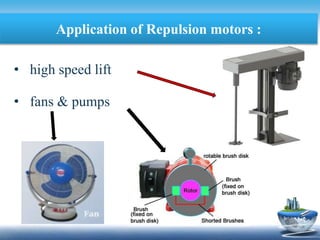
This document discusses repulsion motors, including their construction, types, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Repulsion motors operate based on the principle of magnetic repulsion between the stator and rotor fields. They are classified as single-phase motors and have a stator, rotor connected to a commutator, and brushes. The three main types are compensated repulsion motors, repulsion-start induction-run motors, and repulsion induction motors. Repulsion motors can operate at higher voltages than other commutator motors and are commonly used to power high-speed lifts, fans, pumps, hoists, air compressors, and mining equipment. However, they also have disadvantages like sparking at the brushes and