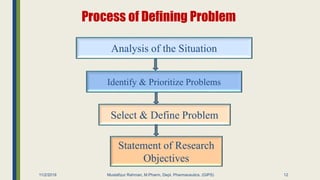
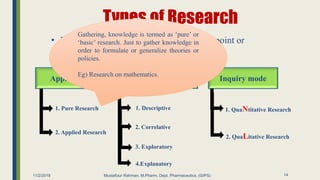
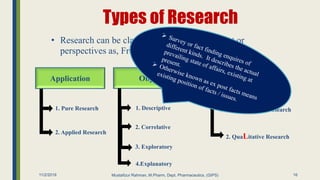
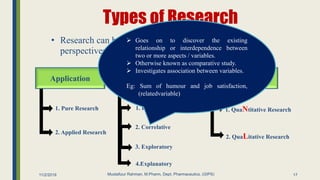
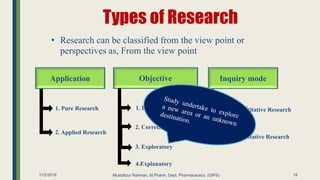
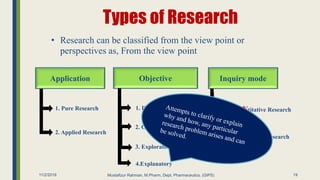
The document outlines research methodology in the context of pharmaceutics, detailing definitions, objectives, significance, and various methods of conducting research. It classifies types of research, including pure, applied, and exploratory studies, while also discussing the importance of literature reviews and the steps involved in the research process. The content provides a framework for understanding how to identify research problems and formulate hypotheses within the pharmaceutical sciences.