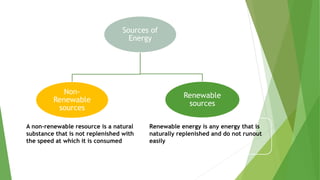
Renewable energy sources include solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, tidal, and biomass. They are naturally replenished and do not run out easily like non-renewable sources. Some key advantages of renewable sources are that they do not cause pollution, are abundant sources, and have lower maintenance costs than non-renewables. However, renewable sources also have disadvantages like high initial installation costs, lower efficiencies than non-renewables, and intermittency issues due to reliance on weather conditions.