Respiratory system – part 2
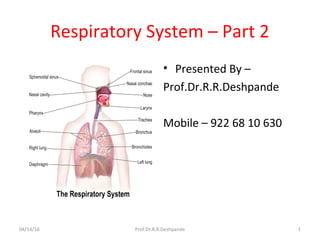
- 1. Respiratory System – Part 2 • Presented By – Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande Mobile – 922 68 10 630 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 1
- 2. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 2 Lung Function Tests / Pulmonary Function Tests • 1) Indications • To differentiate between obstructive (Asthma & Bronchitis) & restrictive (Pneumonia, Pleural effusion) Lung diseases • To study the effect of harmful agents like dust & smoke on lungs in industrial workers. • For the fitness test in players or before employment • In research to study the effect of bronchodilator drugs (Deriphylline)
- 4. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 4 Graph of Spirometer
- 5. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 5 2) Limitations of Lung Function Tests • These tests require co - operation of the patient. In comatose & in children, tests cannot be done. • Because the lung has large functional reserve, early detection of the disease is difficult. • Single test is not useful, multiple tests are required
- 6. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 6 2) Limitations of Lung Function Tests • Findings of the clinical examination must be co - related with the lung function test report. • Patho - anatomical diagnosis of the disease cannot be made (cause & location cannot be detected).
- 7. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 7 Classification of LFT • 1) Static Lung Function Tests • 2) Dynamic Lung Function Tests
- 8. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 8 Static Tests • 1) Tidal volume (TV) = Amount of air taken in or out during quiet • respiration. Normal value = 400 - 500 ml • 2) Inspiratory Reserve volume (IRV) = Amount of air taken in, by forceful inspiration, over & above tidal volume. • Normal value = 2400 - 2800 ml
- 10. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 10 Static Tests • 4) Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV) = Amount of air given out by forceful expiration over & above Tidal volume. • Normal value = 800 - 900 ml • 5) Residual Volume (RV) = Amount of air, that remains in lungs at a end of forceful expiration. Normal Value = 1000 ml
- 11. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 11 Static Tests
- 12. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 12 Static Tests • 7) Vital Capacity (VC) = Amount of air that can be given out by forceful expiration, after forceful inspiration. • VC = IV + IRV + ERV • Normal value - Adult Indian males = 4 - 5 liters • Adult Indian females = 3.3 - 4 liters
- 13. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 13 Physiological Variations • a) Age = With the age, VC increases up to adulthood. • b) Height = VC is more in tall person. • c) Posture = VC is more in standing position. • d) Gender = VC is less in females because average height is low. • e) Exercise & yoga = Increases VC • f) At High Altitude = VC Increases
- 14. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 14 Practical Importance of Tests • 1) Vital capacity is affected in restrictive lung diseases such as pneumonia & VC is not affected in obstructive diseases like Asthma. • 2) VC Test is used in sports people & before joining particular occupation like Military Services. • 3) Total Lung Capacity (TLC) - It is VC+ Residual volume. • (Normal value = 5 to 6 liters)
- 15. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 15 Dynamic Lung Tests • 1) FEV1 - Forced expiratory volume, at the end of 1 second Normal value – • FEV1 = 85 % • FEV2 = 97 % • FEV3 = 100 % • These values are reduced in obstructive lung disease (Asthma & Bronchitis)
- 16. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 16 Dynamic Lung Tests • 2) Resting Minute Ventilation (RMV) • Amount of the air ventilated in 1 minute at rest. • RMV = Tidal volume x Respiratory Rate • (Normal value = 8 to 9 lit. /min)
- 17. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 17 Dynamic Lung Tests • 3) Maximum Breathing Capacity (MBC) Or Maximum Voluntary Ventilation (MVV) • Amount of air which is ventilated by forceful ventilation in 1 minute. (Normal value = 80 to 100 lit. /min) • MBC is reduced in both obstructive & restrictive lung diseases
- 18. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 18 Dynamic Lung Tests • 4) Pick Flow Rate (PFR) • It is the maximum rate at which, air can be expired out. • (Normal value = 450 - 500 lit. /min.) • PFR is measured by ‘Peak Flow Meter’ • PFR is reduced ‘Obstructive lung disease. ’ (Asthma)
- 19. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 19 Types of dead space • 1) Functional Residual Capacity (FRC) • Amount of air remaining in the air passages & the alveoli, at the end of quiet expiration. • 2) Residual volume - Amount of air left behind in the ling at the end of deep expiration (1 to 1.4 lit.)
- 20. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 20 Types of dead space • 3) Dead space air - Air left in the bronchial tree, which does not take part in respiration.
- 21. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 21 Study of Respiration • a) Inspection - Note construction of bony structures, any deformities, asymmetry or rickets, muscles, skin, etc. • Normally movements of chest wall are equal on both sides from midplane.
- 22. Examination of Respiratory system 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 22
- 23. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 23 Study of Respiration • b) Palpation - It is done to confirm the findings of inspection • c) Percussion (Tapping) - Lung tissue normally gives resonant note while solid tissue (fibrous) gives a dull tone.
- 25. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 25 Study of Respiration • d) Auscultation - It is done with stethoscope to hear the normal & abnormal sounds. 3 types of normal sounds are Tracheal sounds at the root of neck. • Bronchial sounds in bronchial region. • Vesicular sounds of lung tissue
- 26. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 26 Special Study • X ray chest – PA view • Screening of chest • MRI of chest • Bronchoscopy • Sputum Examination for AFB • Pleural Tapping
- 27. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 27 A few important terms • Eupnoea - Normal breathing. • Hyperpnoea - Increase in amplitude of rate of respiration. • Dyspnoea - Difficulty in breathing
- 28. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 28 Note • 1) In male, breathing is predominantly abdominal & in females it is thoracic. • 2) Artificial respiration is needed in some emergencies like drowning, an electric shock, operations, greater doses of anesthesia etc, suffocation due to smoke, Paralysis of respiratory muscles • When breathing suddenly stops but heart keeps on breathing.
- 29. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 29 2) Respiratory Insufficiency • 2A) Hypoxia (Less O2) - This is deficiency of O2 at tissue level. • Types – • 1) Hypoxic Hypoxia • 2) Anaemic Hypoxia • 3) Stagnant Hypoxia • 4) Histotoxic Hypoxia
- 30. 1) Hypoxic Hypoxia • Atmospheric O2 is less (high altitude) • Ventilation in the lung is improper (Bronchitis & Asthma) Narrow bronchi. • Improper diffusion across pulmonary membrane (pulmonary oedema, fibrosis of lung, T. B.) • Improper mixing of arterial & venous blood (congenital atrial septal defect (P. D. A. - Patent Ductus Arteriosus) 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 30
- 31. 2) Anaemic Hypoxia • Atmospheric O2 is normal • Diffusion of O2 is normal but ---- • Hb% is less or defective. • So O2 is not transported properly. (Severe anemia or CO2 poisoning) 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 31
- 32. 3) Stagnant hypoxia • Atmospheric O2 normal, • Diffusion normal, • Hb normal but ----- • Circulation is defective. • So O2 is not transported properly (C.C.F. or obstruction of arteries due to thrombo embolism) 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 32
- 33. 4) Histo - toxic hypoxia • Atmospheric O2 normal, • diffusion normal, • Hb normal, circulation is normal but --- • Cellular mitochondrial enzymes are damaged. • So O2 cannot be utilized 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 33
- 34. Effects of Hypoxia • 1) R. S. - To begin with Respiration is stimulated but when CO2 is washed out, no further rise in respiration. • 2) C. V. S. - To begin with H. R. increases but if hypoxia persist for longer time, Myocardial weakening occurs. • 3) Excretory system - Due to washing of CO2 alkalosis occurs. Urinary pH becomes alkaline 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 34
- 35. Effects of Hypoxia • 4) Why there is polycythemia at high altitude? • J. G. cells are stimulated by hypoxia. Erythropoietin formation increases Bone marrow is stimulated → R. B. C. count ↑ → Hb ↑ 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 35
- 36. Effects of Hypoxia • 5) Digestive System (GIT) --- Nausea & vomiting occur due to hypoxia of GIT. • 6) Nervous System - Throbbing headache, mental concentration becomes less & irritability increases. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 36
- 37. Treatment of Hypoxia • 1) Treat the basic cause • 2) O2 therapy is useful in Hypoxic hypoxia & few cases of anaemic hypoxia. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 37
- 38. 2B) Asphyxia • Lack of O2 & excess of CO2 in the body • Causes – • 1) Drowning • 2) Suffocation in the smoke • 3) Foreign body obstruction in trachea • 4) Paralysis of respiratory muscles 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 38
- 39. Pathological stages of Asphyxia • 1) 1st stage – Hyperpnea -last for 1 min due to excess of CO2 & so R. R. increases. • 2) 2nd stage - Central excitation • Duration - 2 min. Due to excess of CO2 complete CNS stimulates, H. R., B. P. increases. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 39
- 40. Pathological stages of Asphyxia • 3) 3rd stage - Central failure • Lasts for 3 min. due to lack of O2, irreversible damage to N. S. • H. R., B. P., decreases. • Lastly pupils are dilated & death occurs. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 40
- 41. Treatment of Asphyxia • 1) Treat the cause • 2) First Aid - CPR - Cardio pulmonary Resiscitation. • 3) Emergency - Tracheostomy & 100% O2 is given. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 41
- 42. 2C) Dyspnoea (Breathlessness) • 1) Dysponea = Difficulty in breathing • 2) Hyperopnea = Double the normal respiration • 3) Dysponea = when R. R. becomes 3 to 4 times more than normal, the patient starts feeling breathless. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 42
- 43. Causes of Dyspnoea • 1) Respiratory causes - Bronchial asthma, Acute bronchitis, pneumonia etc. • 2) Cardio vascular problems - C.C.F. = congestive card • 3) Metabolic causes - Uremia, Diabetic Ketoacidosis • 4) Blood diseases - Severe Anemiaiac failure, I.H.D. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 43
- 44. Grades of Dyspnoea • 1) Grade I = Dyspnoea after accustomed exertion. • 2) Grade II = Dyspnoea after climbing up • 3) Grade III = Dyspnoea after walking on flat surface • 4) Grade IV = Dyspnoea at rest 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 44
- 45. 3) Artificial Respiration • In the event of accidental drowning, electric shock, artificial respiration may be given as first aid, treatment. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 45
- 46. 1) Mouth to mouth breathing • a) The patient is laid flat on the back on the table or on ground, higher than that on which rescuer stands • Under the patient’s shoulders some soft Towel or pillow is placed so that the patient’s head falls well back. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 46
- 47. 1) Mouth to mouth breathing • Standing or kneeling opposite to the patient’s head, the rescuer presses with one hand on the crown of the patient’s head gently so that the head is fully extended. • Other hand is placed on the patient’s jaw so that the jaw is drawn well forward. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 47
- 48. 1) Mouth to mouth breathing • b) Breathing in deeply the rescuer’s mouth is placed over the patient’s mouth whilst pinching the patient’s nose to block the nasal orifice. • The rescuer breaths out forcibly into the patient’s lungs. When the patient is a child or baby the rescuer should breath delicately. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 48
- 49. 1) Mouth to mouth breathing • c) The patient expires passively & the jaw is kept drawn well forward so that the patient’s air passage is always kept patent 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 49
- 50. 1) Mouth to mouth breathing • In this method, which in fact is very simple; the doctor takes a deep breath and exhales that air in the patient’s mouth. • This process is repeated for 10-12 times per min. • This method was somewhat neglected in recent past because of the misconception that the air exhaled by the Doctor into the patient’s mouth is not appropriate for the patient. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 50
- 51. 1) Mouth to mouth breathing • But medically, this proposition is wrong, as • Exhaled air also contains sufficient amount of Oxygen which certainly helps the patient. • Also, the carbon di oxide exhaled by the Doctor assists in exciting the respiratory center of the patient. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 51
- 52. 1) Mouth to mouth breathing 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 52
- 53. 1) Mouth to mouth breathing 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 53
- 54. 2) Sharpey Shaffer’s Method 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 54
- 55. Artificial Respiration – Chin Lift 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 55
- 58. 2) Sharpey Shaffer’s Method • a) Lying casualty’s face downwards ( Prone position) with head turned to one side arms bent & forehead resting on his hands with neck extended • kneeling to one side of casualty’s hips facing his head & placing hands flat on the small of the casualty’s back just above the top of the pelvic bones, thumbs almost touched each other in the midline, fingers being spread over the loins & pointing towards the ground. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 58
- 59. 2) Sharpey Shaffer’s Method • b) Seating on heals & swinging body slowly forward from knees being kept arms straight & hands in place all the time only applying gentle pressure by the body weight. • Forcing air out of the lungs (expiration) to be maintained this position for 2 sec. counting 1, 2. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 59
- 60. 2) Sharpey Shaffer’s Method • c) Relaxing the pressure by swinging quietly & gradually backwards on to heals allowing inspiration & counting 3, 4, 5 in 3 sec. • Before swinging forwards again to first movement being kept arms straight & hands in place all the time 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 60
- 61. 3) Holger - Nielsen Method • The subject is placed in the prone position with the arms abducted at the shoulders & elbows remaining flexed. • The face is turned to one side & rests on the hands. • The mouth is cleaned (by wiping the mucus, fluid etc.) The operator kneels down in front of the subject facing towards the head. 2 hands are placed on the 2 side of the chest. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 61
- 62. 3) Holger - Nielsen Method • With the thumbs & fingers spread apart. Then the operator puts his body weight leaning forwards upon the subject’s back. • This compresses the chest & helps in expiration. • The operator then makes himself straight & at the same time draws the subject’s arms forwards by holding them above the elbows. • This helps in natural inspiration. This process is repeated about 10 - 12 times a min. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 62
- 63. 3) Holger - Nielsen Method 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 63
- 64. 3) Holger - Nielsen Method • a) Rocking forwards quietly with arms straight & applying light pressure to back by weight of the upper part of body only counting for 2 sec. 1, 2 (Expiration). • b) Rocking back with arms straight releasing pressure gradually & sliding hands to elbows of casualty counting 3 for 1 sec. • c) Raising & pulling casualty’s arms until tension being felt for 2 sec. counting 4, 5 causing inspiration. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 64
- 65. 3) Holger - Nielsen Method 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 65
- 66. 4) Hospital Management • Artificial Respiration • Respiration is a vital sign. • Inadequate airway is the main cause for the death. • WHO has mentioned that 50 to 60% deaths occur due to improper ventilation. • So airway management & ventilation is important. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 66
- 67. Causes of breathlessness – In conscious patient • 1) Foreign body obstruction. • 2) Aspiration of food or any other secretion in the respiratory tract. (eg. Fast eating habits). 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 67
- 68. Symptoms 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 68 • i) Deep breathing • ii) Difficulty in expiration (Grasping)
- 70. Symptoms • During inspiration trachea dilates & during expiration trachea recoil. • Foreign body sticks to the mucous. • Due to the irritation of mucosa - secretion increases - so obstruction also increases. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 70
- 71. Symptoms • a) In upper air way obstruction patient express the chocking by holding his hand around the throat. - Universal sign. • b) The doctor must see the important sign Cyanosis • 2 types of Cyanosis • I) Central Cyanosis - Tip of the tongue become bluish. II) Peripheral Cyanosis - Tip of the finger become bluish. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 71
- 73. Treatment • 1) Patient has to be sited in relax position. Lift up the neck, put the left hand on the chest & do the stumping (stroke by the pump) at the neck. • 2) Or patient can be asked to lie down & do the chest physiotherapy. Extend the neck (Head lift, chin tilt position) Tapping is done from lower lobe to upper lobe of the lungs on both the side. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 73
- 74. Treatment • 3) Hot fomentation can be given. • 4) Mostly with this efforts, airway opens. These are primary efforts. • If needed. • Injection Atropine IV 0.6 mg (It reduces the mucous secretion) • Bronchodilators are given. For eg. • ‘Inj. Deriphylline’ 1 ampoule. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 74
- 75. Treatment • 5) Advise - Bronchoscopy = Planned bronchoscopy or Emergency bronchoscopy • Note - Foreign body can be hydroscopic or non - hygroscopic • Basic principle about foreign body removal is to push the F. B. from down to the upper side. If the foreign body sticks, lung infection chances are more. So, it is necessary to start higher antibiotics. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 75
- 76. If the patient is unconscious • 2 important features indicate the dyspnoea. • 1) Aphonia 2) Absence of cough reflex / Gag reflex • Causes • 1) Status asthmaticus 2) Foreign body in the air - way 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 76
- 77. If the patient is unconscious • In unconscious patient first treat the symptoms & then ask the patient. • In emergency like shock gasping respiration, peripheral & central cyanosis - 3 parameters are observed. • Rate of the respiration (14 - 18 / min.) • Regularity & rhythm (observe the chest expansion) • Efforts to take breathing. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 77
- 78. To activate the Respiratory Centers • Mouth to mouth breathing is very important (Head low position, Head lift & chin tilt position, Pinching of the nose & then mouth to mouth breathing). • In the patients of HIV or Hepatitis in spite of mouth to mouth breathing the patient is directly taken on the ventilator 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 78
- 79. To activate the Respiratory Centers • If the air way is not open, endotracheal intubation is done. 2 types of endotracheal tubes are available nasal & oral. Size No. is 2. 5 up to 8. For endotracheal intubation direct laryngoscope is also use. Endotracheal tube is connected to ‘Ambu bag’. During the procedure observe the chest expansion & check the air entry by stethoscope 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 79
- 80. To activate the Respiratory Centers • After 48 hours if the patient is not out, tracheostomy is done. Number of tracheostomy tube is decided according to age. • Tracheostomy tube is of 2 types, metal & plastic. Vertical incision is taken on the trachea & with proper sterilization care the tube is introduced with stirrer. 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 80
- 81. To activate the Respiratory Centers • After observing PO2 by pulse oxymeter, the decision of O2 administration is taken. • Tracheostomy care - 1) daily dressing 2) antibiotic coverage 04/14/16 Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande 81
- 82. Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande • Sharing of Knowledge • FOR • Propagating Ayurved 04/14/16 82Prof.Dr.R.R.Deshpande
