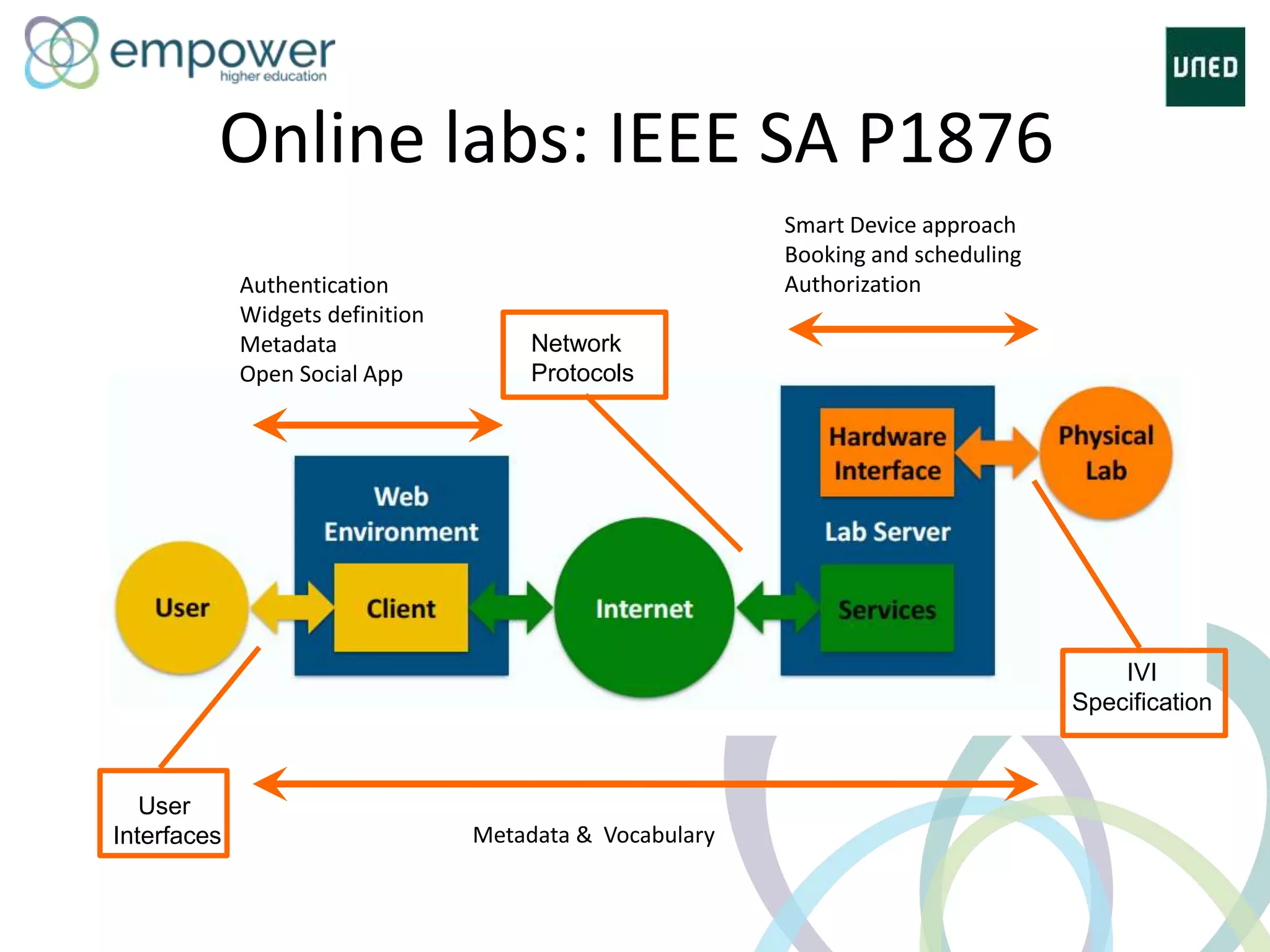
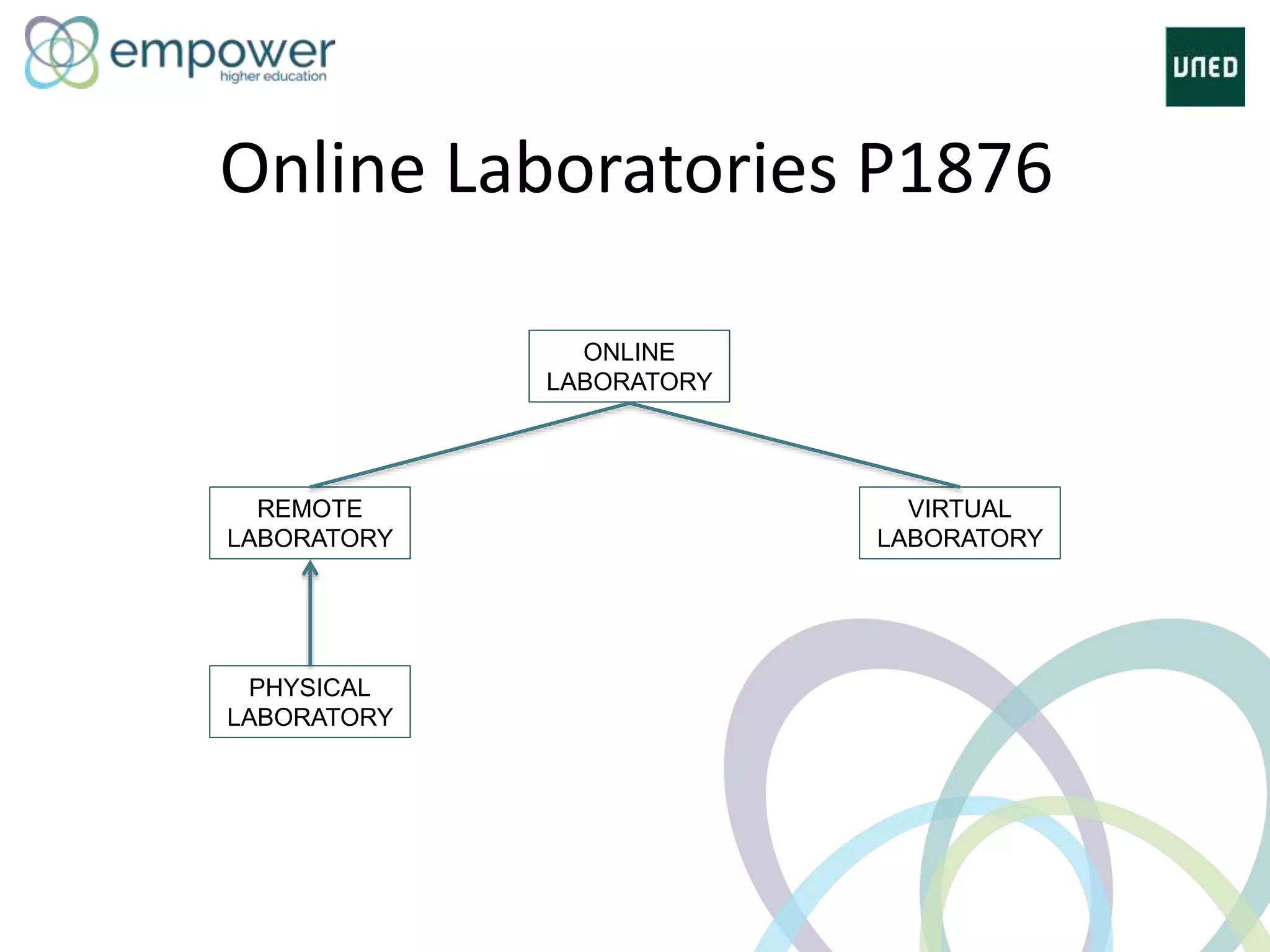
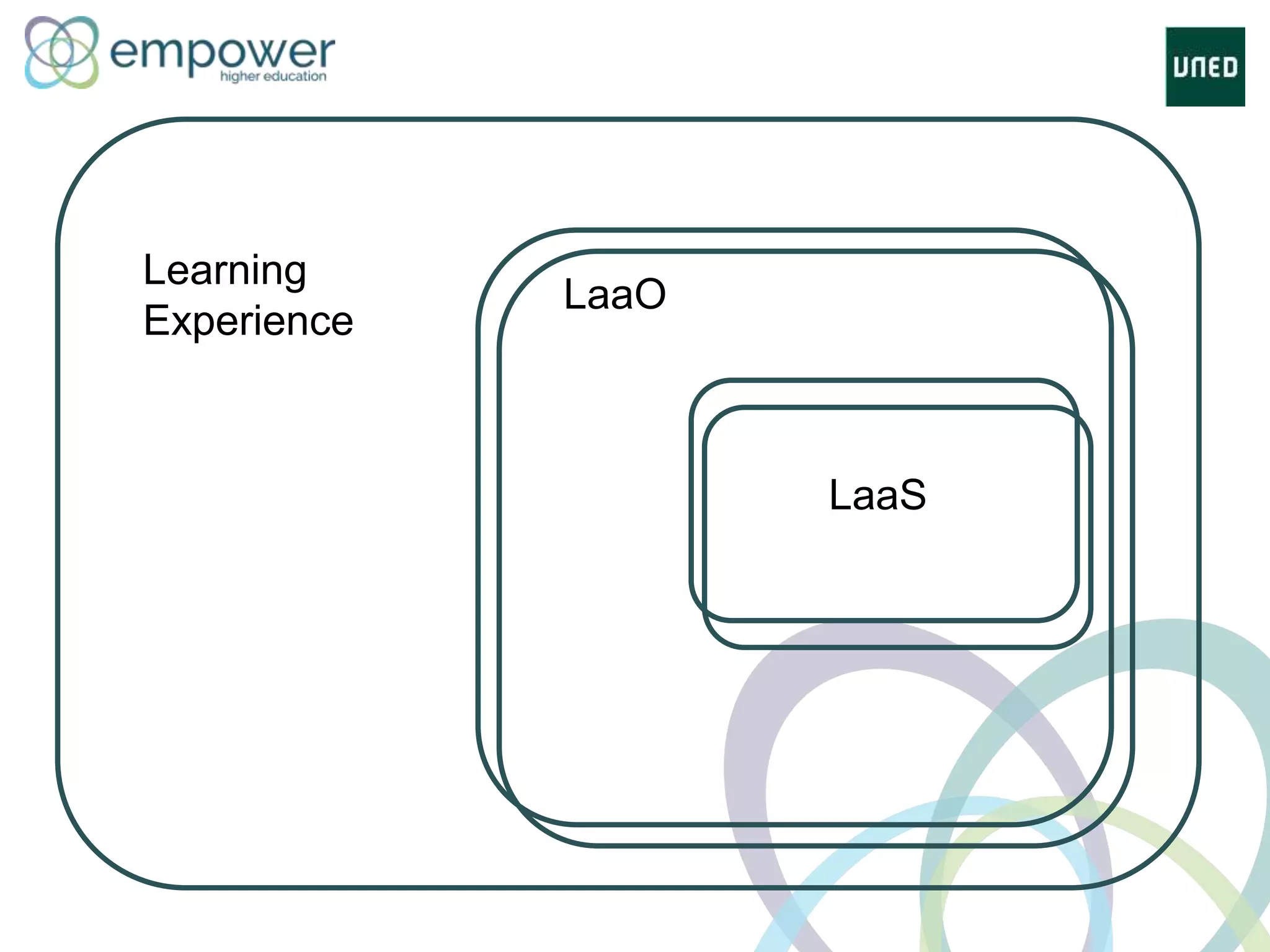
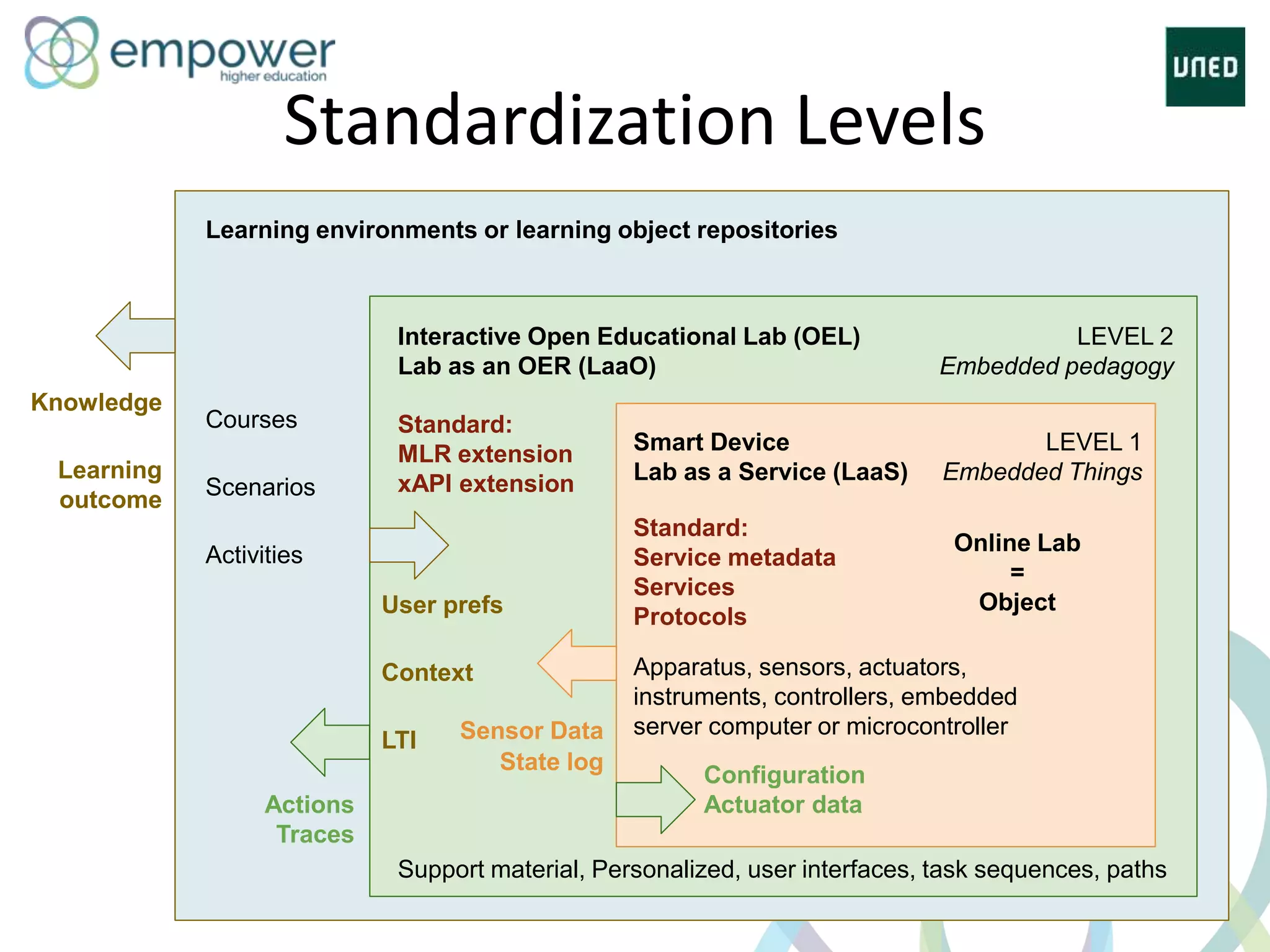
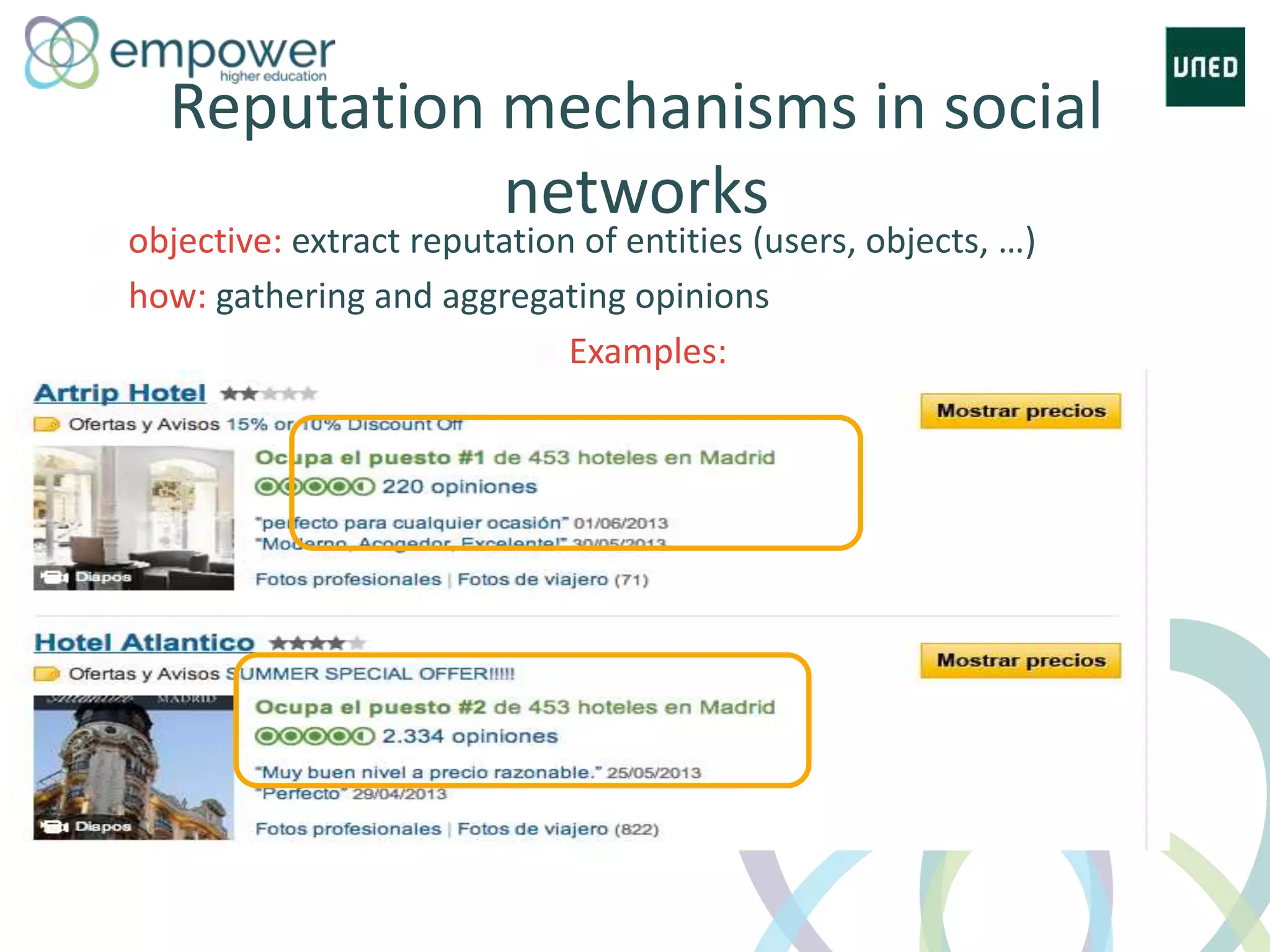
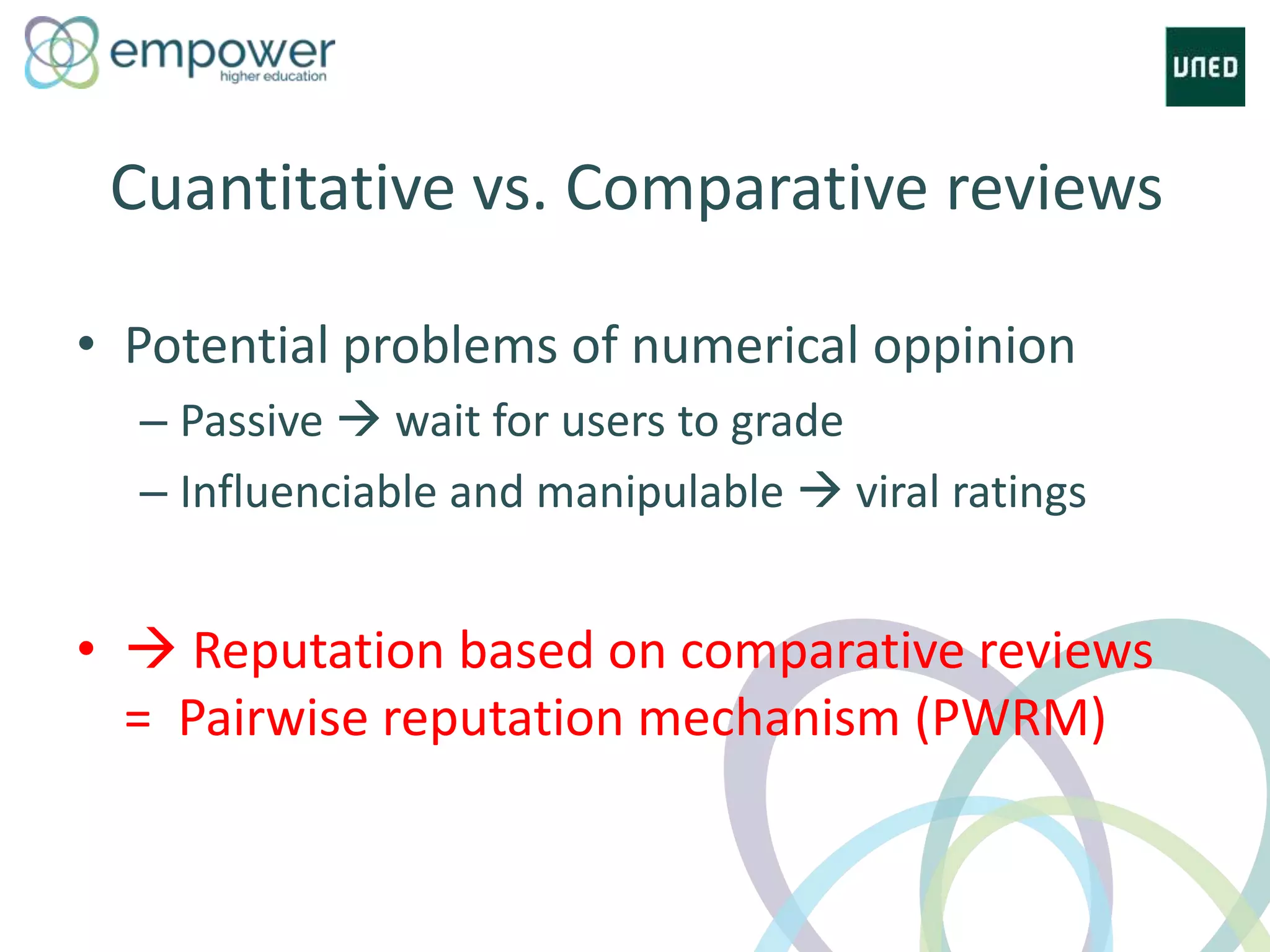
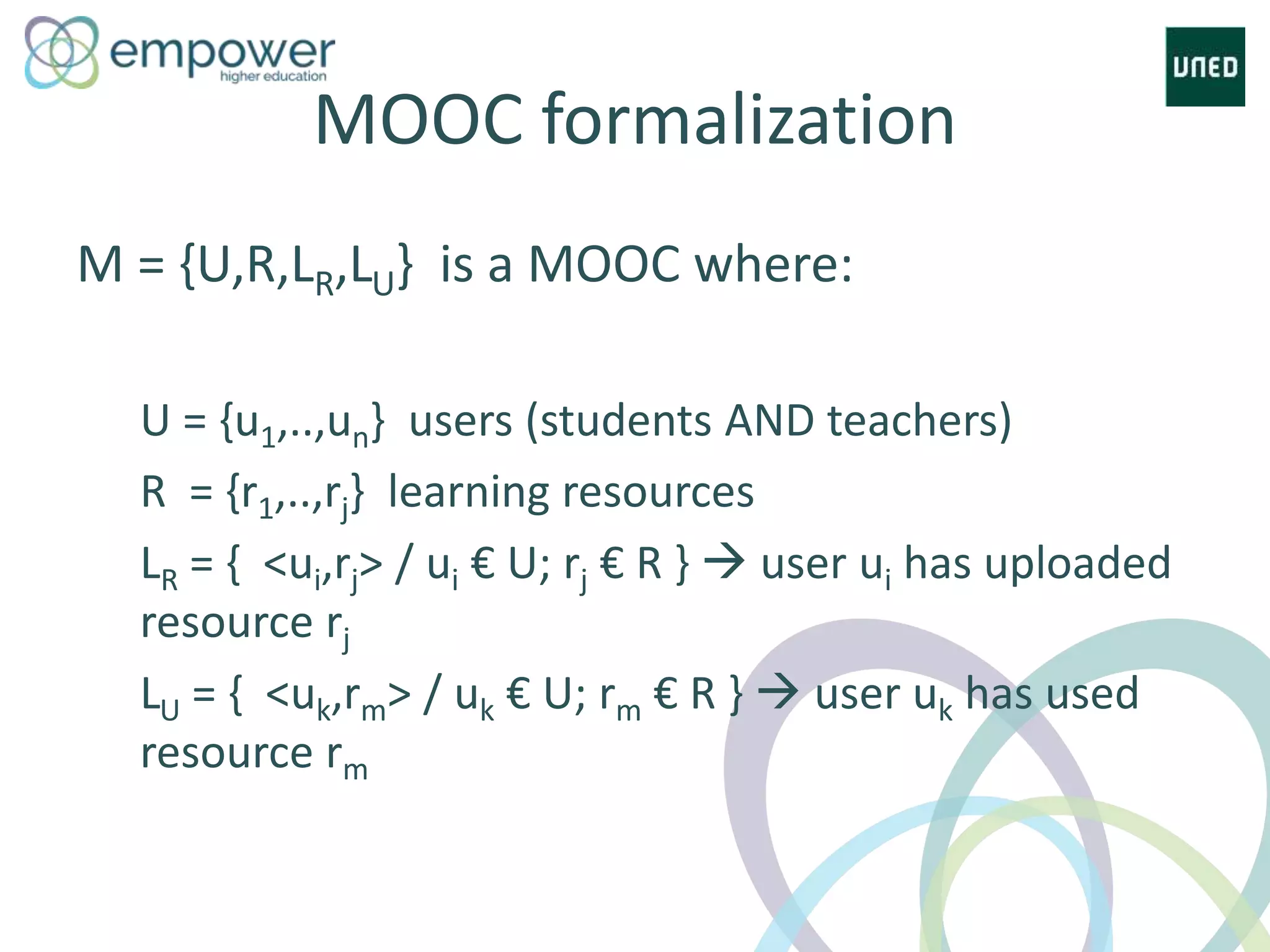
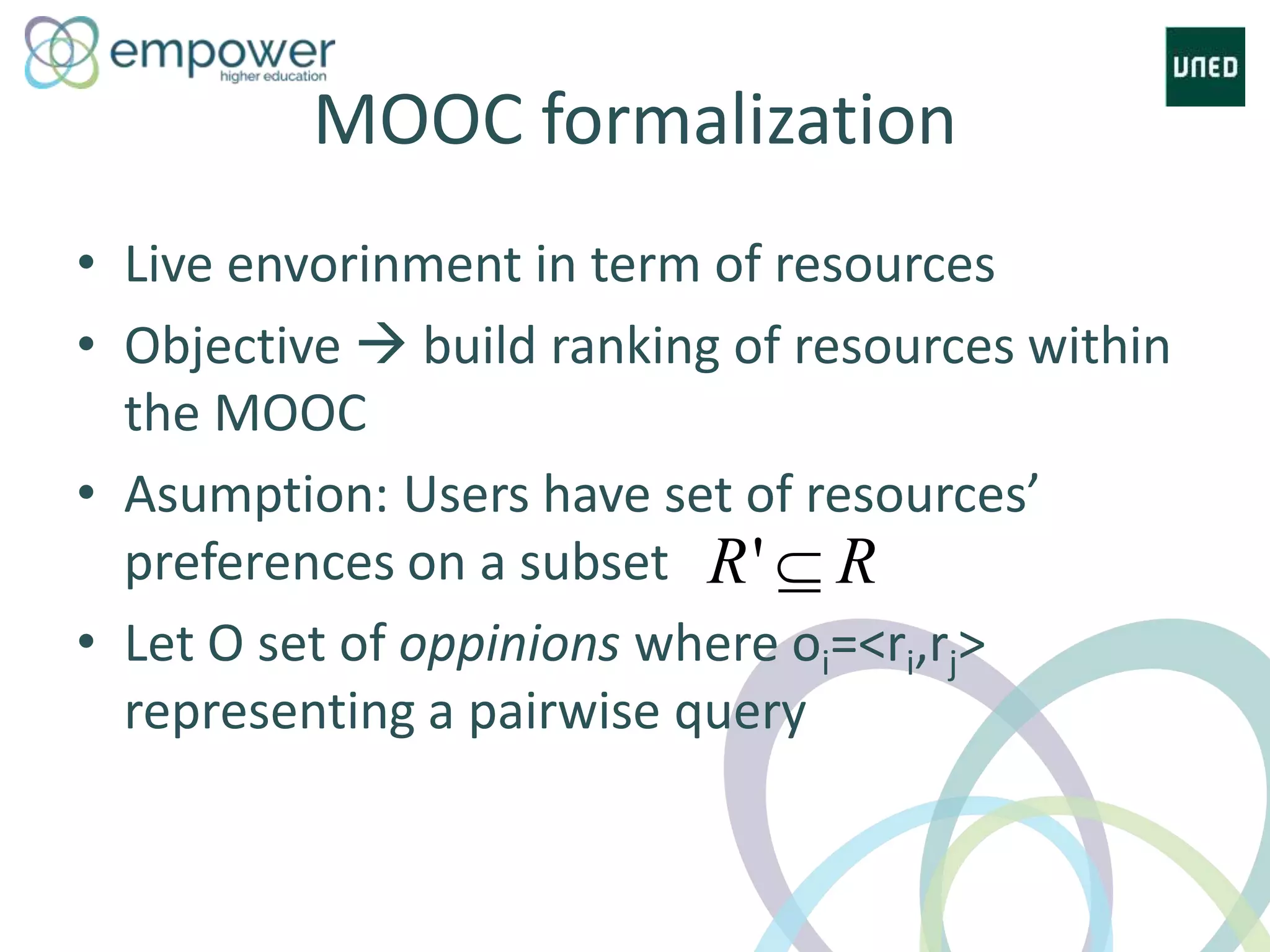
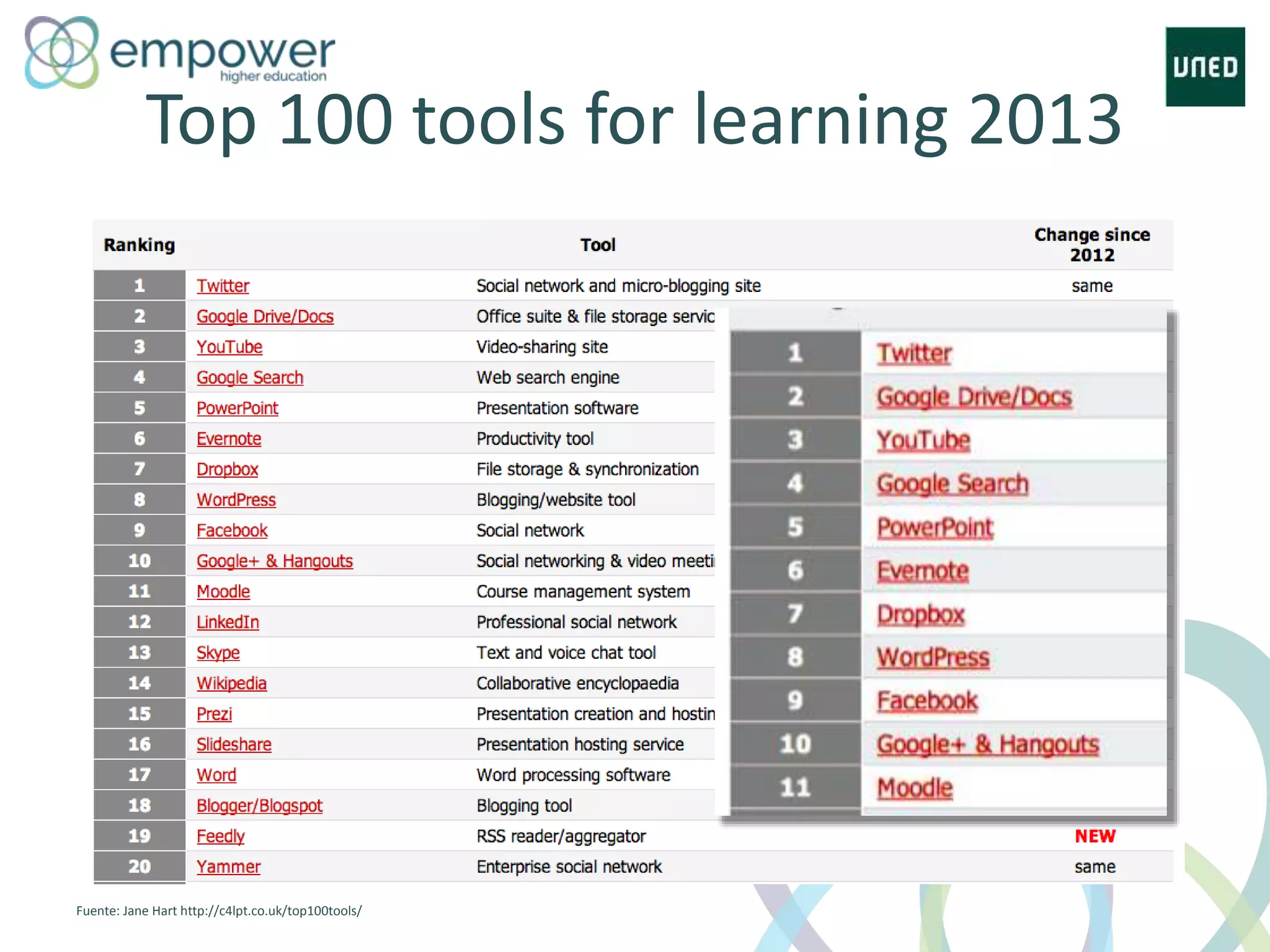
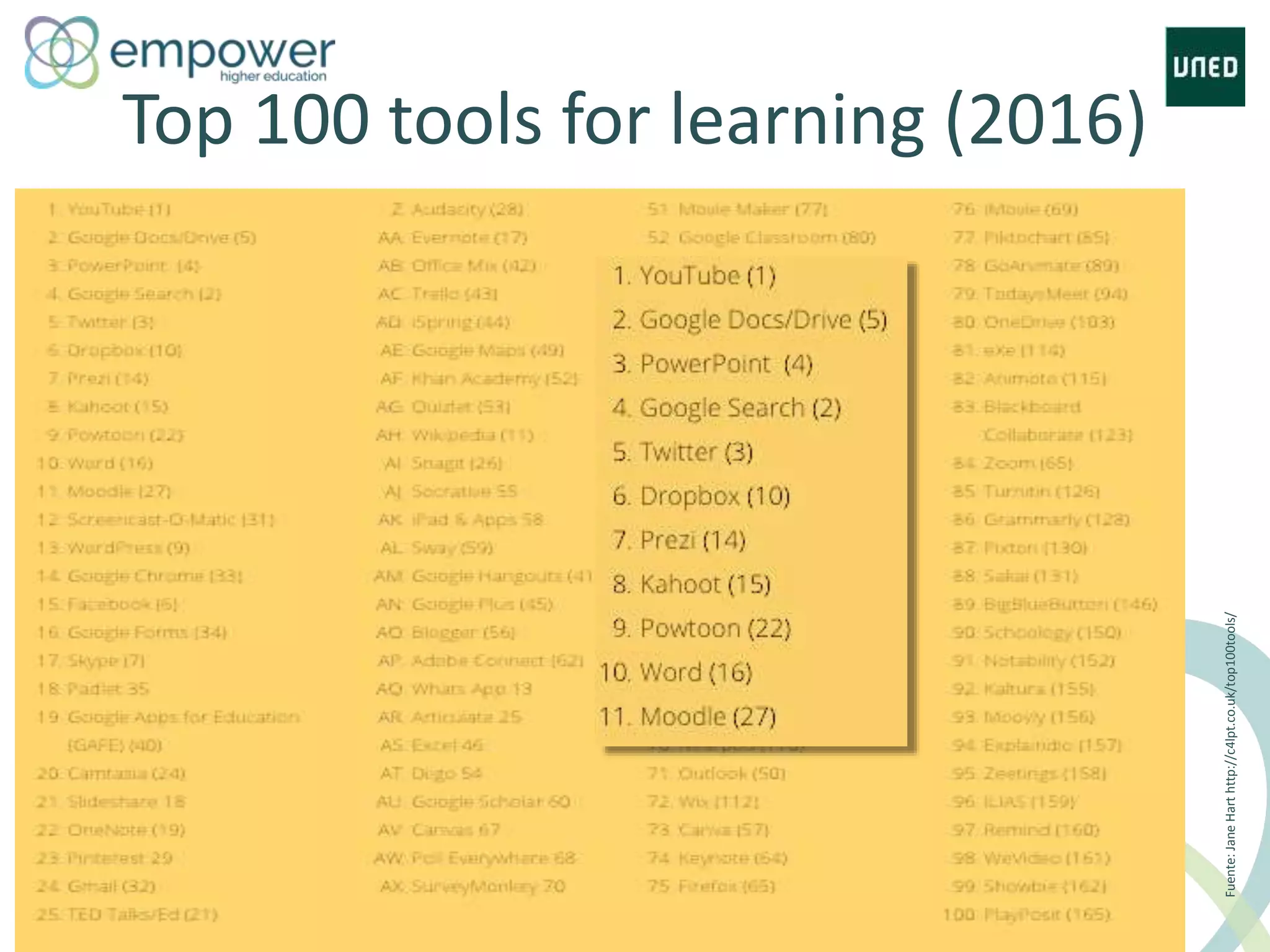
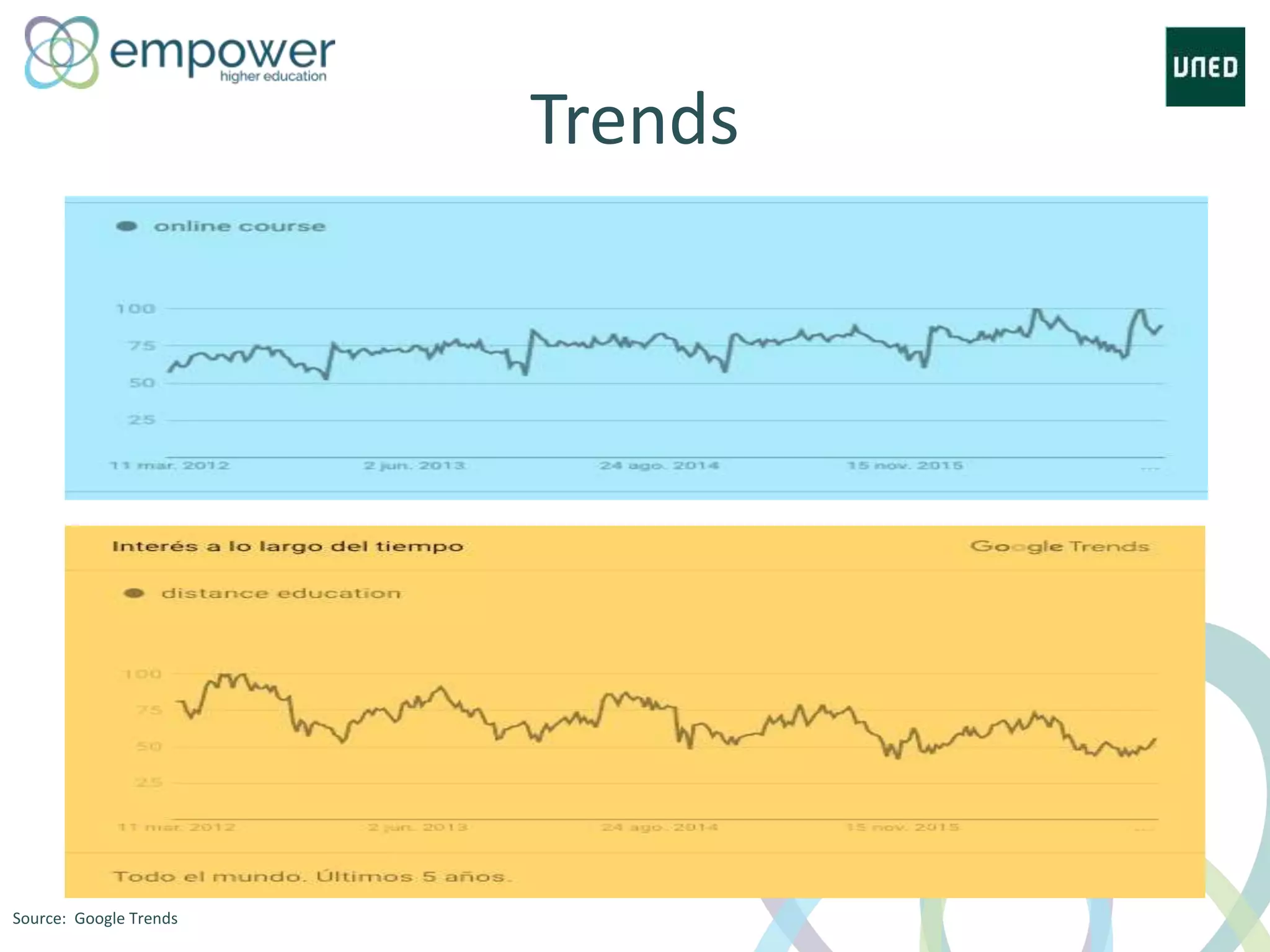
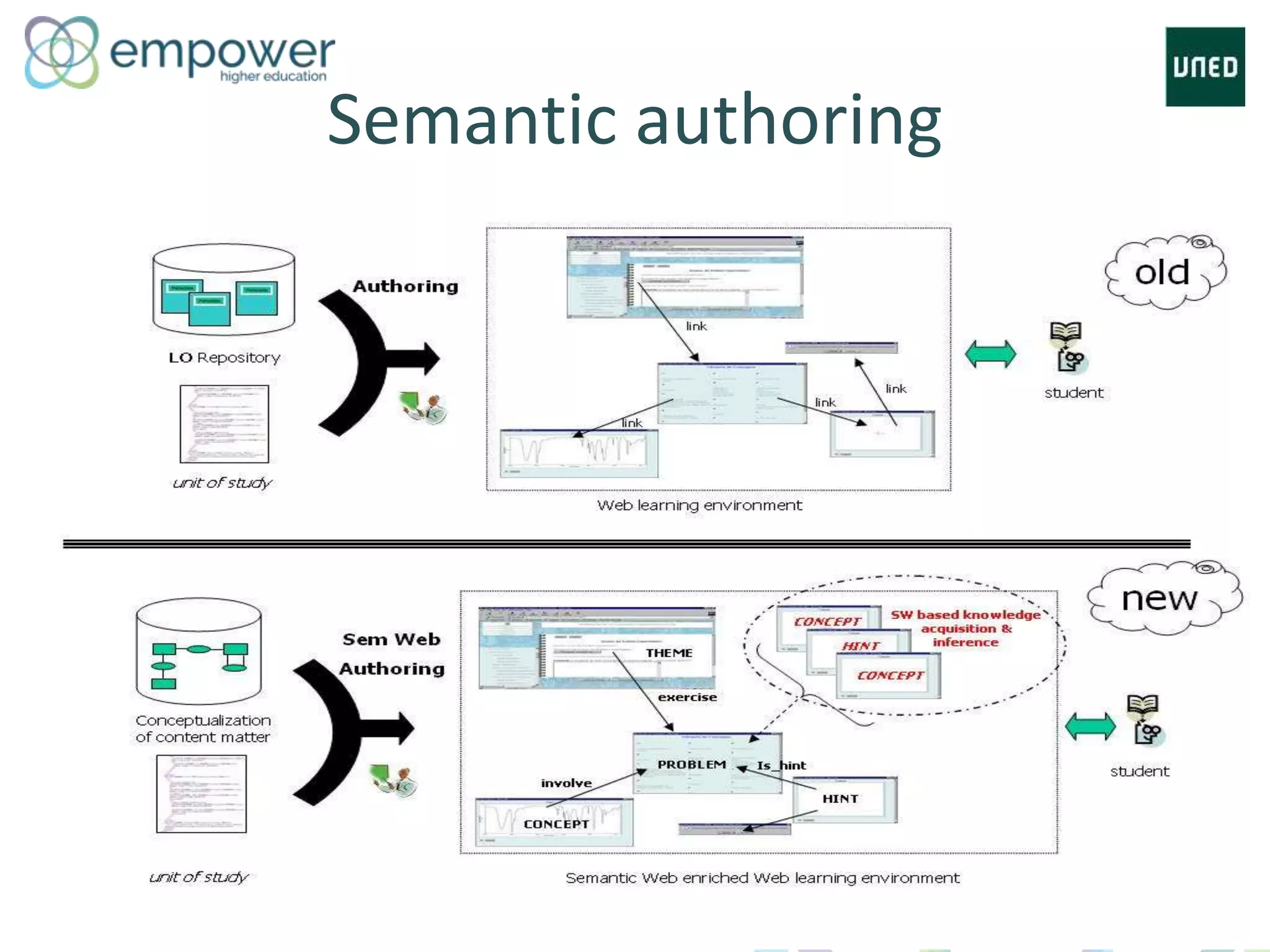
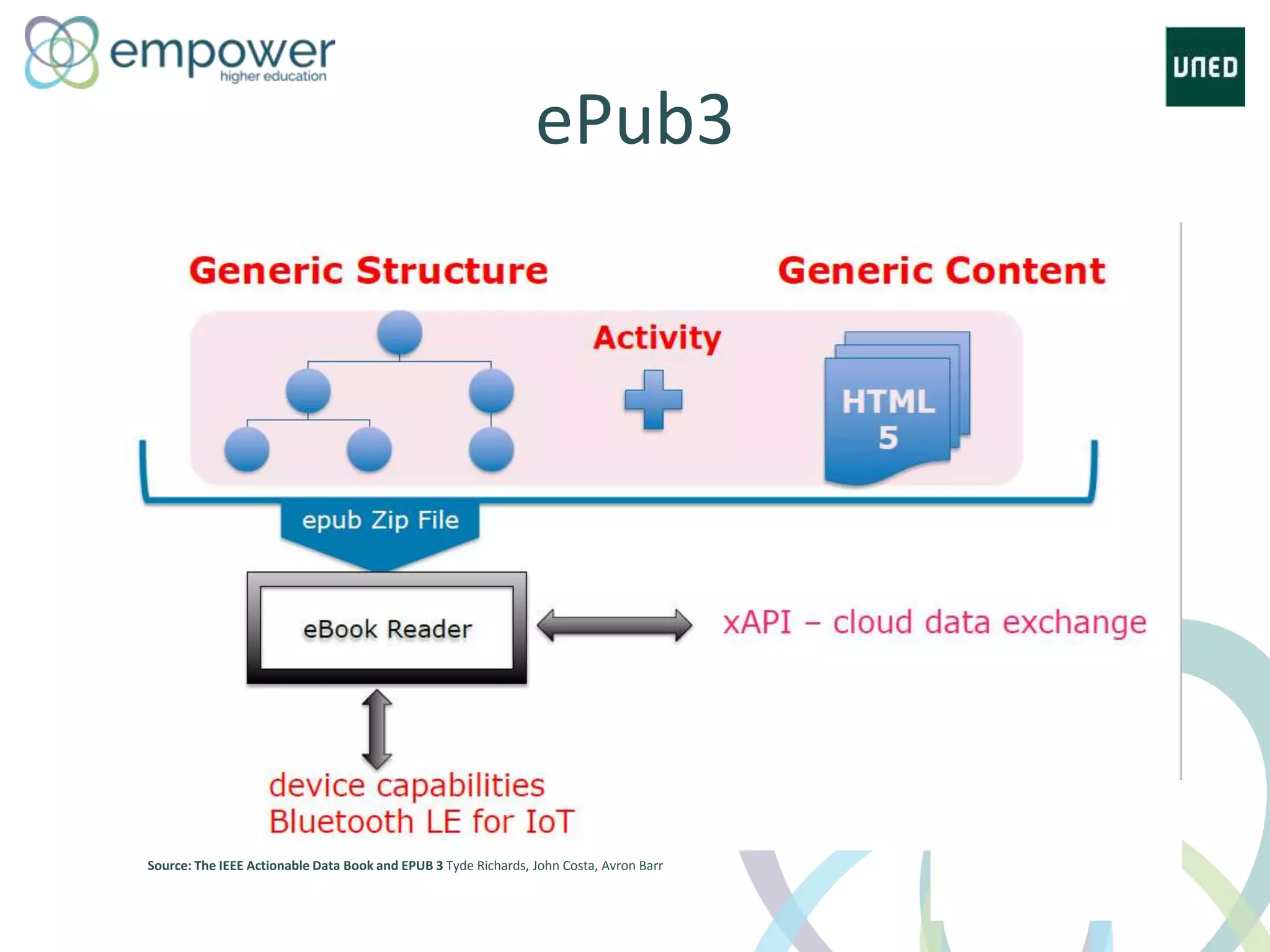
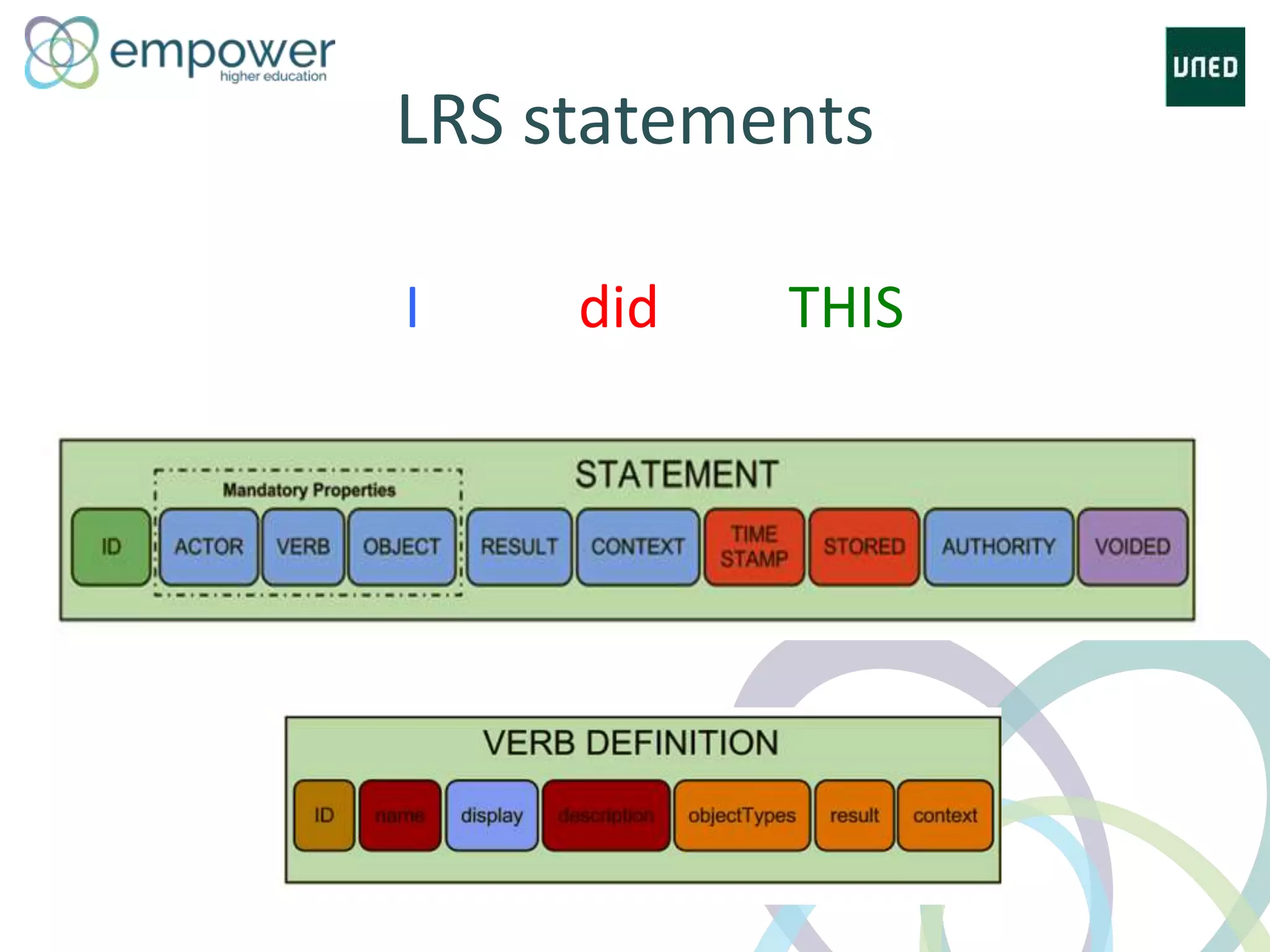
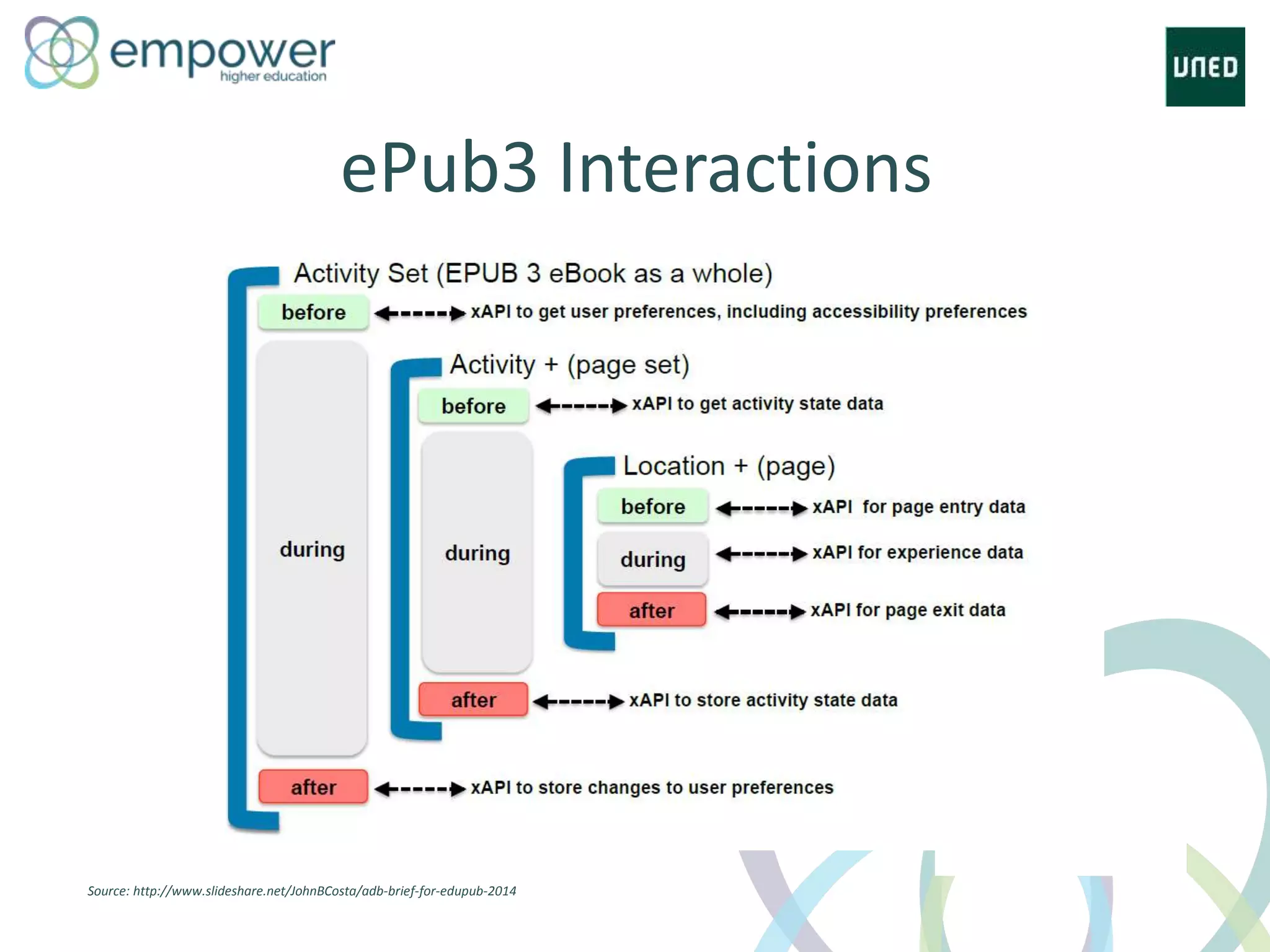
The document discusses the evolution of technology enhanced learning from traditional classroom-based models to modern cloud-based approaches. It describes how learning management systems introduced online communities, tracking, and other features. More recent trends include open educational resources, social and peer-to-peer learning, and adaptive intelligent tutoring systems. The document also provides examples of integrating interactive elements into eBooks, standardizing online laboratories, and using reputation systems to evaluate educational resources in MOOCs. Overall, it outlines how technology is reshaping education to be more flexible, competency-based, and driven by new online and collaborative learning models.







![Activity example
<john> <launched> <cool book>
<john> <read> <page 1> ( d: "PT45S" ) { p: ["chapter 1"], g: ["cool book", "cool class"] }
<john> <read> <page 2> ( d: "PT15S" ) { p: ["chapter 1"], g: ["cool book", "cool class"] }
<john> <read> <page 3> ( d: "PT55S" ) { p: ["chapter 1"], g: ["cool book", "cool class"] }
<john> <read> <page 4> ( d: "PT45S" ) { p: ["chapter 1"], g: ["cool book", "cool class"] }
<john> <watched> <video 1> ( d: "PT3M" ) { p: ["page 4"], g: ["chapter 1", "cool book", "cool class"] }
<john> <paused> <video 1> { p: ["page 4"], g: ["chapter 1", "cool book", "cool class"] }
<john> <resumed> <video 1> { p: ["page 4"], g: ["chapter 1", "cool book", "cool class"] }
<john> <watch> <video 1> ( d: "PT2M" ) { p: ["page 4"], g: ["chapter 1", "cool book", "cool class"] }
<john> <completed> <video 1> ( d: "PT5M" ) { p: ["page 4"], g: ["chapter 1", "cool book", "cool class"] }
<john> <read> <page 5> ( d: "PT45S" ) { p: ["chapter 1"], g: ["cool book", "cool class"] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/empowermiguel2017webinarv3-170308105335/75/Deconstructing-Technology-Enhanced-learning-from-platforms-to-the-cloud-19-2048.jpg)