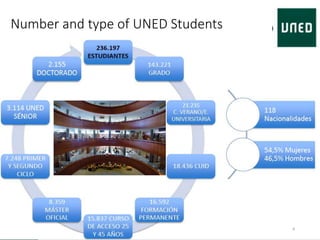
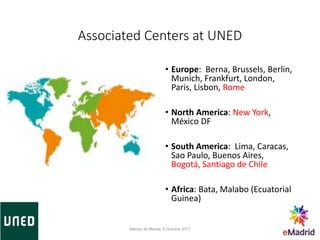
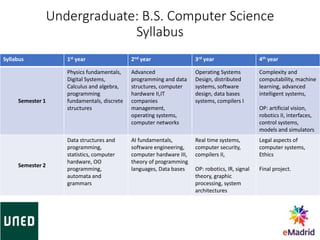
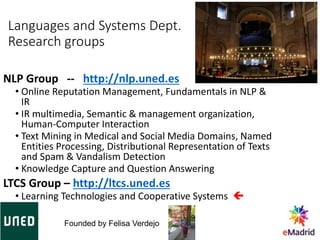
Miguel Rodríguez Artacho is a professor at the Computer Science School of UNED University. UNED has over 236,000 students who study through distance and blended learning models across Spain and abroad. The Computer Science School offers undergraduate and graduate degrees, and has research groups in areas like natural language processing and learning technologies. It also participates in international standardization efforts and EU funded projects to support curriculum development, teaching tools, and university reform.