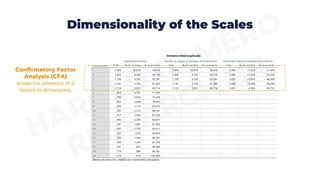
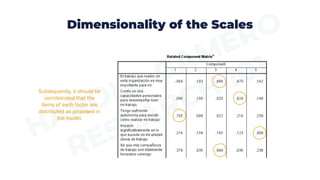
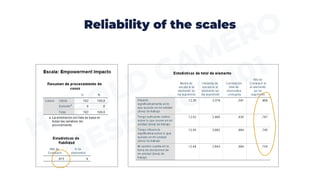
This document provides an overview of important steps in data preparation for research, including data coding, entry, checking for missing values and outliers, testing for normality, assessing dimensionality and reliability of scales. Specifically, it discusses coding survey responses numerically, entering data into statistical programs, identifying and addressing missing data, transforming variables as needed, identifying outlier data, testing data for normal distribution, confirming the dimensionality of multi-dimensional constructs using factor analysis, and calculating reliability coefficients of scales. The goal is to prepare data for statistical analysis and ensure it meets necessary assumptions of different statistical tests.