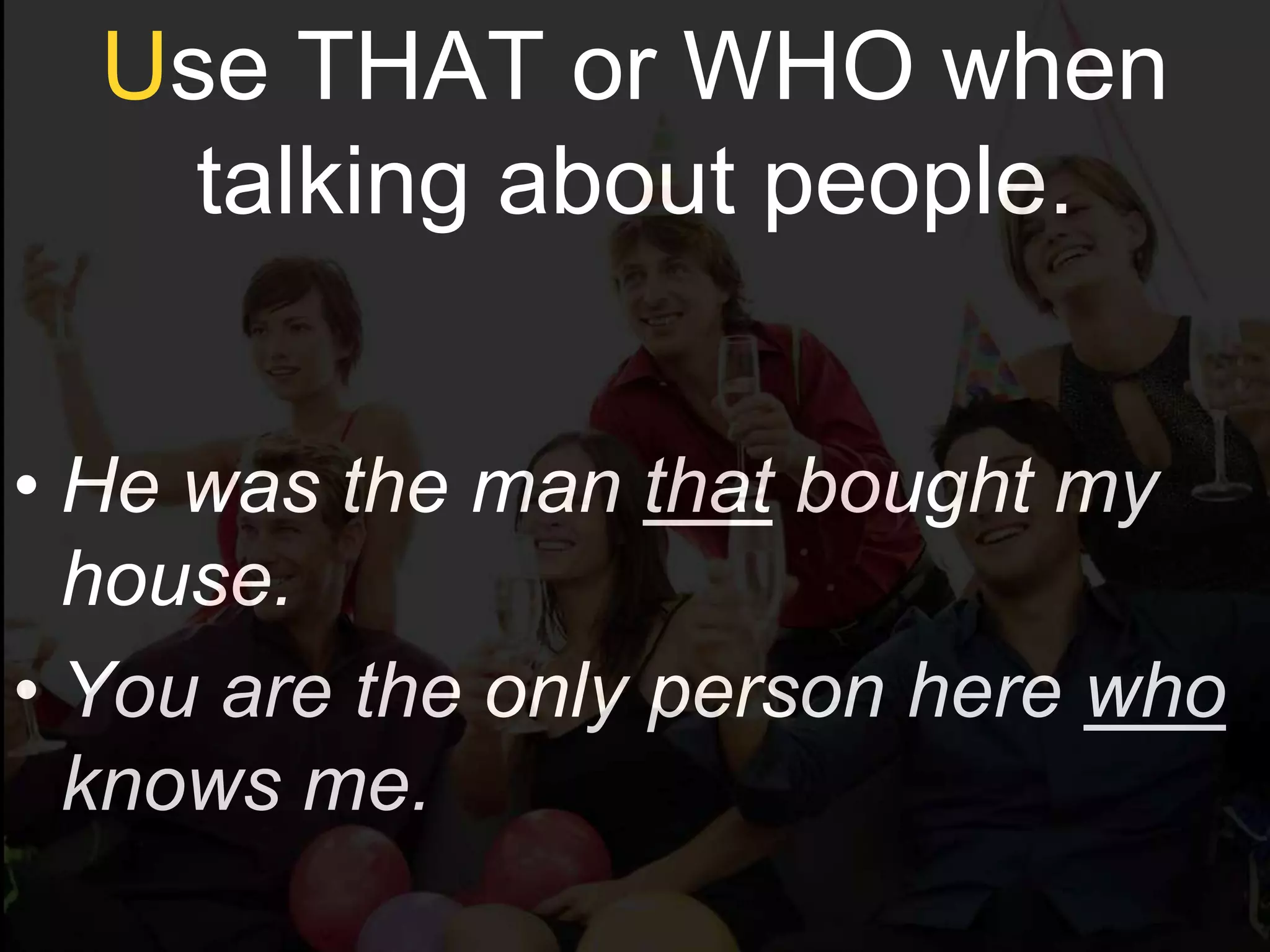
Defining relative clauses provide information to identify a person or thing and can use that, who, which, whom, whose, when, where, or why. That or who is used for people and that or which for things. The relative pronoun can be the subject or object of the verb in the relative clause. In formal English whom is used instead of who as the object. The relative pronoun can be omitted if it is the object of a preposition. Whose indicates possession. When, where, and why are used after time, place, and reason nouns, respectively. Defining relative clauses concisely identify people and things.