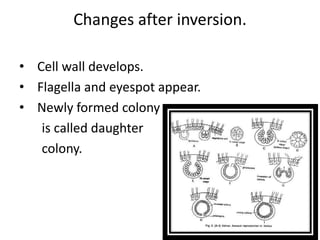
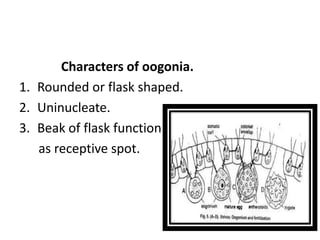
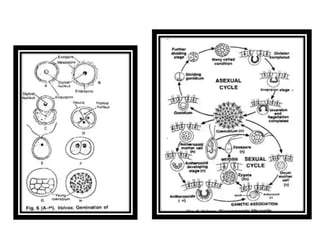
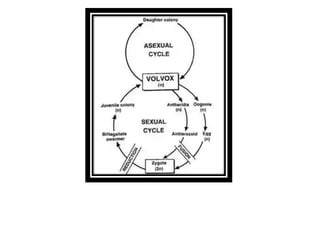
Volvox can reproduce both asexually and sexually. Asexual reproduction involves gonidia forming from posterior cells that undergo multiple longitudinal divisions, developing into a plakea stage before inverting to form a new daughter colony. Sexual reproduction is oogamous, with antheridia and oogonia forming from posterior cells and differentiating into antherozoids and oogonia. Antherozoids fertilize oogonia through chemotaxis, forming a zygote that germinates into a new colony.