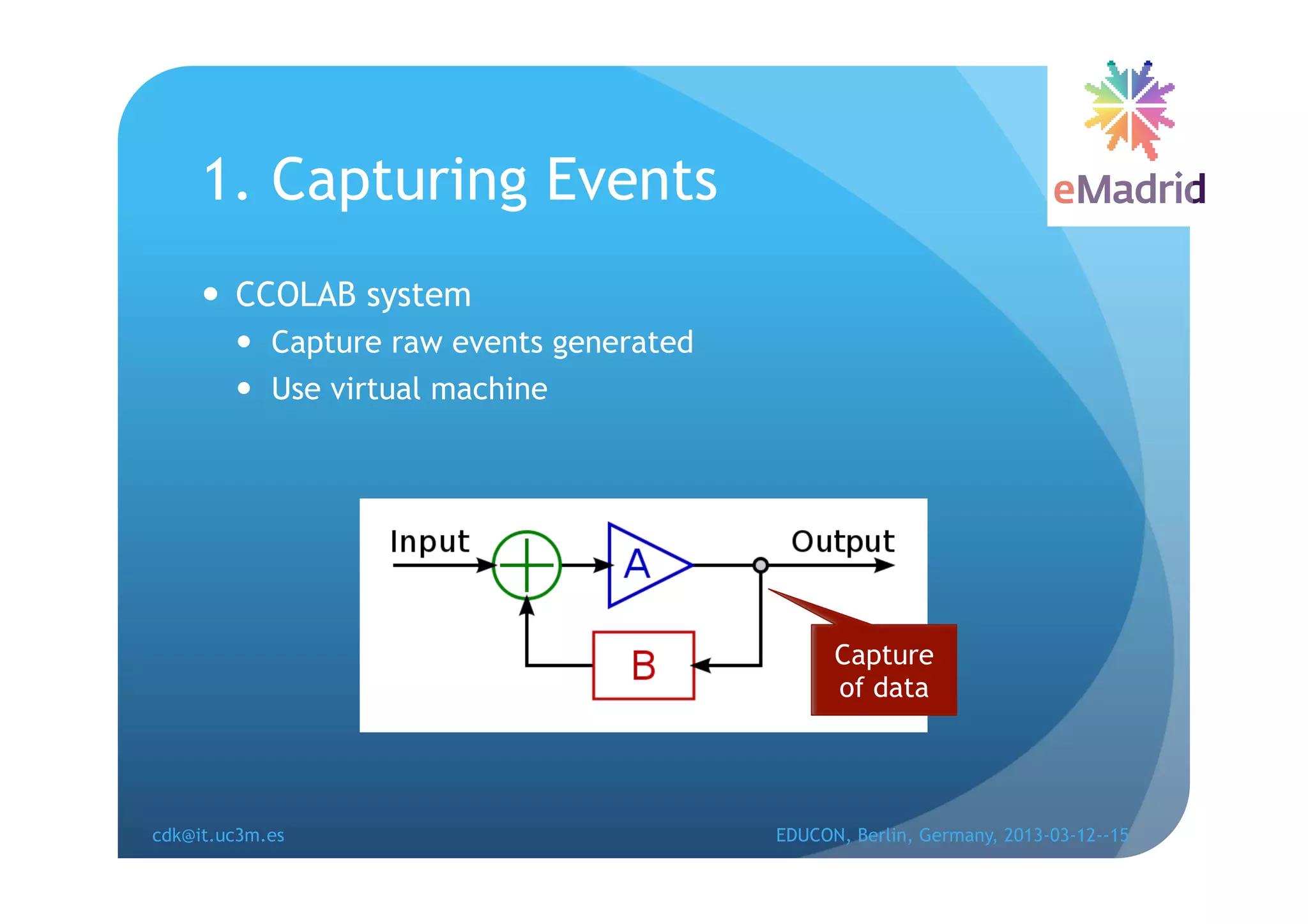
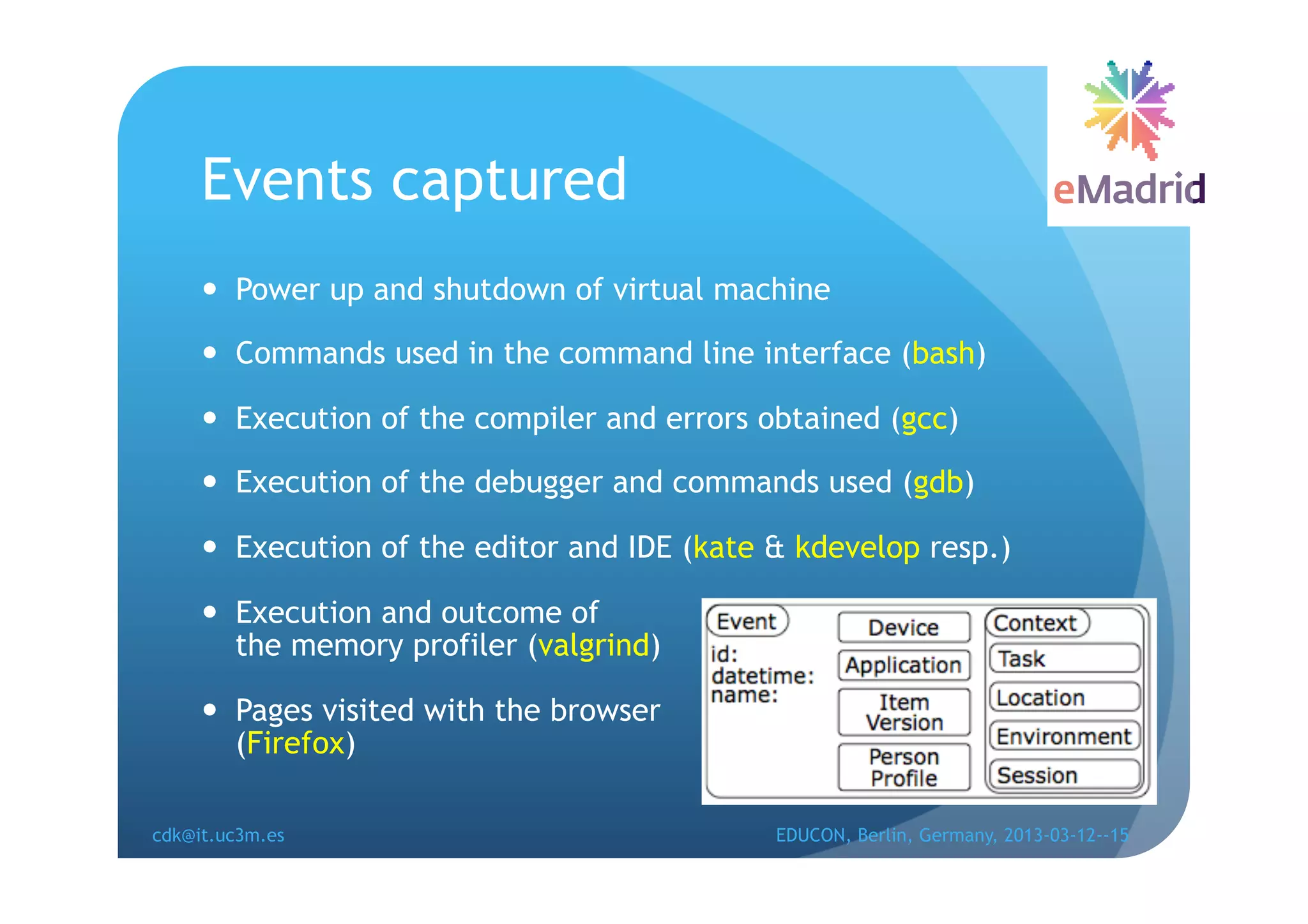
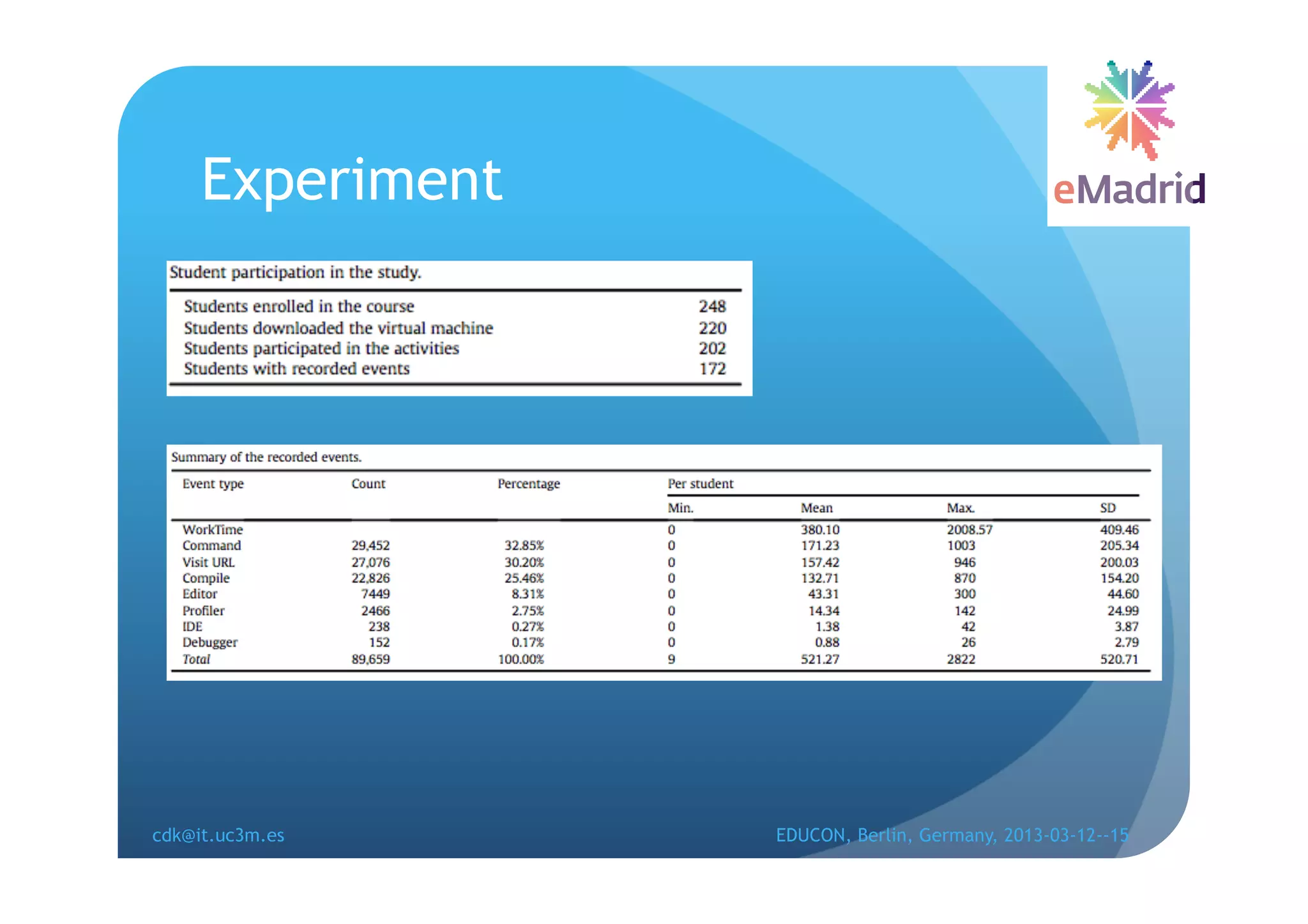
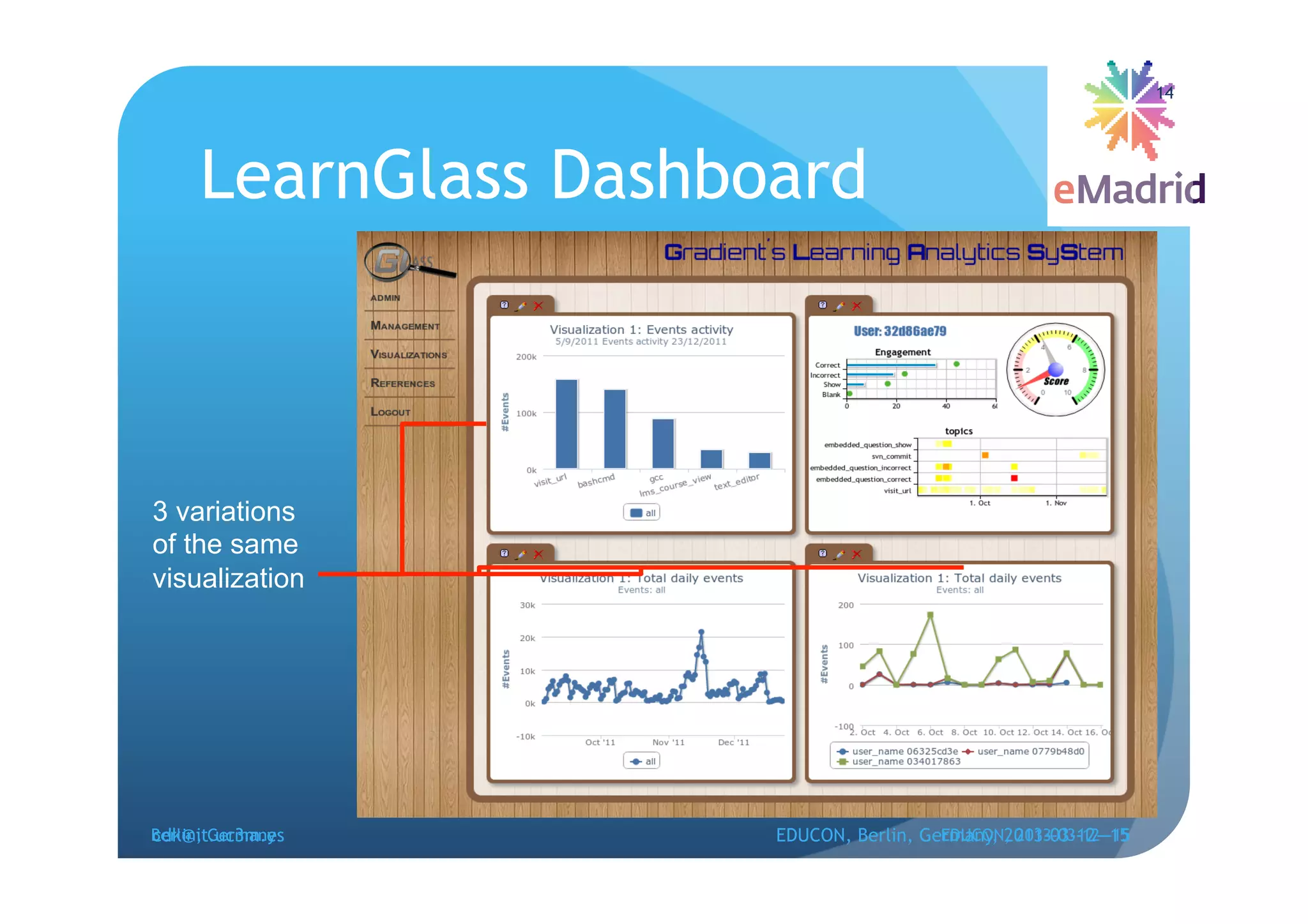
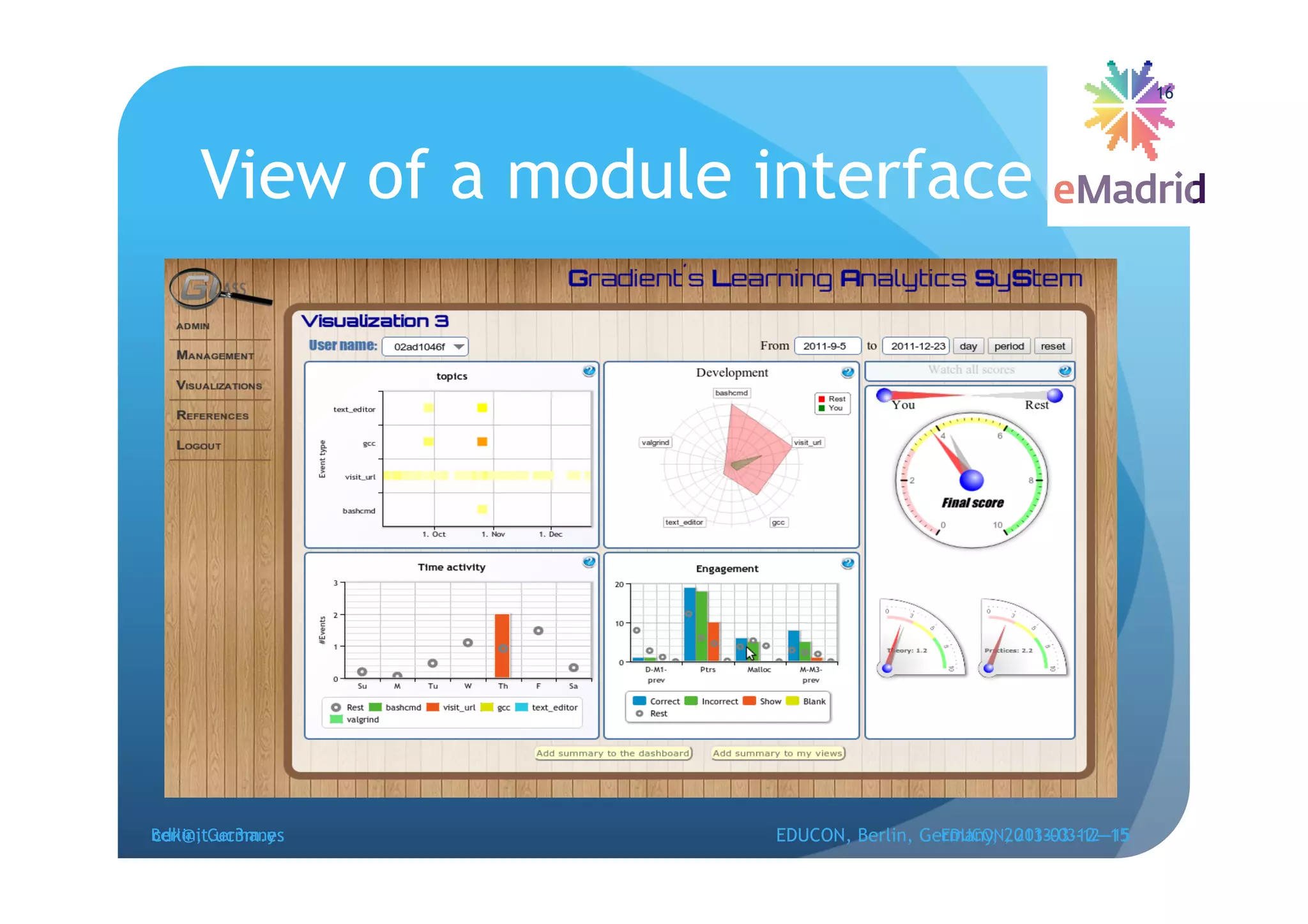
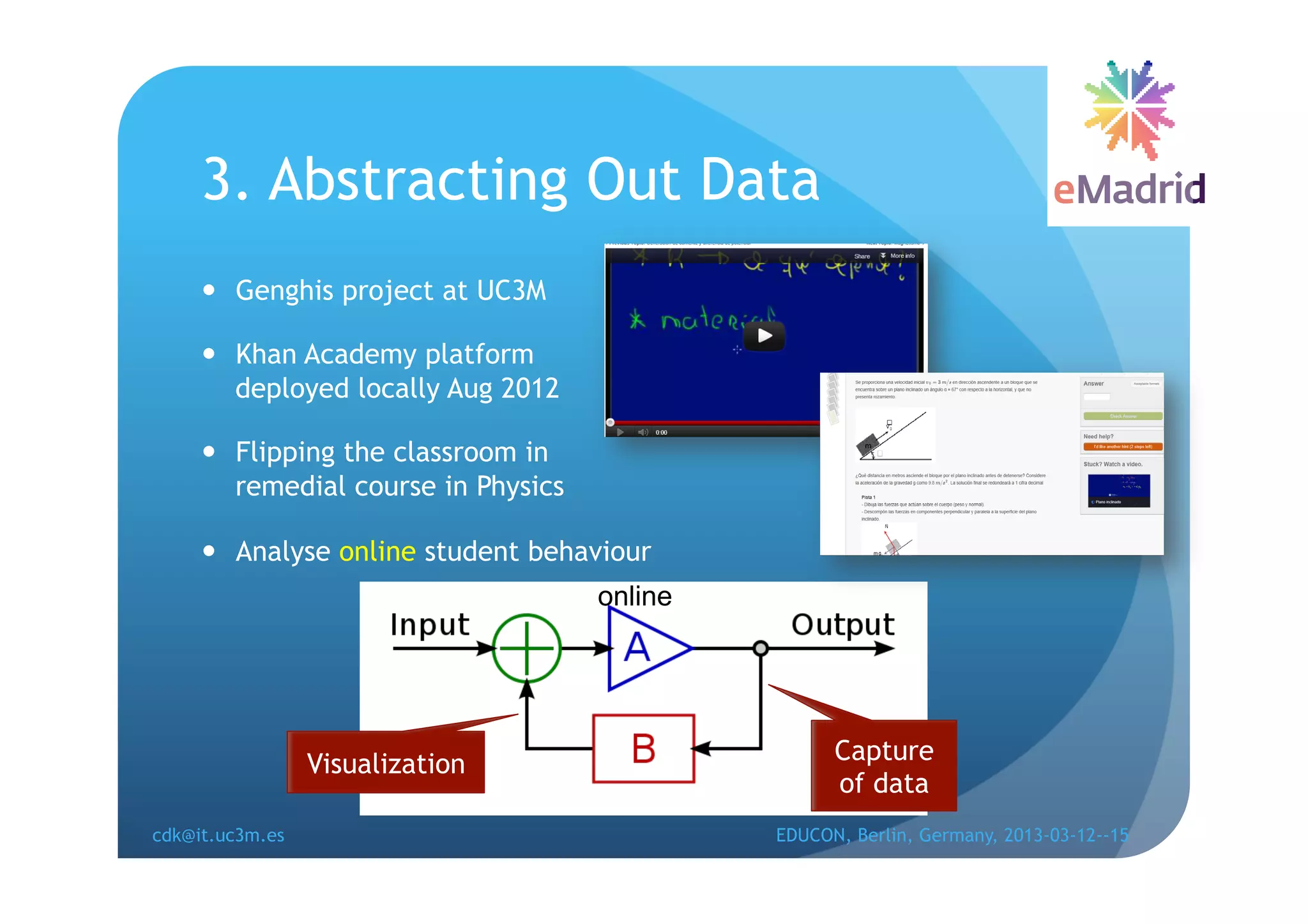
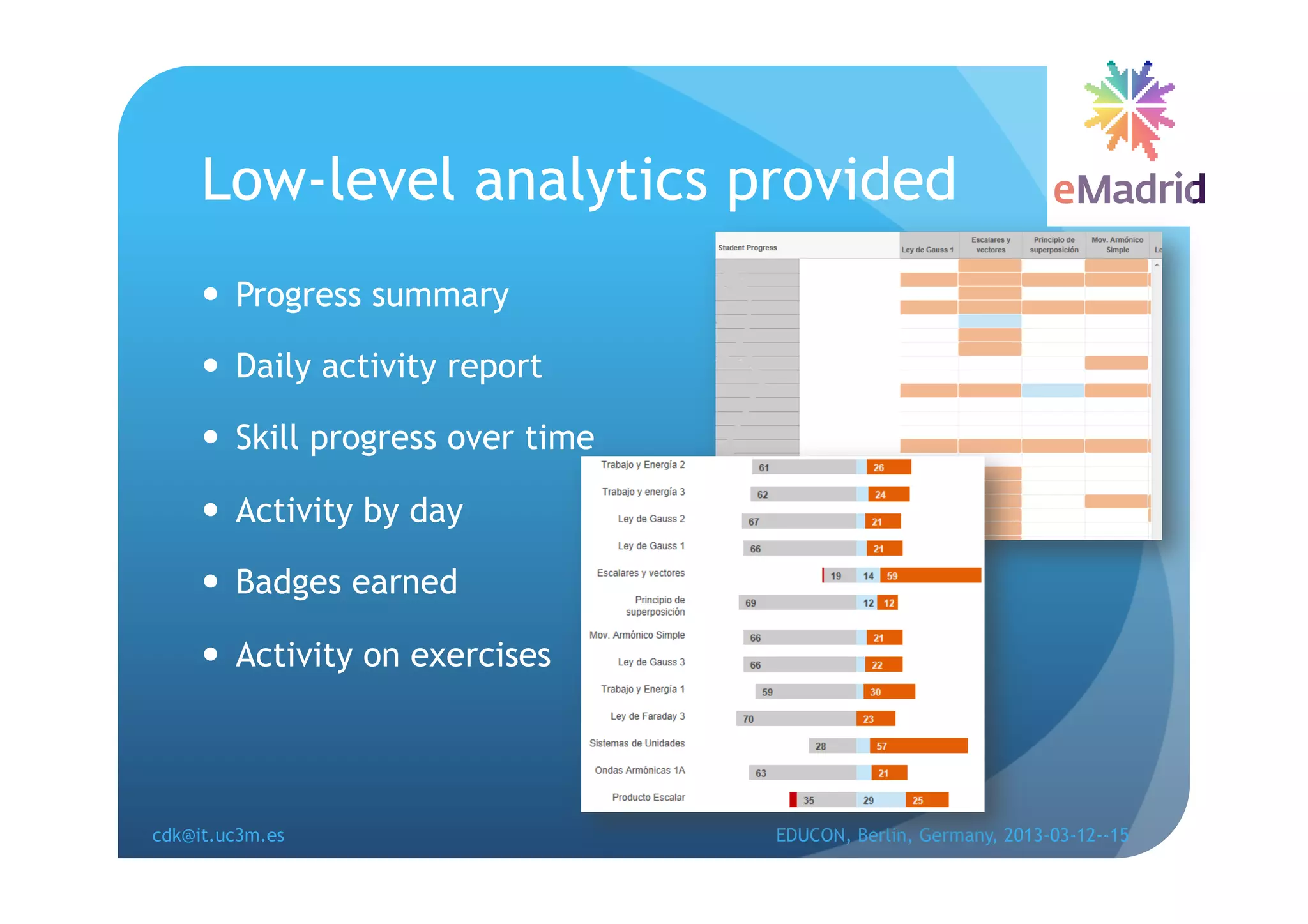
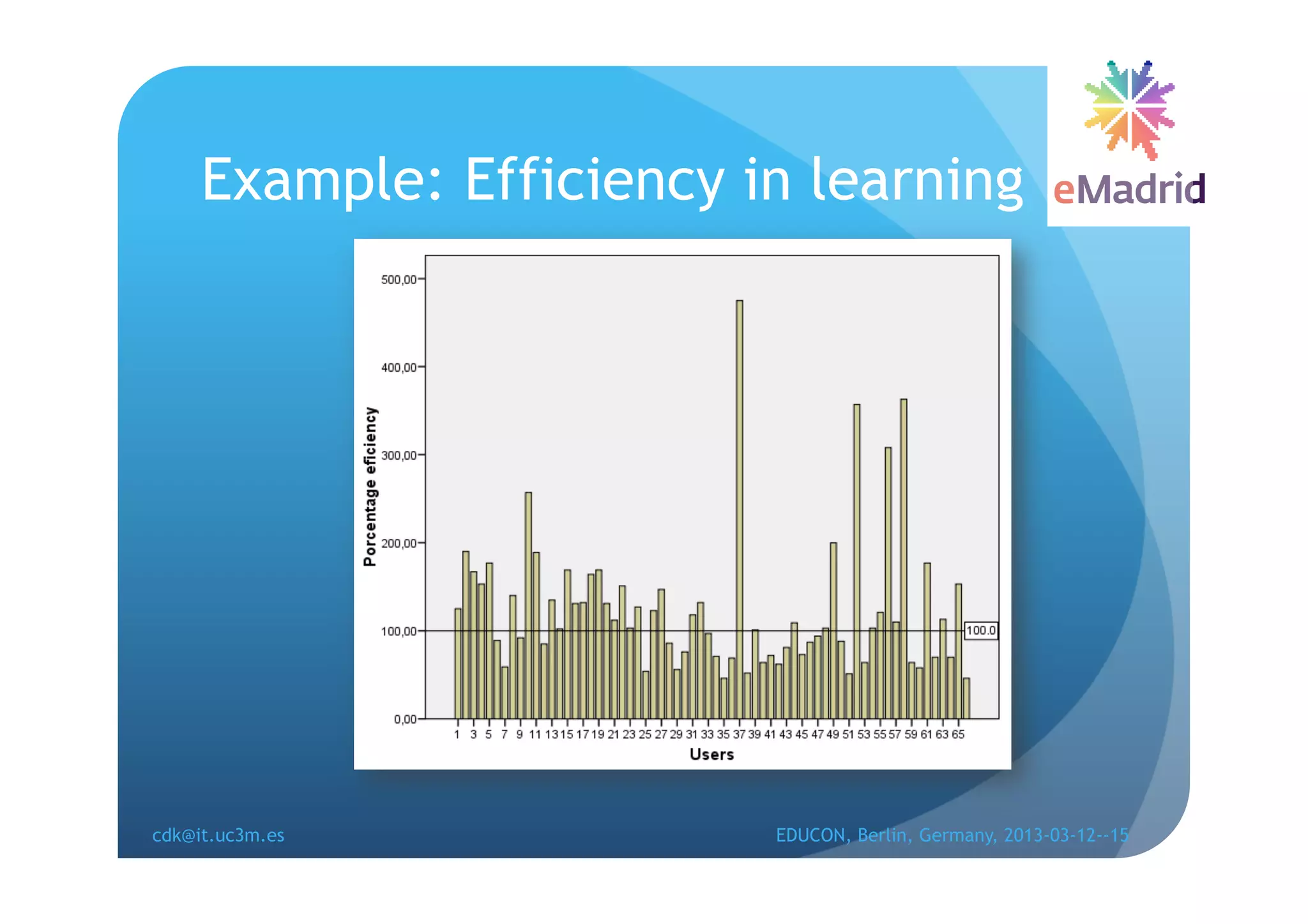
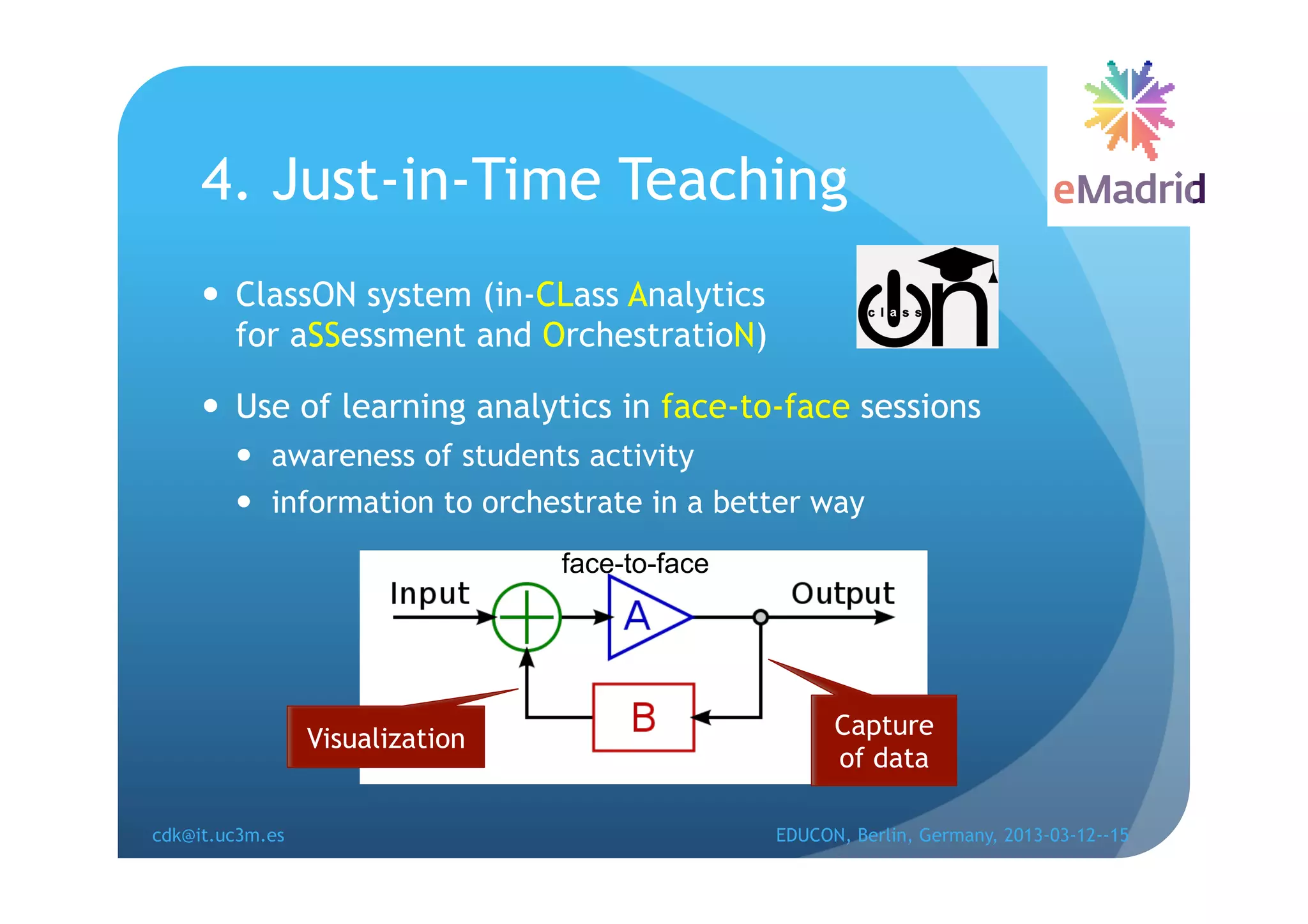
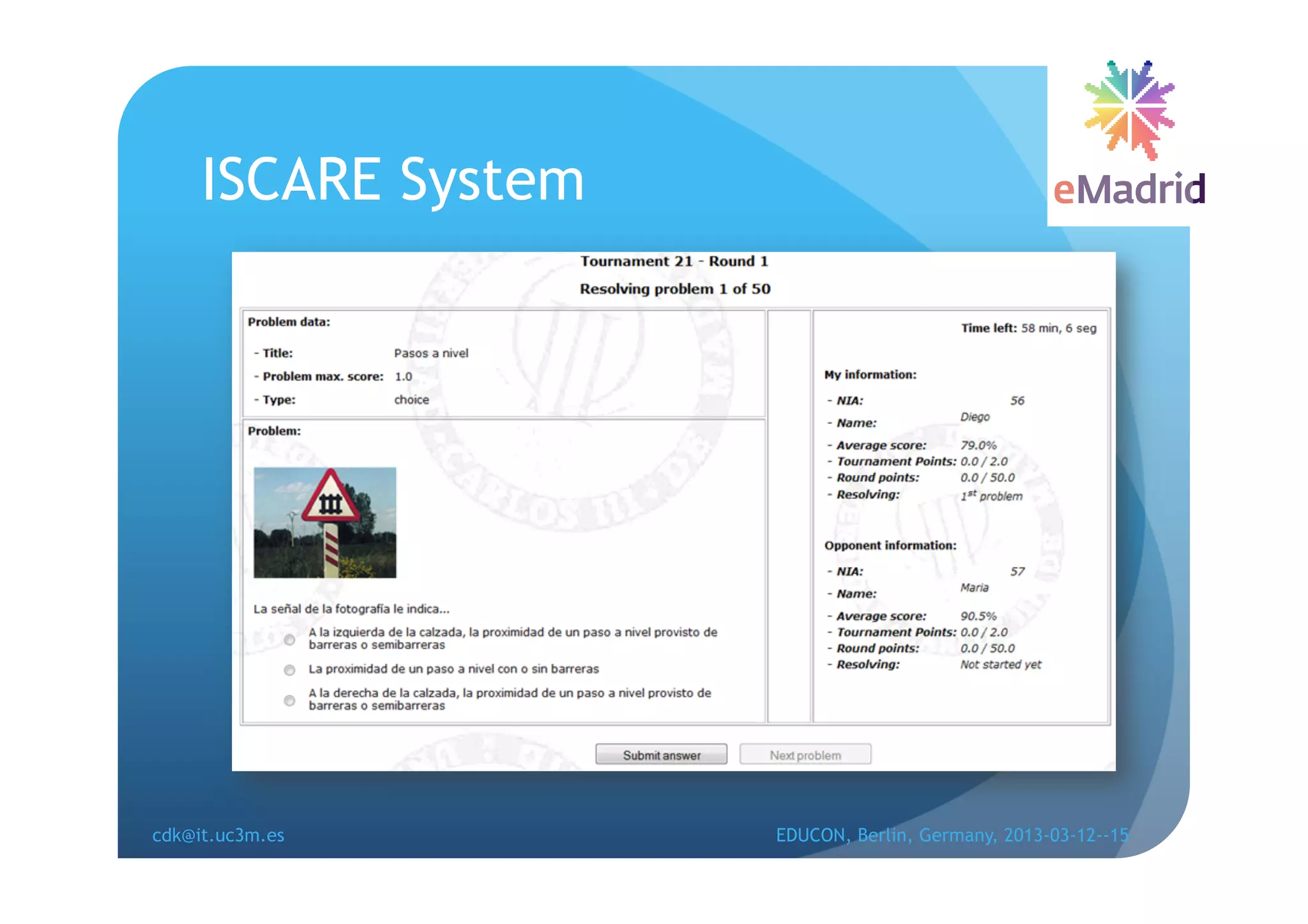
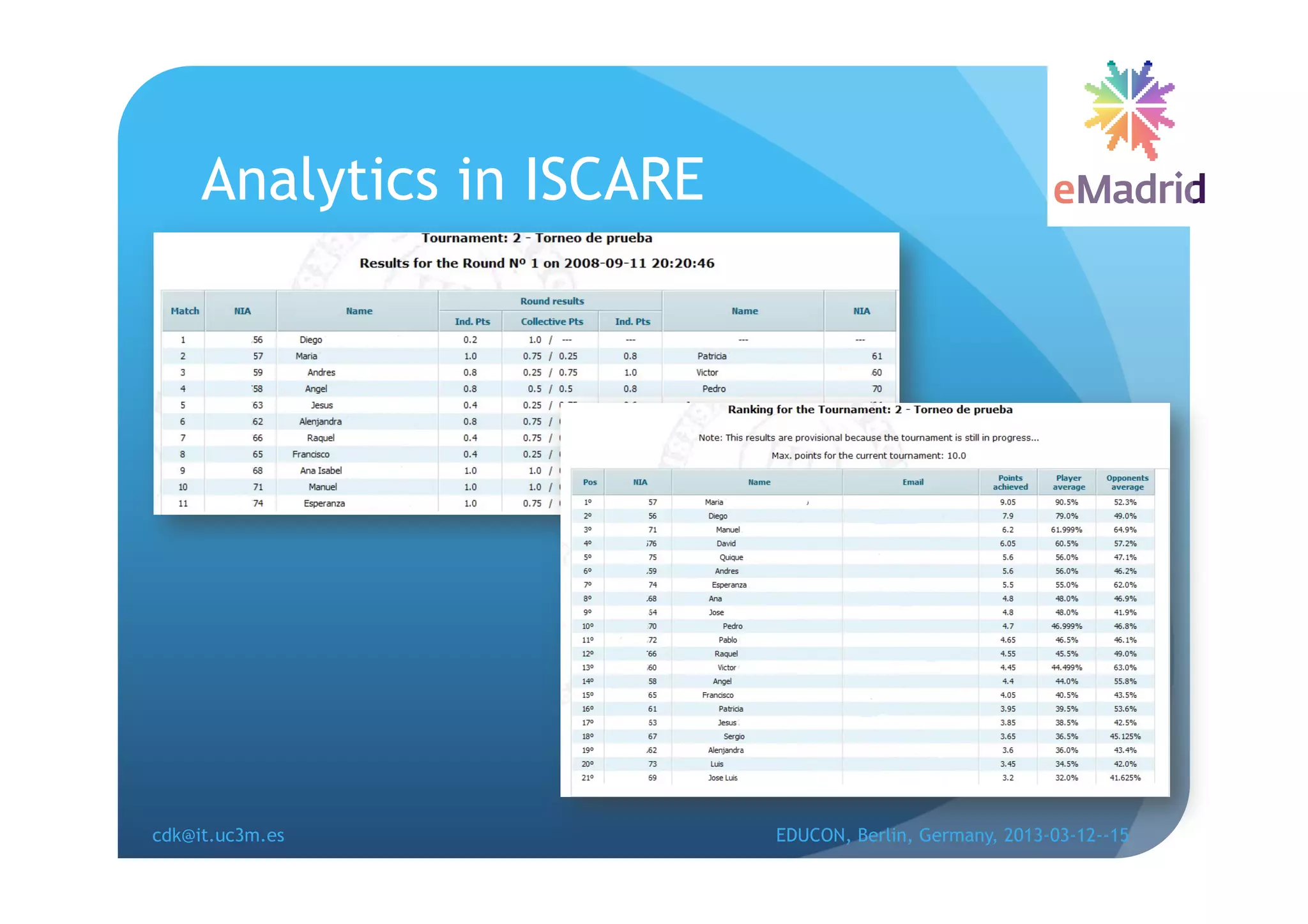
The document discusses learning analytics research at UC3M. It describes 5 developments: 1) The CCOLAB system captures raw learning events in a virtual environment. 2) The LearnGlass platform facilitates creating visualizations of captured data. 3) The Genghis project analyzes online student behavior data from the Khan Academy platform. 4) The ClassON system uses analytics to provide just-in-time feedback to teachers and students in classrooms. 5) The ISCARE system applies analytics and gamification to motivate students through competitive exercises.