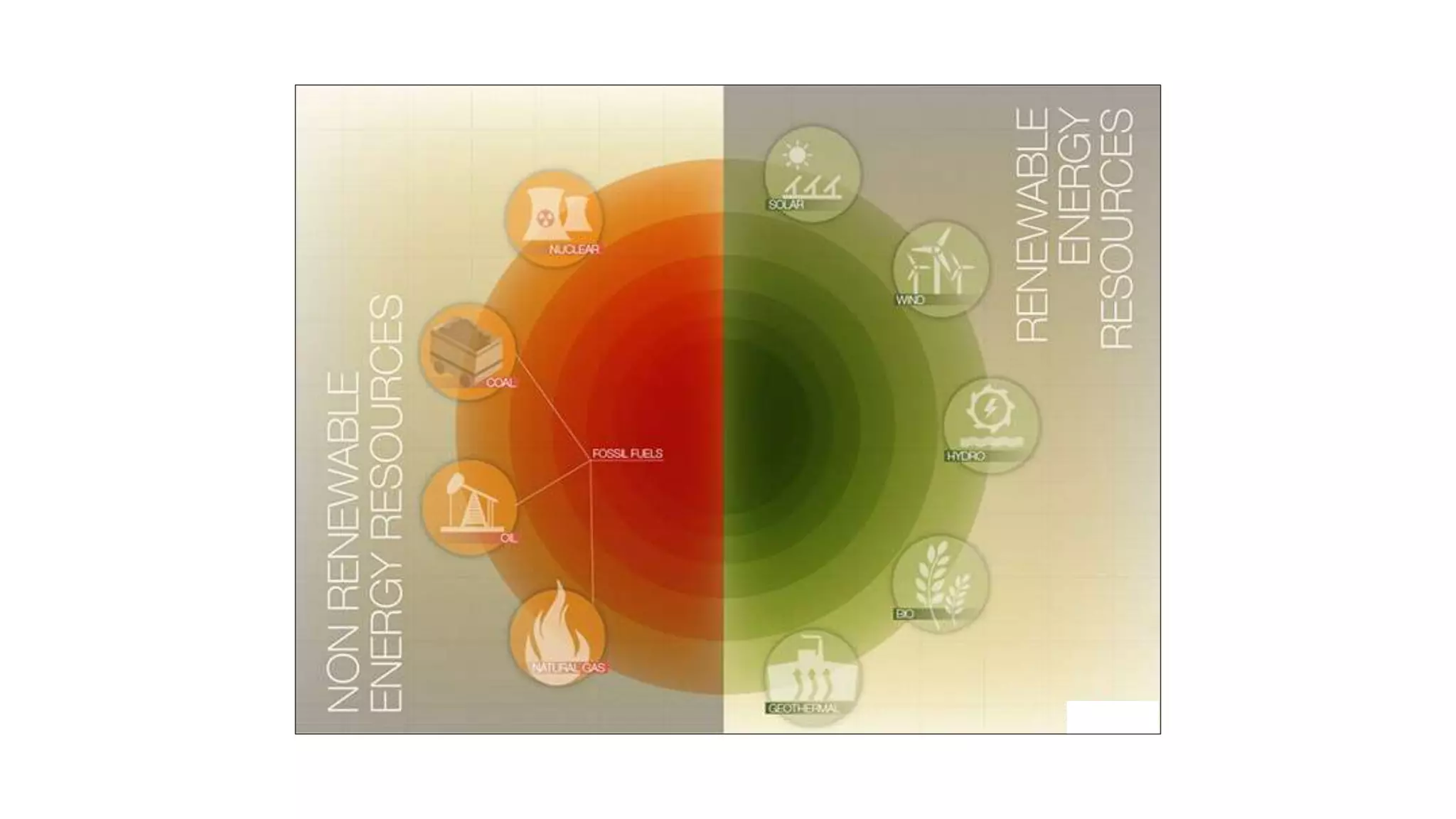
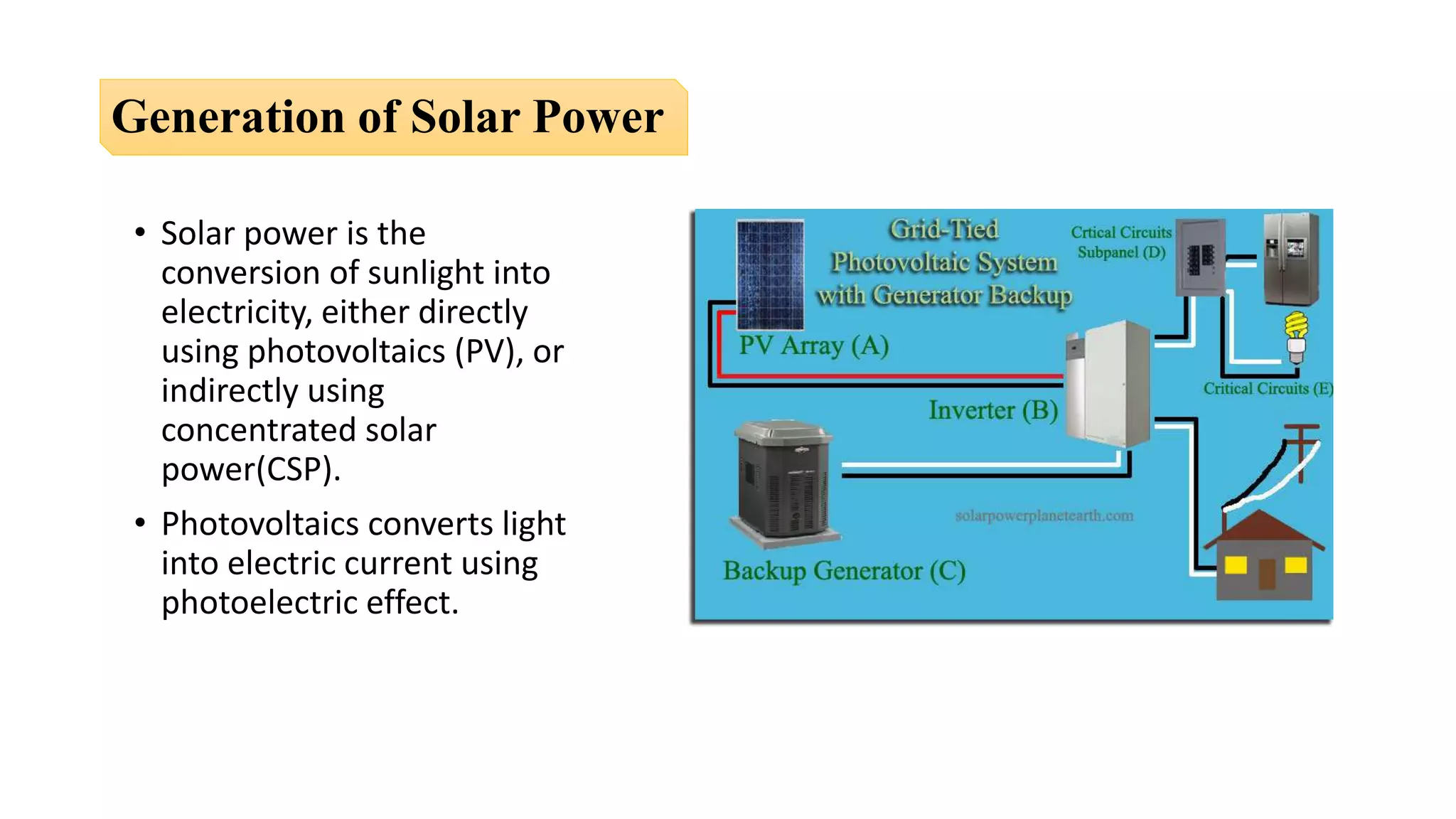
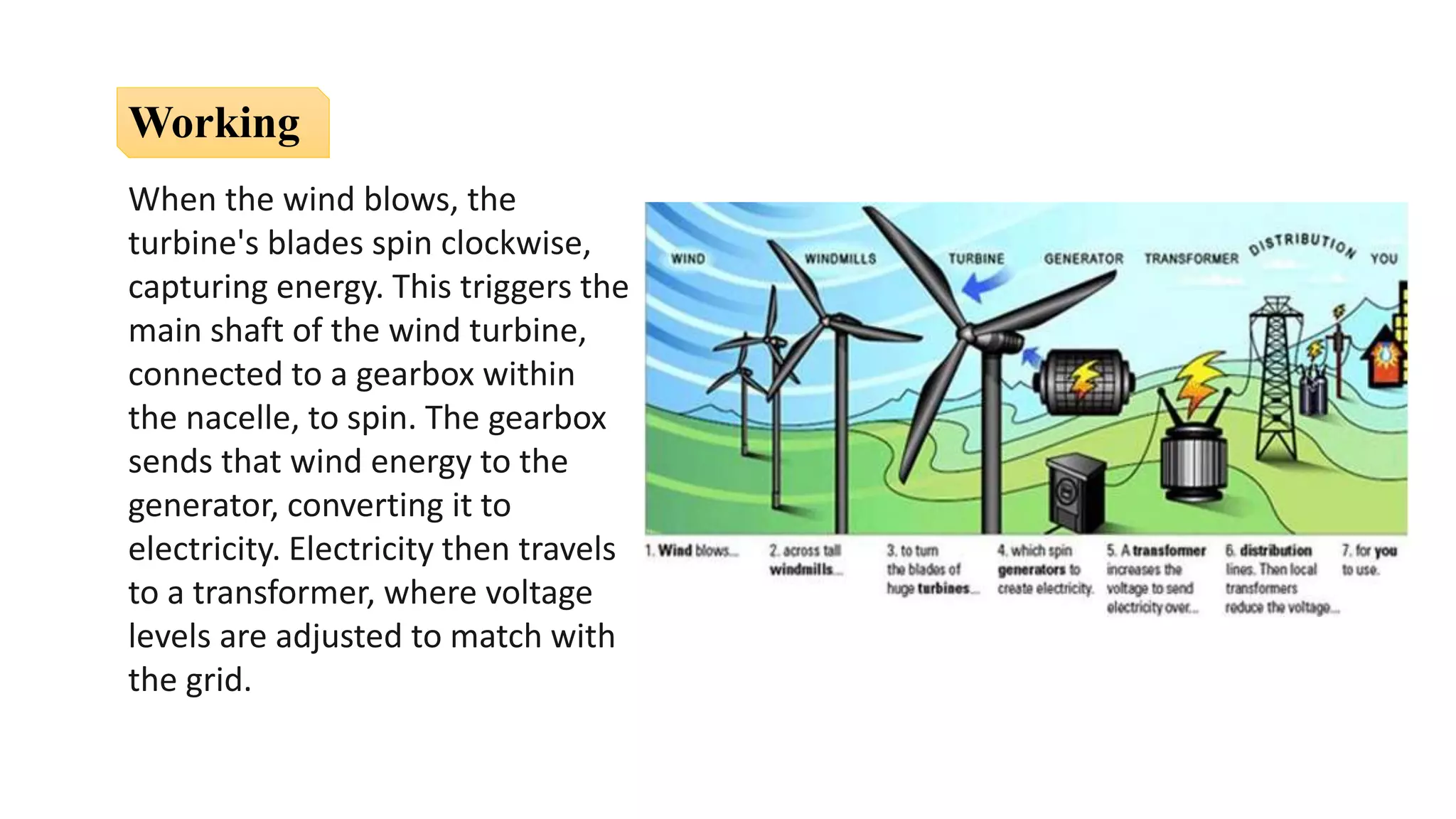
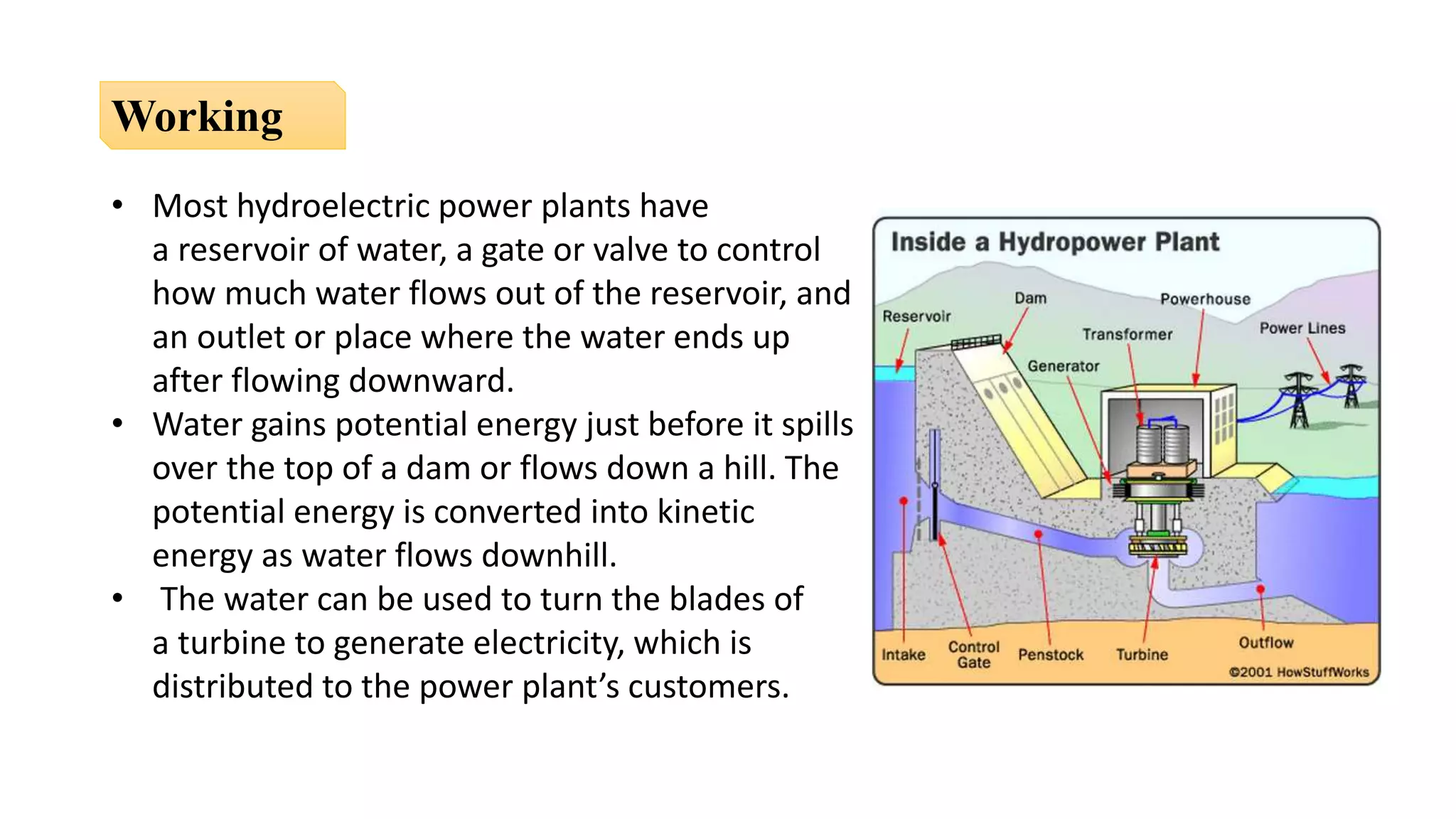
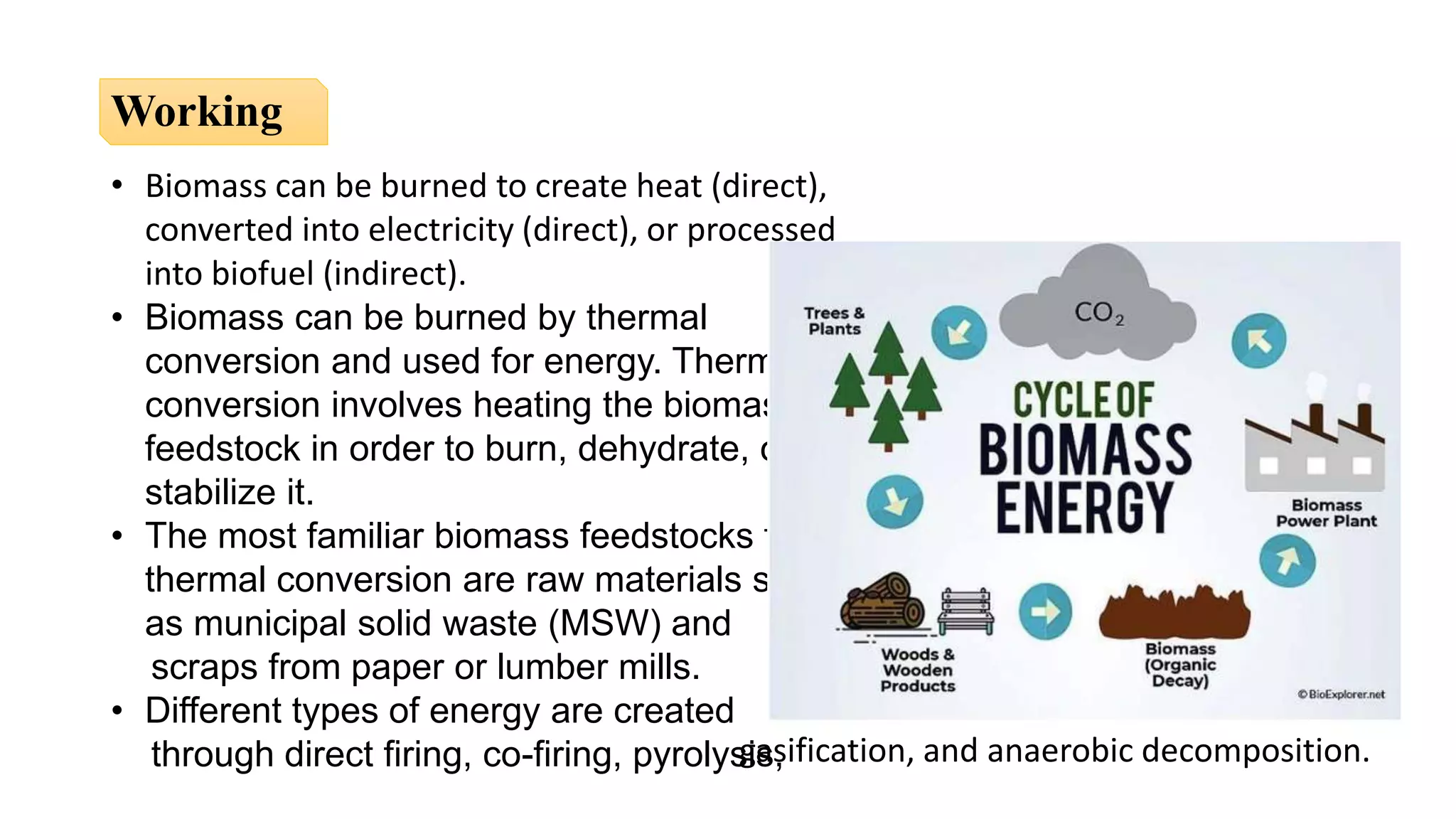
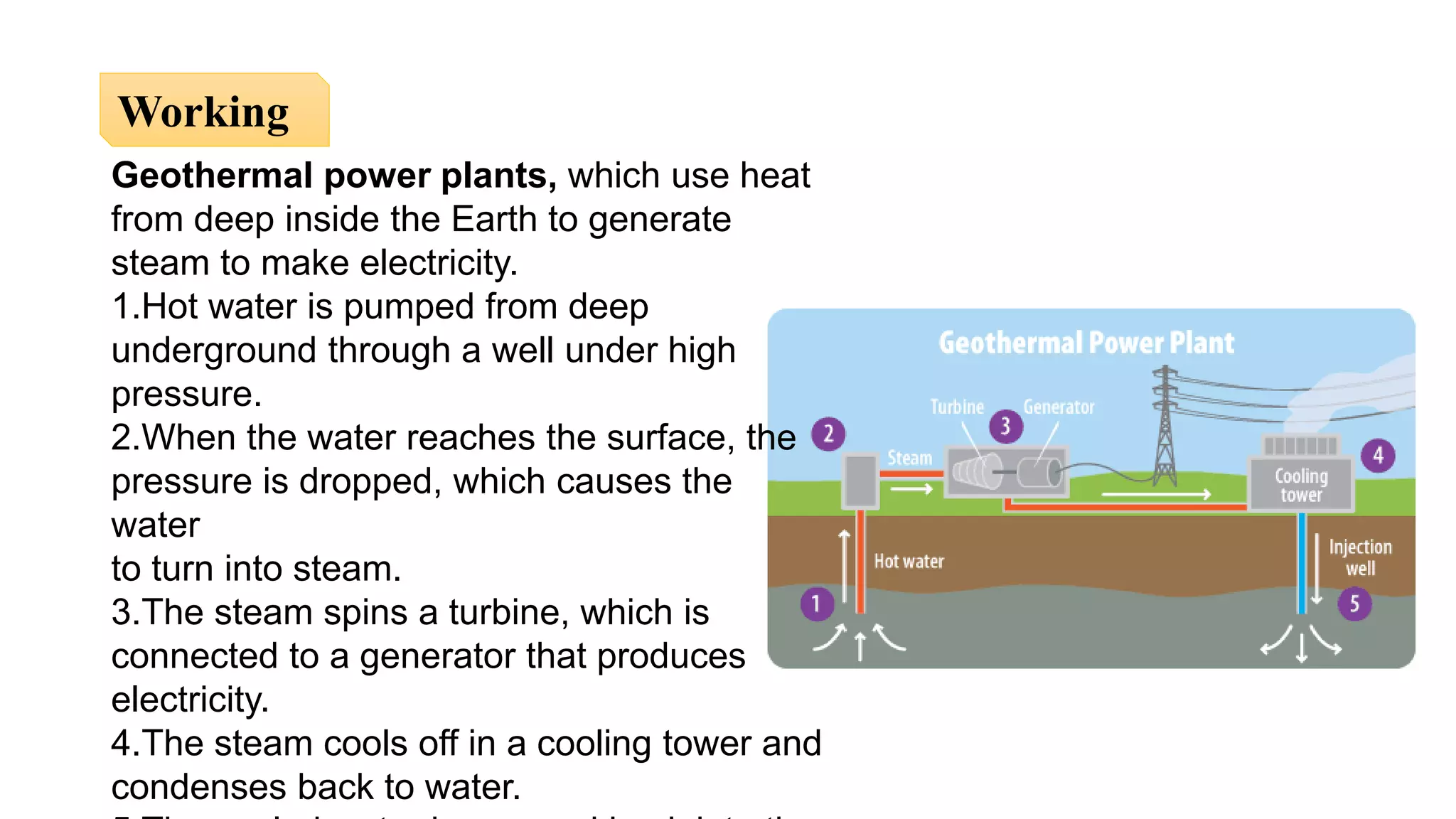
The document presents an overview of renewable and non-renewable resources, emphasizing the importance of maintaining biodiversity and the environment. It details various types of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, biomass, and geothermal energy, along with their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it explains the processes of energy conversion and the characteristics that define renewable resources.