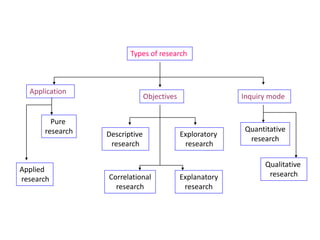
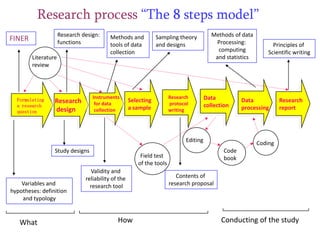
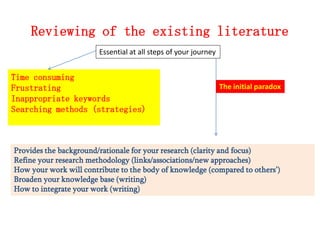
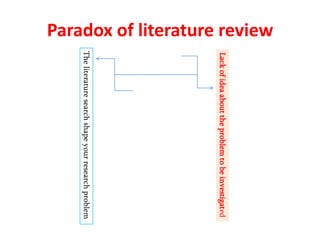
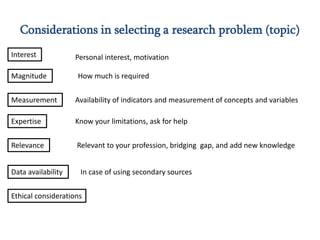
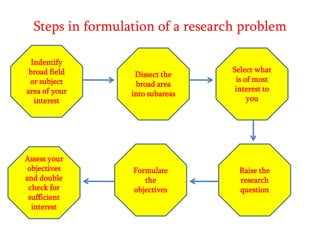
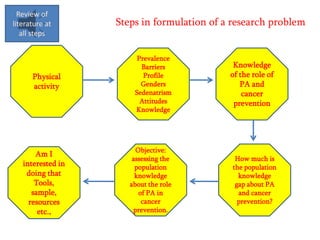
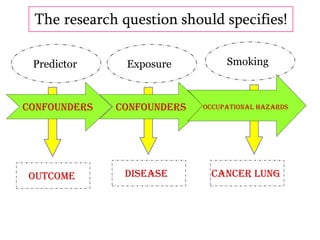
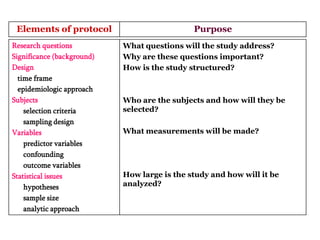
Here are potential research questions that could be formulated for each setting:
A. Rural community and available health facilities:
What are the barriers to accessing primary health care services among residents in rural communities?
B. Urban primary health care facility:
How does wait time in the emergency department impact patient satisfaction at an urban primary health care clinic?
C. Primary schools:
What is the association between screen time (time spent on digital devices) and obesity among primary school children?