The document summarizes several qualitative research designs:
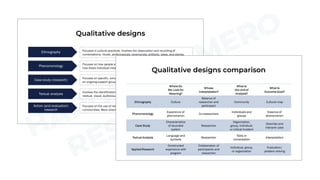
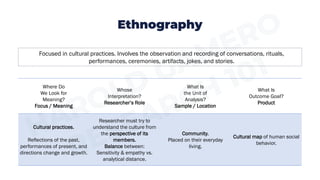
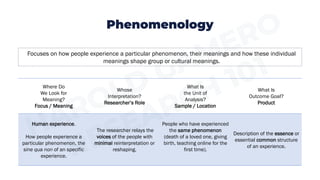
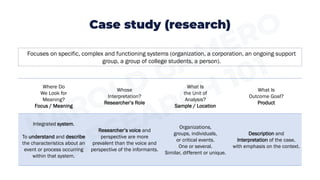
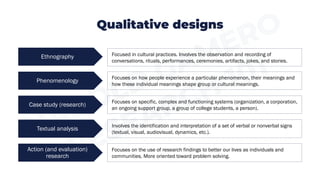
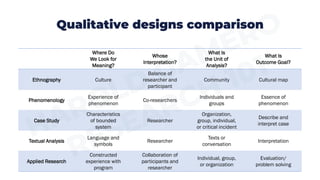
Ethnography focuses on observing cultural practices and aims to understand a culture from the members' perspectives. Phenomenology focuses on how people experience phenomena and aims to describe the essence of shared experiences. Case study research focuses on complex systems like organizations and aims to describe and interpret the case. Textual analysis involves interpreting verbal and nonverbal signs like films or books and aims for the researcher's interpretation. Action research focuses on using findings to solve problems through collaboration and aims to evaluate solutions and recommend improvements.