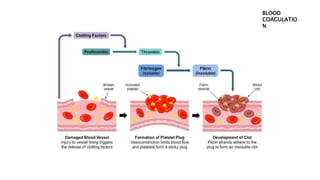
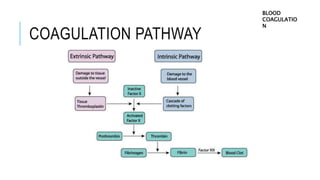
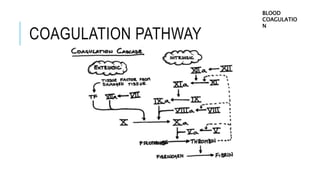
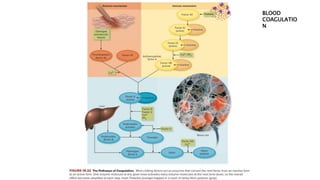
Blood coagulation is a complex process involving over 20 proteins and enzymes that interact to form blood clots and prevent excessive blood loss from cuts or injuries. It normally activates when tissue is damaged. The process involves platelets releasing clotting factors that convert prothrombin into thrombin, which then converts fibrinogen into fibrin strands that form a mesh to trap red blood cells. Deficiencies in coagulation factors can cause hemorrhaging, as seen in hemophilia where inherited defects prevent proper clotting. Diseases like thrombosis can also affect clotting and increase risks of heart attack and stroke. Treatment involves anticoagulant drugs or fibrinolytic agents depending on the condition.