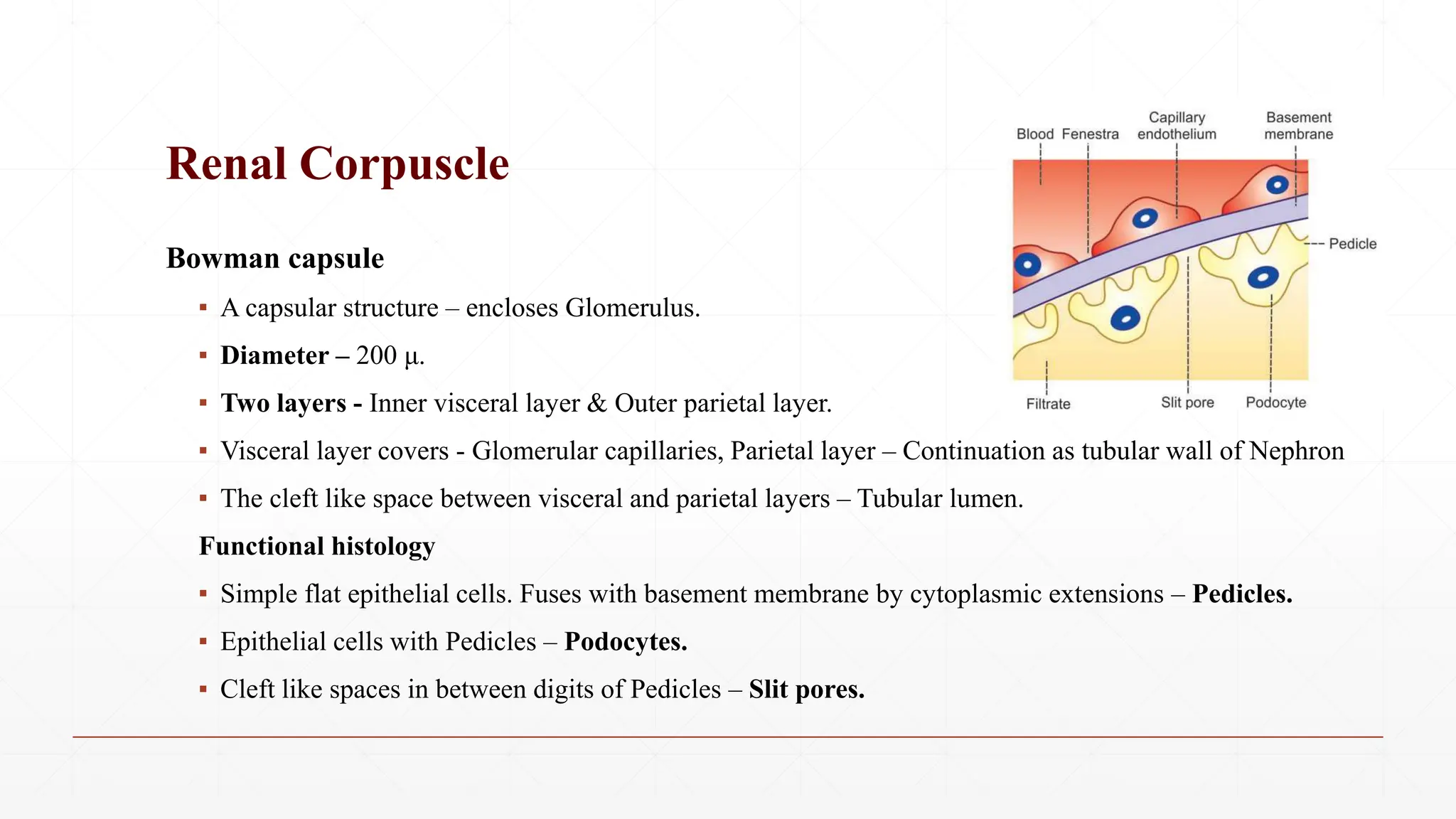
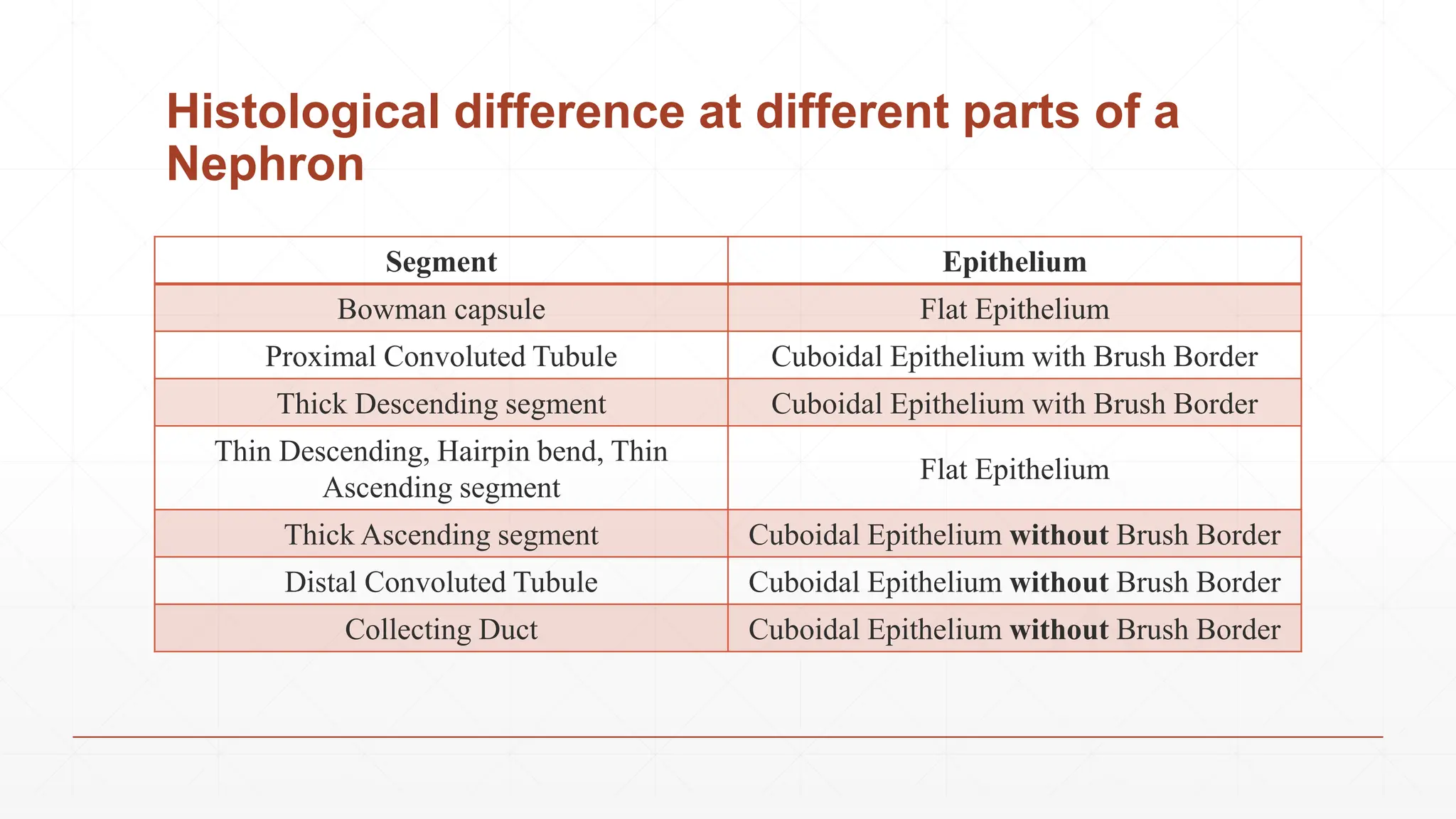
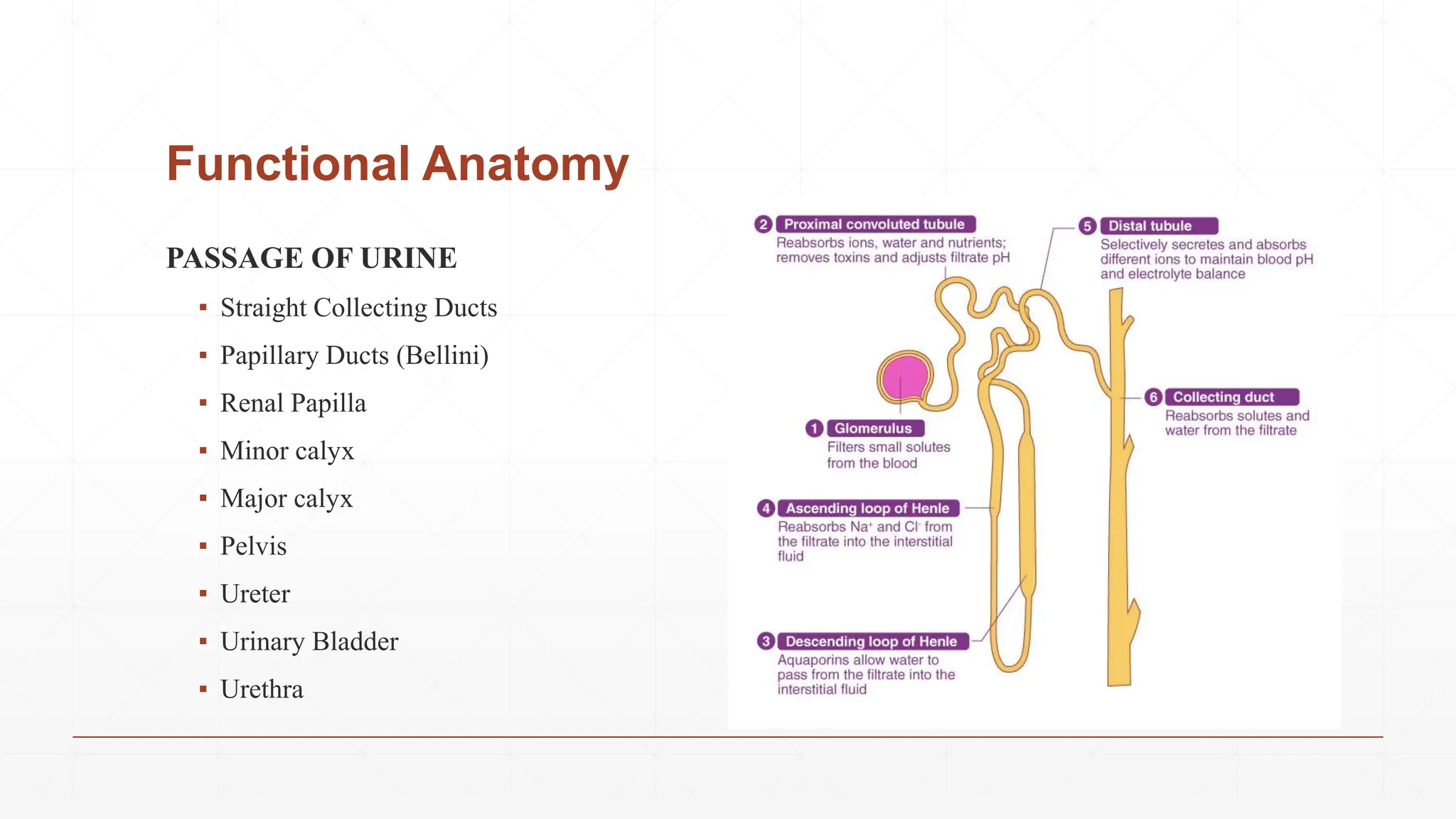
The nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. There are approximately 1-1.3 million nephrons in each kidney. Each nephron contains a renal corpuscle and renal tubule. The renal corpuscle contains the glomerulus, which is a tuft of capillaries enclosed in the Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule consists of the proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, and distal convoluted tubule. Nephrons come in two types - cortical nephrons and juxtamedullary nephrons. The juxtamedullary nephrons have longer loops of Henle that penetrate deeper into the kidney. Urine is formed as