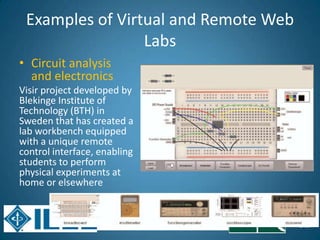
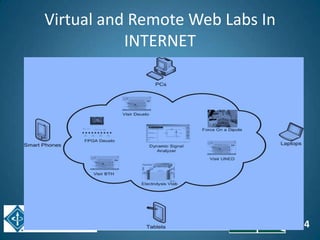
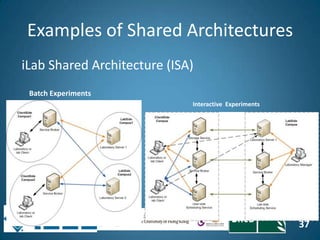
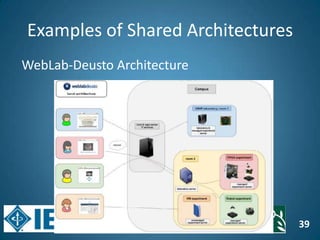
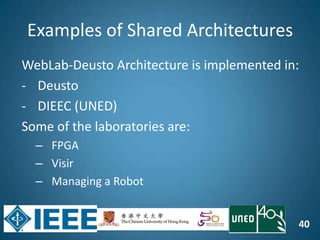
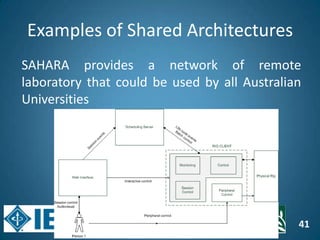
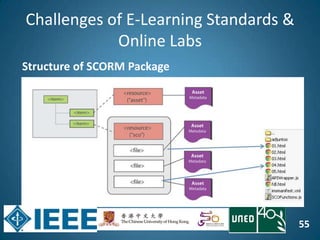
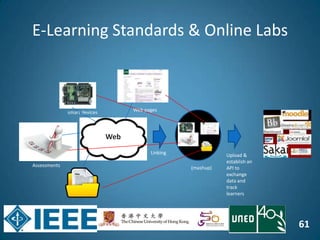
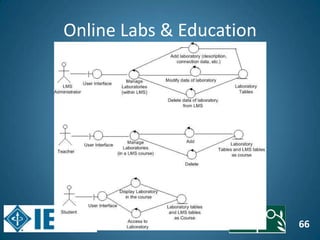
The document discusses the evolution of engineering education through advancements in technology, including practical competencies, MOOCs, and online labs. It emphasizes the importance of open education resources, shared architectures, and e-learning standards to enhance learning experiences and accessibility. Furthermore, it addresses the challenges and future potential of integrating innovative technologies, such as IoT and cloud computing, into educational frameworks.