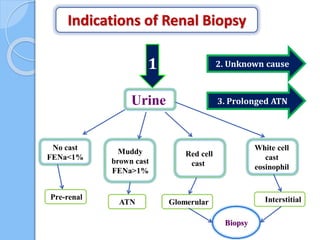
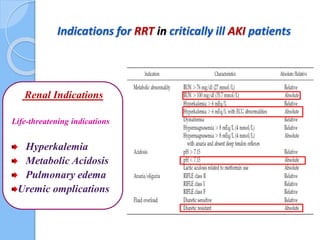
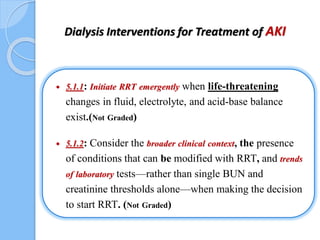
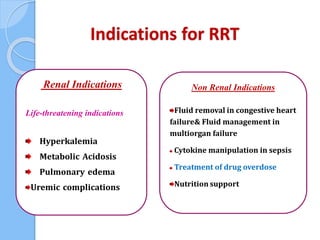
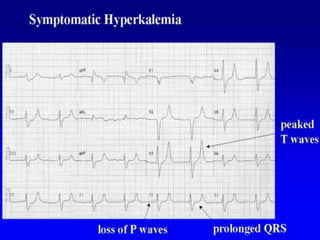
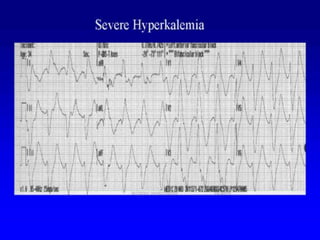
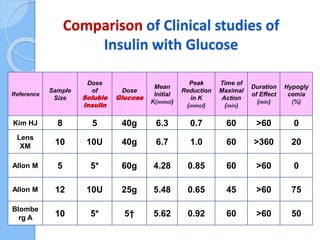
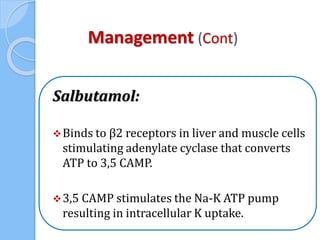
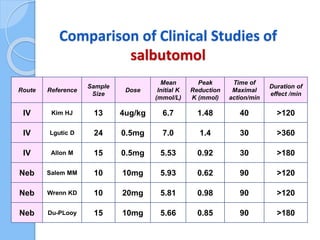
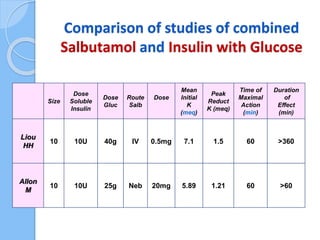
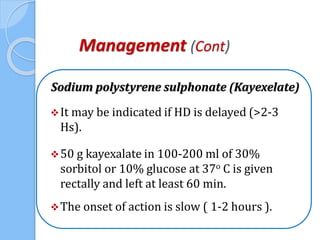
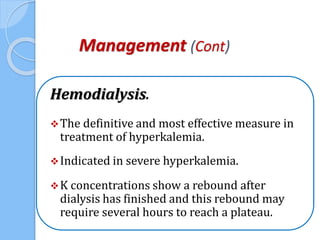
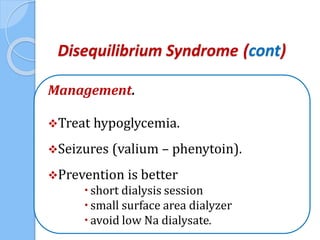
This document provides an overview of intensive care nephrology, including acute kidney injury (AKI), indications for acute dialysis, complications of dialysis, and management of certain drug overdoses. It defines AKI as an acute decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and loss of small solute clearance. Staging criteria for AKI like RIFLE are discussed. Biomarkers for early detection of AKI like neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and cystatin C are presented. Indications for renal replacement therapy in AKI, management of hyperkalemia, and use of bicarbonate, insulin, and salbutamol for hyperkal