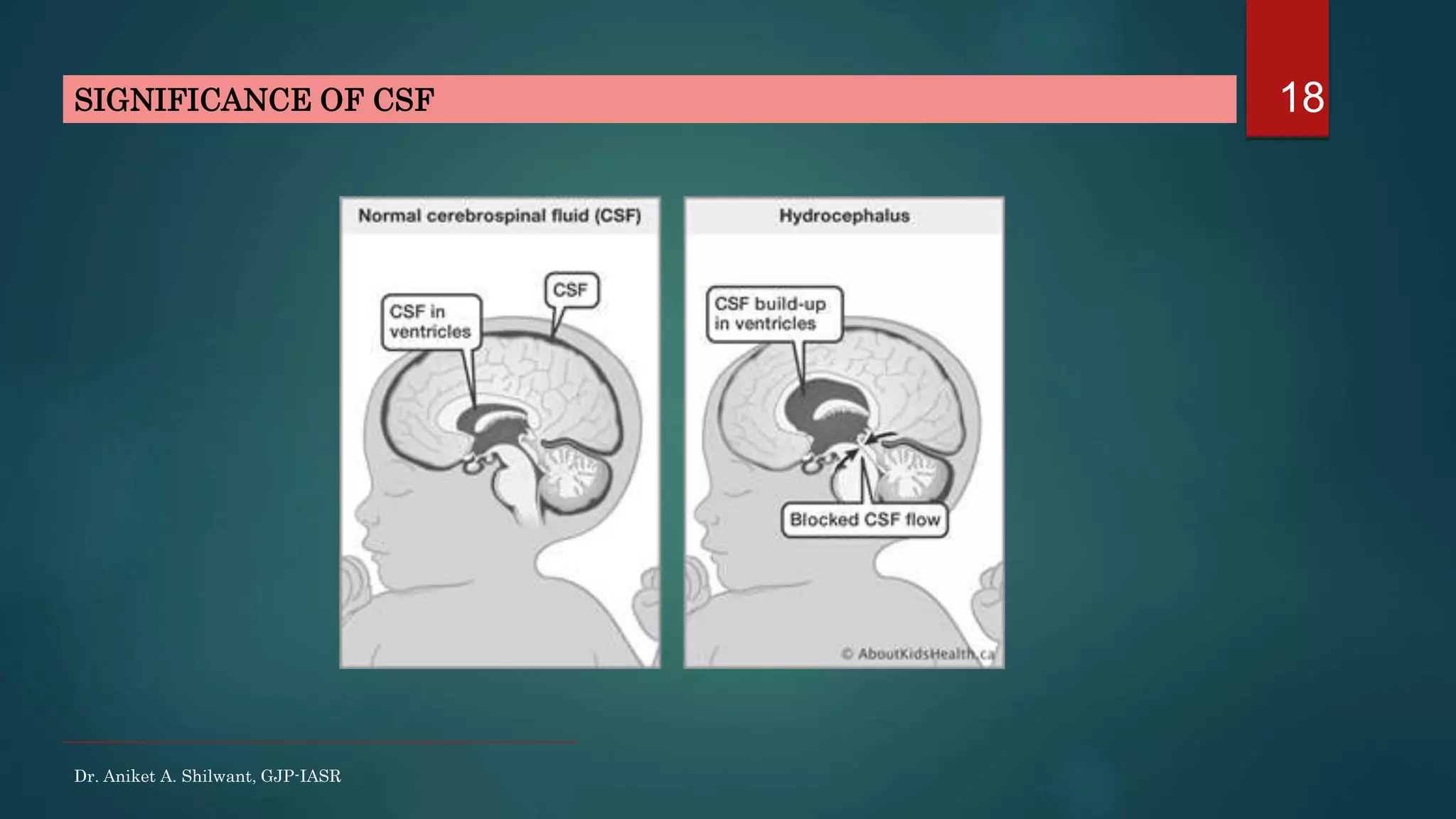
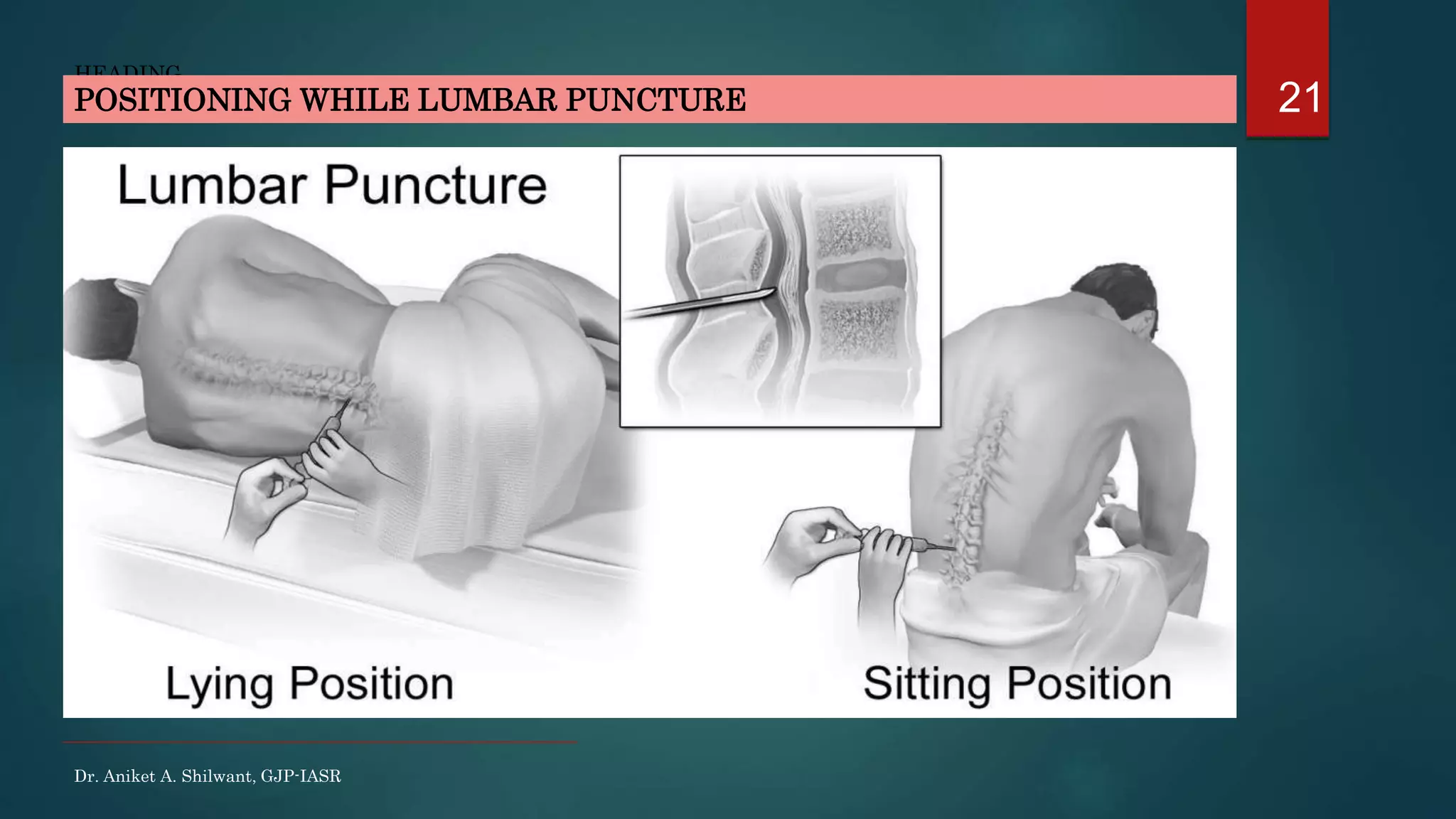
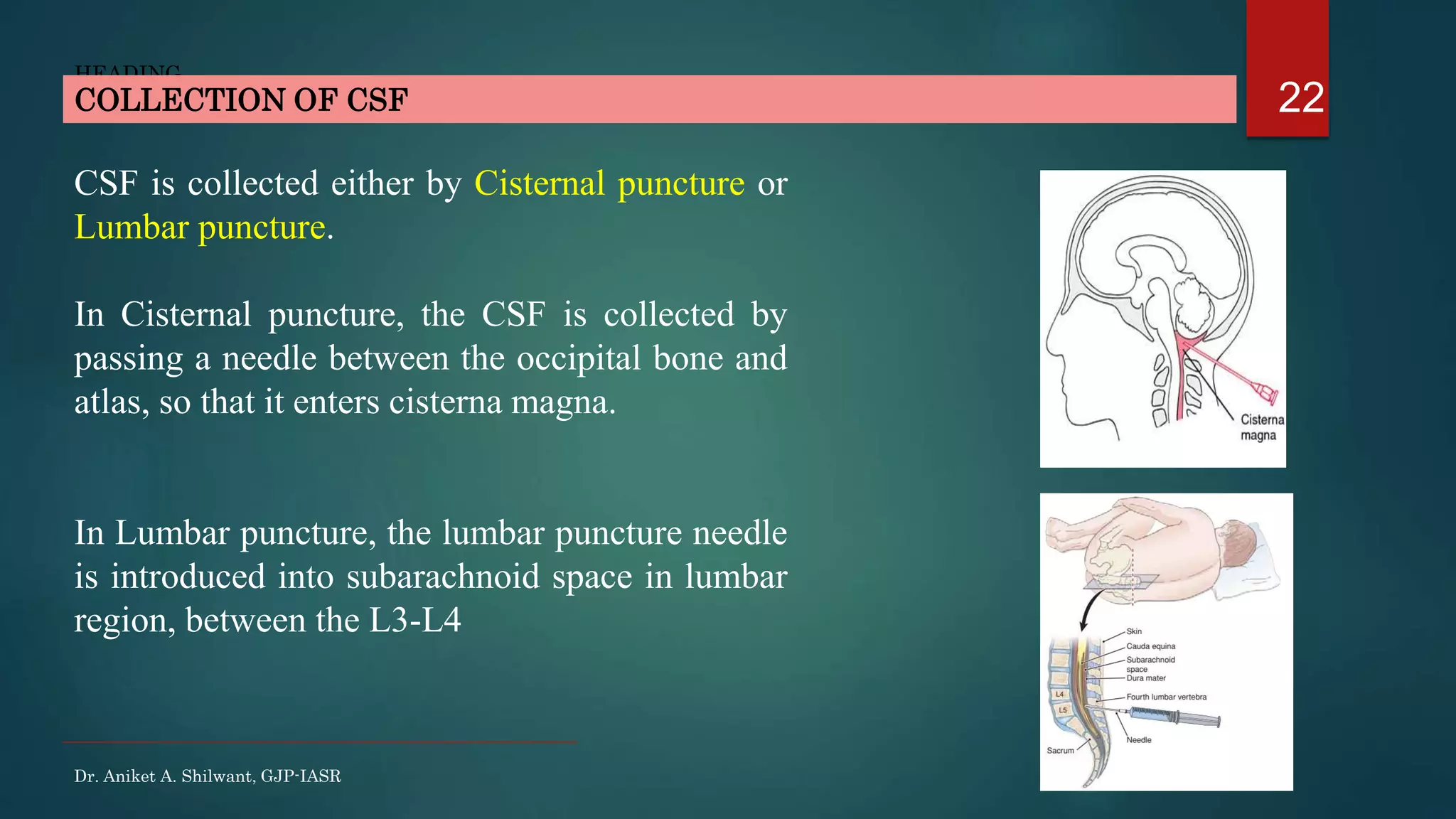
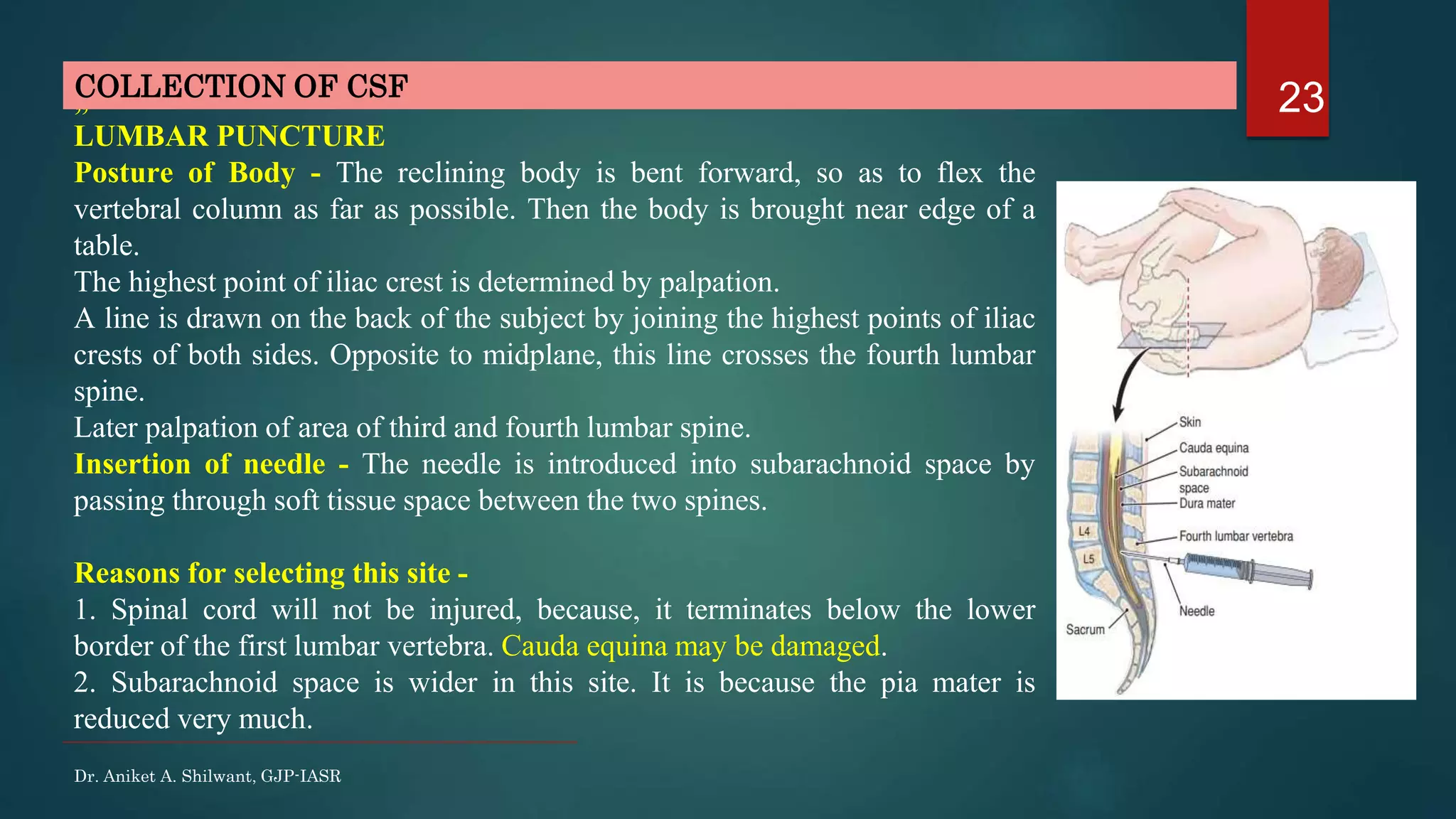
This document discusses cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), including its formation, circulation, absorption, and functions. It notes that CSF is formed by the choroid plexus in the ventricles of the brain at a rate of 0.3 mL per minute. CSF circulates through the ventricles and subarachnoid spaces before being absorbed into venous sinuses by arachnoid villi. The key functions of CSF are to protect the brain, serve as a medium of exchange, and help regulate cranial pressure. The document also describes how lumbar puncture is performed to measure CSF pressure or collect samples for diagnostic purposes.