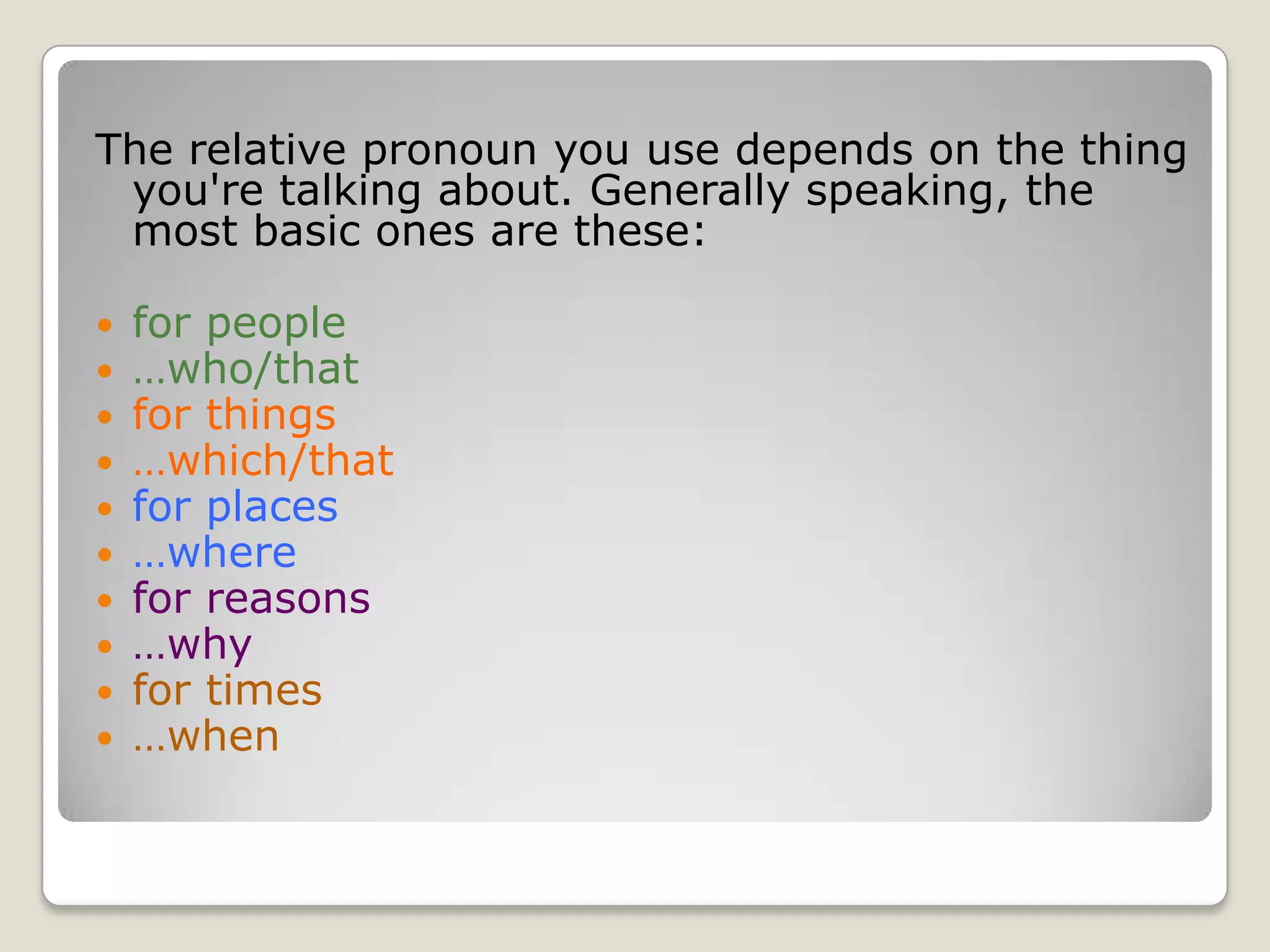
The document discusses relative clauses, which are parts of sentences that begin with relative pronouns like who, which, that, where, when, and why. It explains the difference between defining and non-defining relative clauses. Defining clauses provide essential information to identify a noun, while non-defining clauses provide extra, non-essential information. The document provides examples of forming relative clauses and choosing the correct relative pronouns, and emphasizes the importance of punctuation in non-defining clauses. It concludes by noting that practice is needed to fully understand relative clauses.





![Ok… Lets review how we choose relative pronouns.Who is a subject or object pronoun for peopleExample - I told you about the woman who lives next door.Which is asubject or object pronoun for animals, buildings, and things Example - Do you see the cat which is lying on the roof?Which alsorefers to a whole sentence Example - He couldn’t read which surprised me.Whose is a possession for people animals and things Example - Do you know the boy whose mother is a nurse?Whom is an object pronoun for people. [especially in non-defining relative clauses] [in defining relative clauses we colloquially prefer who] Example - I was invited by the professor whom I met at the conference.That is a subject or object pronoun for people, animals and things in defining relative clauses (who or which are also possible) Example - I don’t like the table that stands in the kitchen.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relativeclauses-091014150754-phpapp01/75/Relative-Clauses-8-2048.jpg)



![Defining relative clauses are also often used in definitions.Example:A seaman is someone who works on a ship.Object pronouns in defining relative clauses can be dropped. (Sentences with a relative clause without the relative pronoun are called Contact Clauses.)The boy (who/whom) we met yesterday is very nice.[we can drop who/whom, and it sounds like this].The boy we met yesterday is very nice.[Contact clause]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relativeclauses-091014150754-phpapp01/75/Relative-Clauses-12-2048.jpg)


![An easy way to remember Defining Relative Clauses is that they answer the question which what or whose?Example sentence: People are fools.Defining relative clause sentence:Peoplewho do such things are fools.In the relative clause sentence the people are restricted to a specific group only. [specific group– fools]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relativeclauses-091014150754-phpapp01/75/Relative-Clauses-15-2048.jpg)

![Non-defining relative clausesNon-defining relative clausesThese are the ones that give extra information. They are always written between commas. If you leave out the relative clause between the commas it still makes sense. For example: Valencia, which is Spain's third largest city, is on the Mediterranean coast. [We all know Valencia, so this is extra information not needed for understanding] My parents, who are retired, come to Spain every year. [ I've only got one set of parents]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relativeclauses-091014150754-phpapp01/75/Relative-Clauses-17-2048.jpg)






