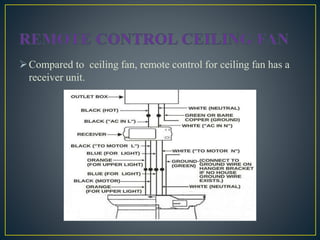
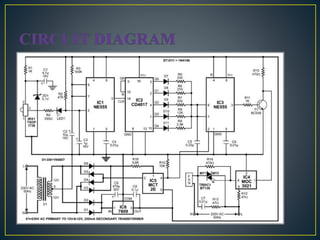
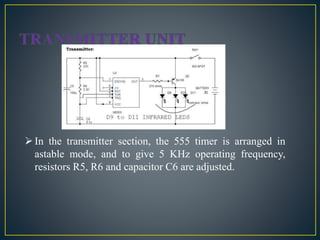
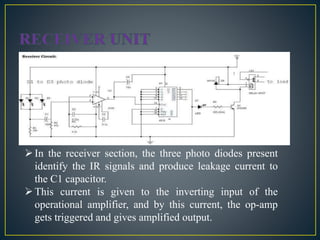
The document describes the circuit design and working of a remote control for ceiling fans. It contains a transmitter unit with a 555 timer and IR LEDs that transmit signals and a receiver unit with a photodiode, op-amp and 4018 counter integrated circuit. The receiver converts the infrared signals into electrical pulses that control a relay and change the fan speed. Remote control provides convenience for switching appliances on/off from a distance and is useful for elderly and disabled people. The system can control ceiling fans and lights with a maximum range of around 10 meters.



















![[1] "DC vs AC Ceiling Fans". www.hunterfan.co.uk. Retrieved 25 May 2015.
[2] Savage, Adam (co-host); Hyneman, Jamie (co-host); Chapman, Scottie (Build Team); Belleci, Tory (Build Team); Byron,
Kari (Build Team) (December 5, 2004). "Ming Dynasty Astronaut". MythBusters. Season 2. Episode 24. Begins at 25:45.
Discovery.
[3] Gromicko, Nick. "Ceiling Fan Inspection". International Association of Certified Home Inspectors. Retrieved May 31, 2013.
[4] K. J. Ayala 8051 Microcontroller, Architecture, Programming & Applications, Second Edition, 1997, Singapore, Penram
International Publishing Pvt. Ltd. (2005)
[5] Atmel Corporation, 8-bit Microcontroller with 8K Bytes Flash
http://www.atmel.com/dyn/resources/prod_documents/doc0313.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarppt-remotecontrolfan-180127091530/85/REMOTE-CONTROL-FOR-FAN-SLIDE-SHARE-24-320.jpg)
