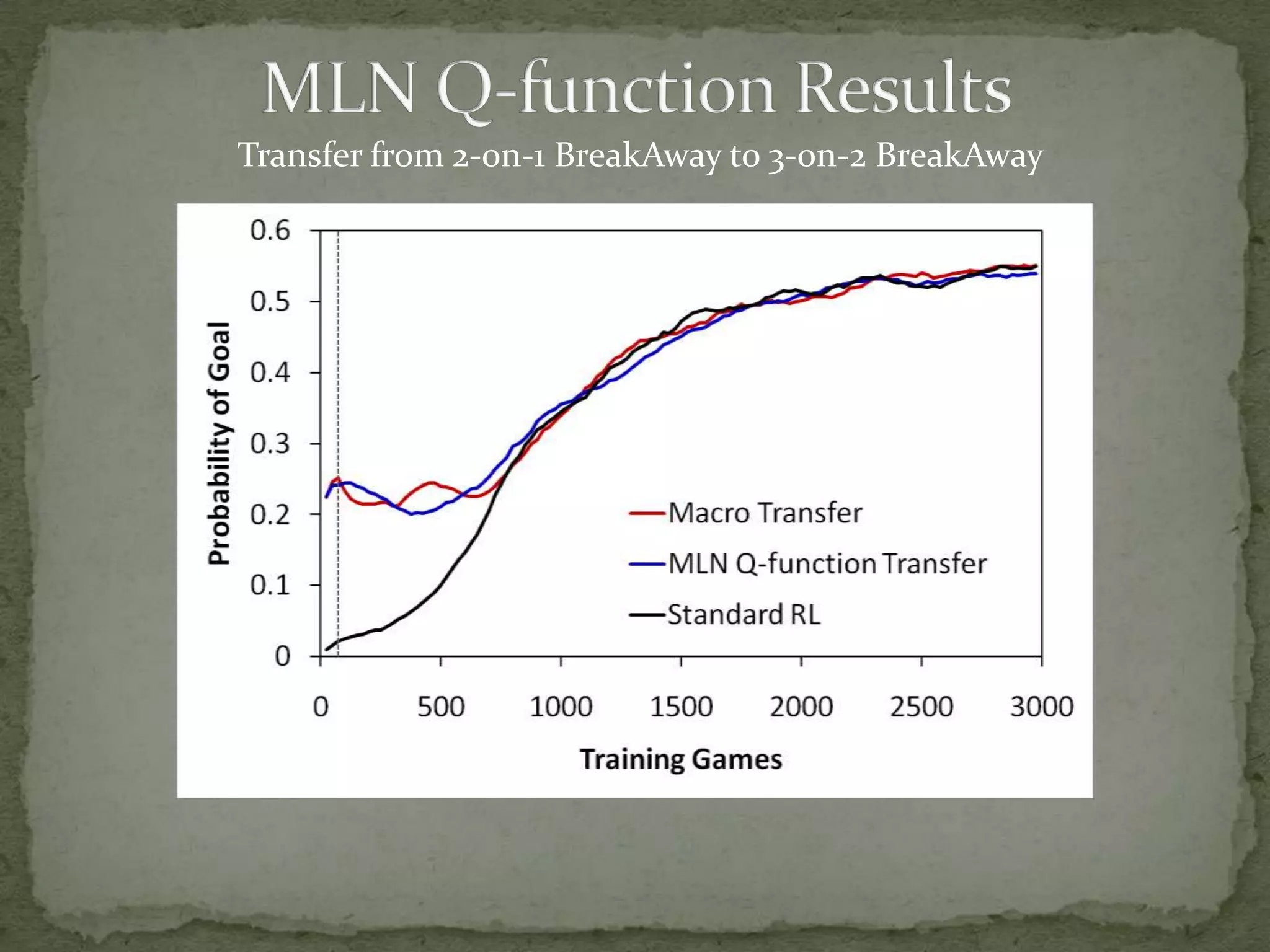
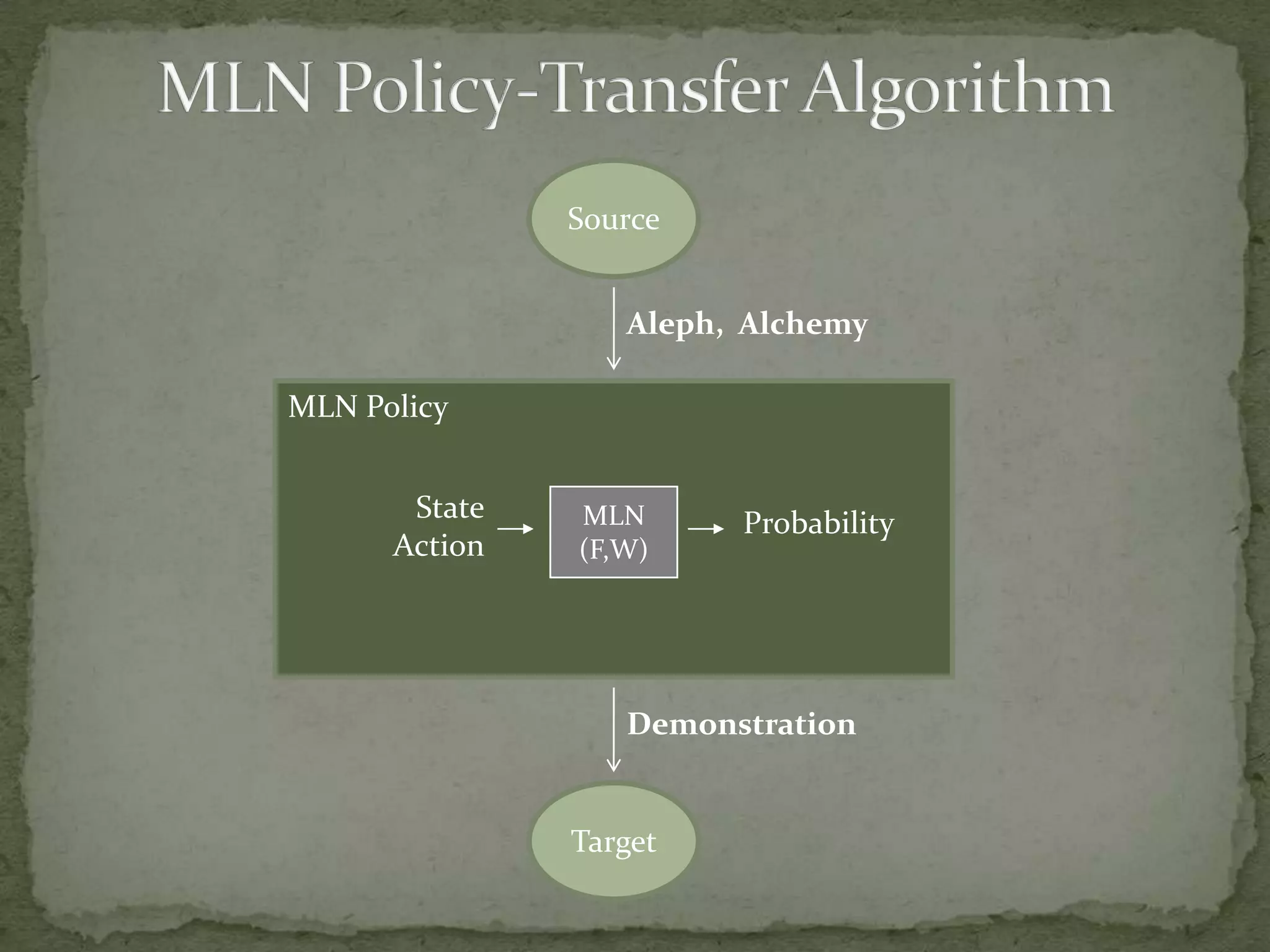
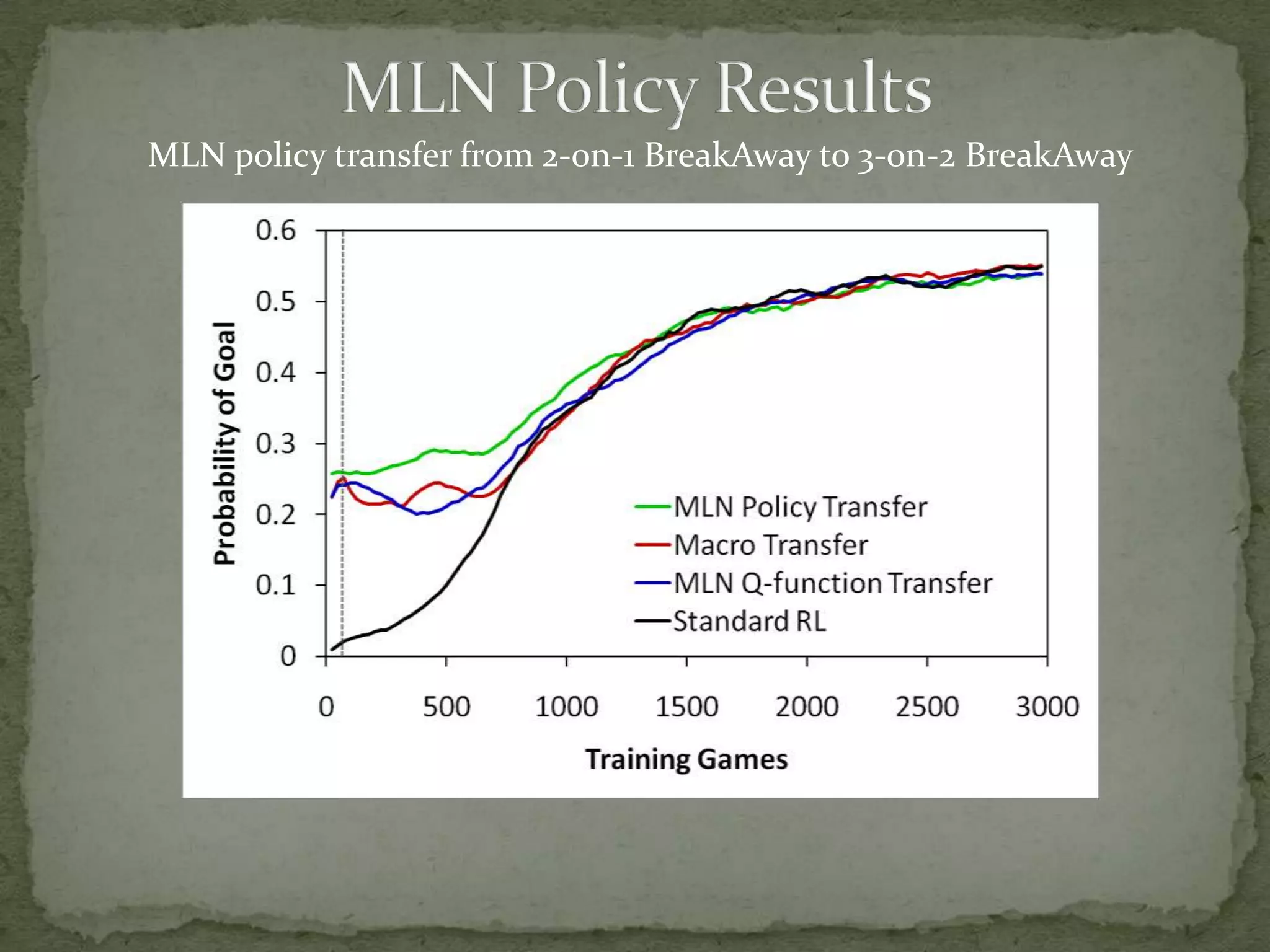
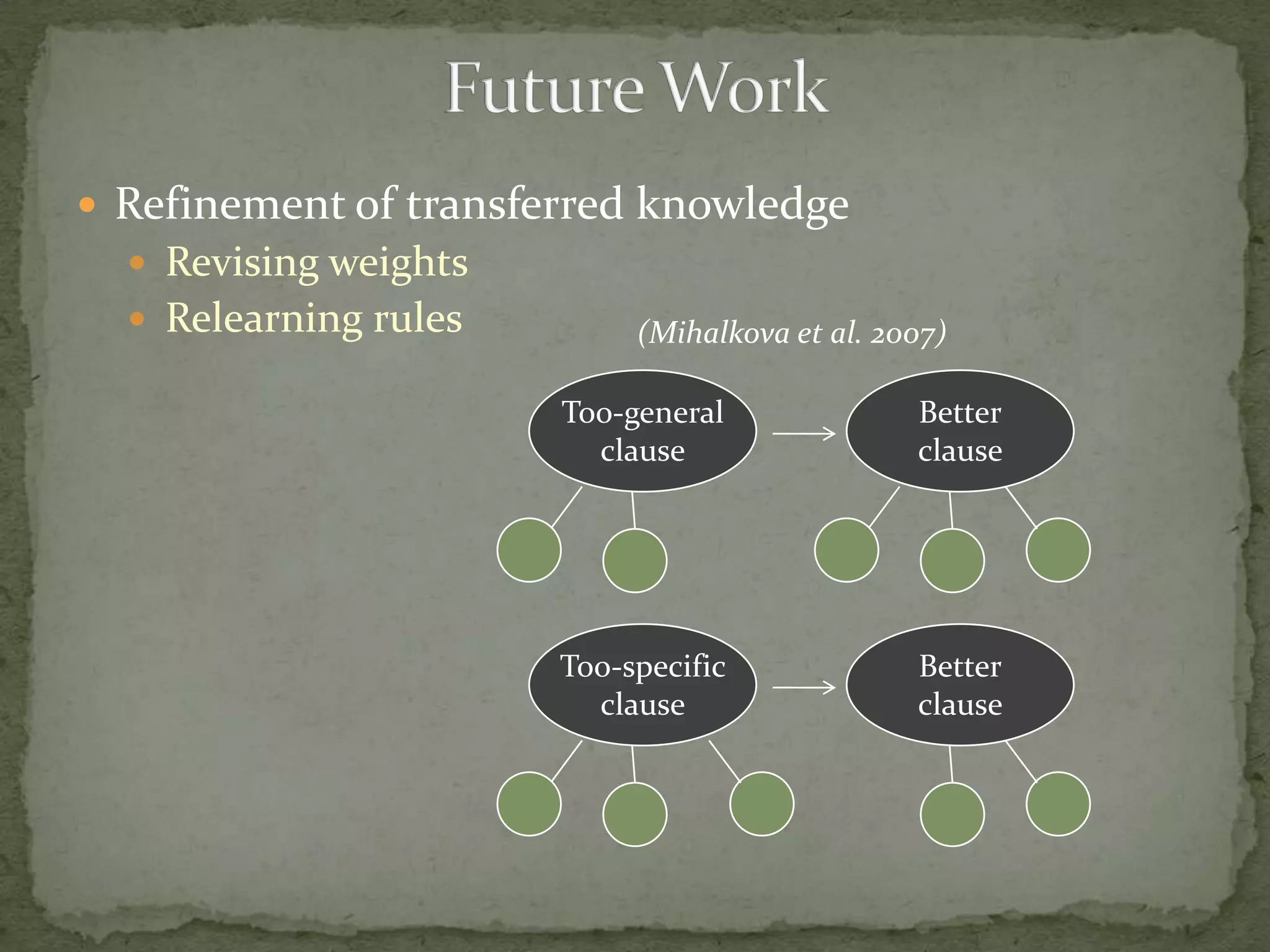
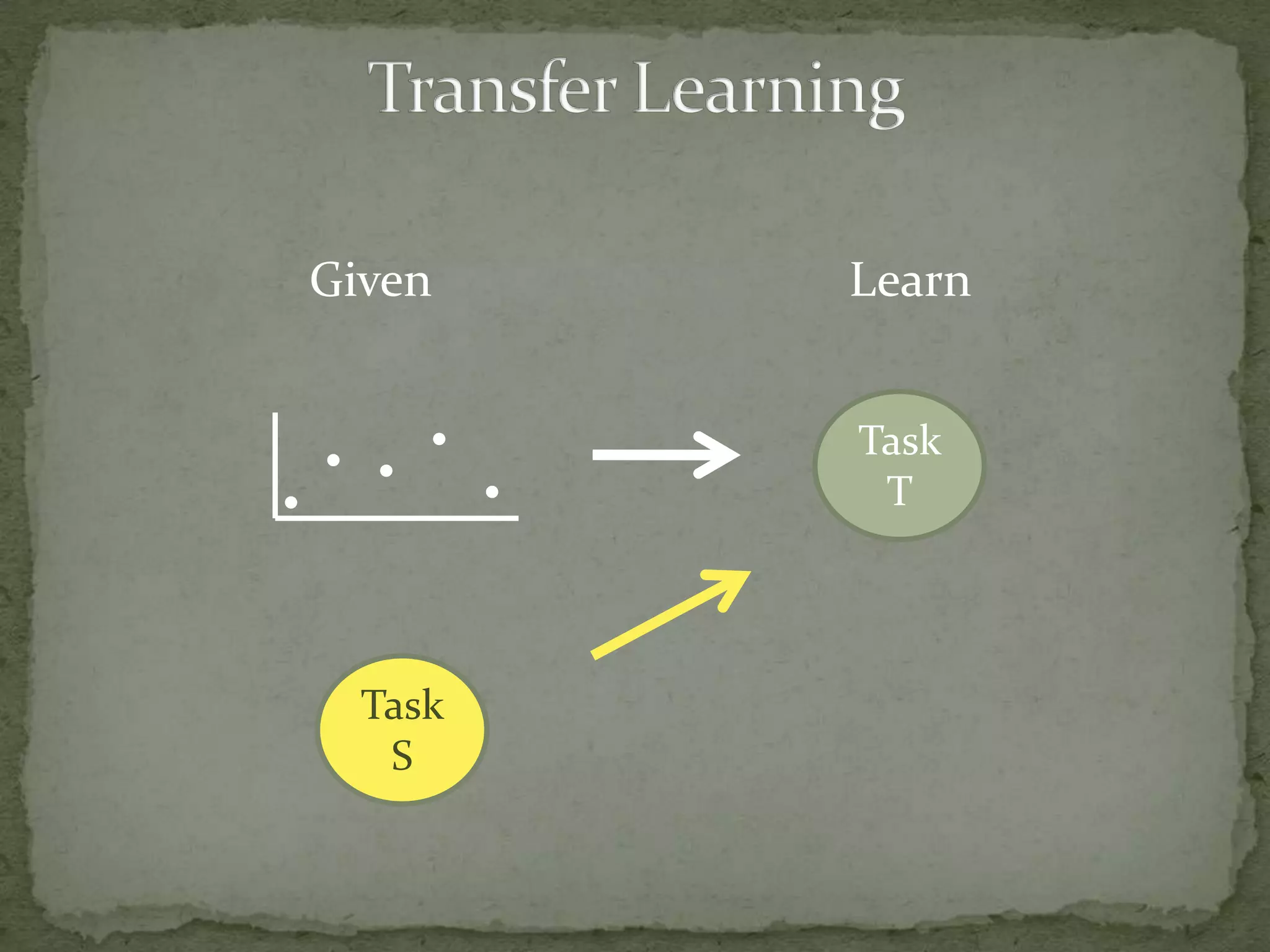
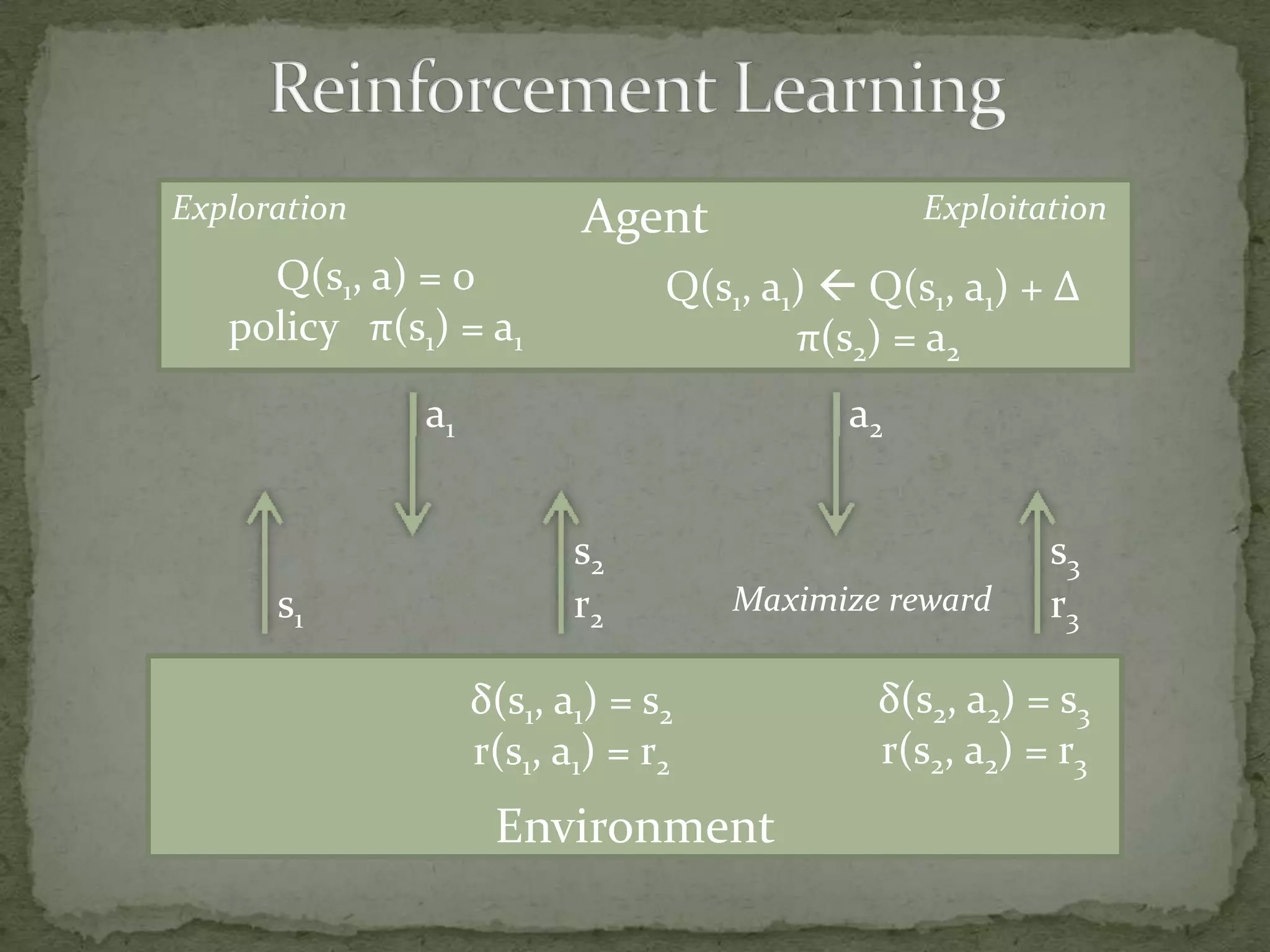
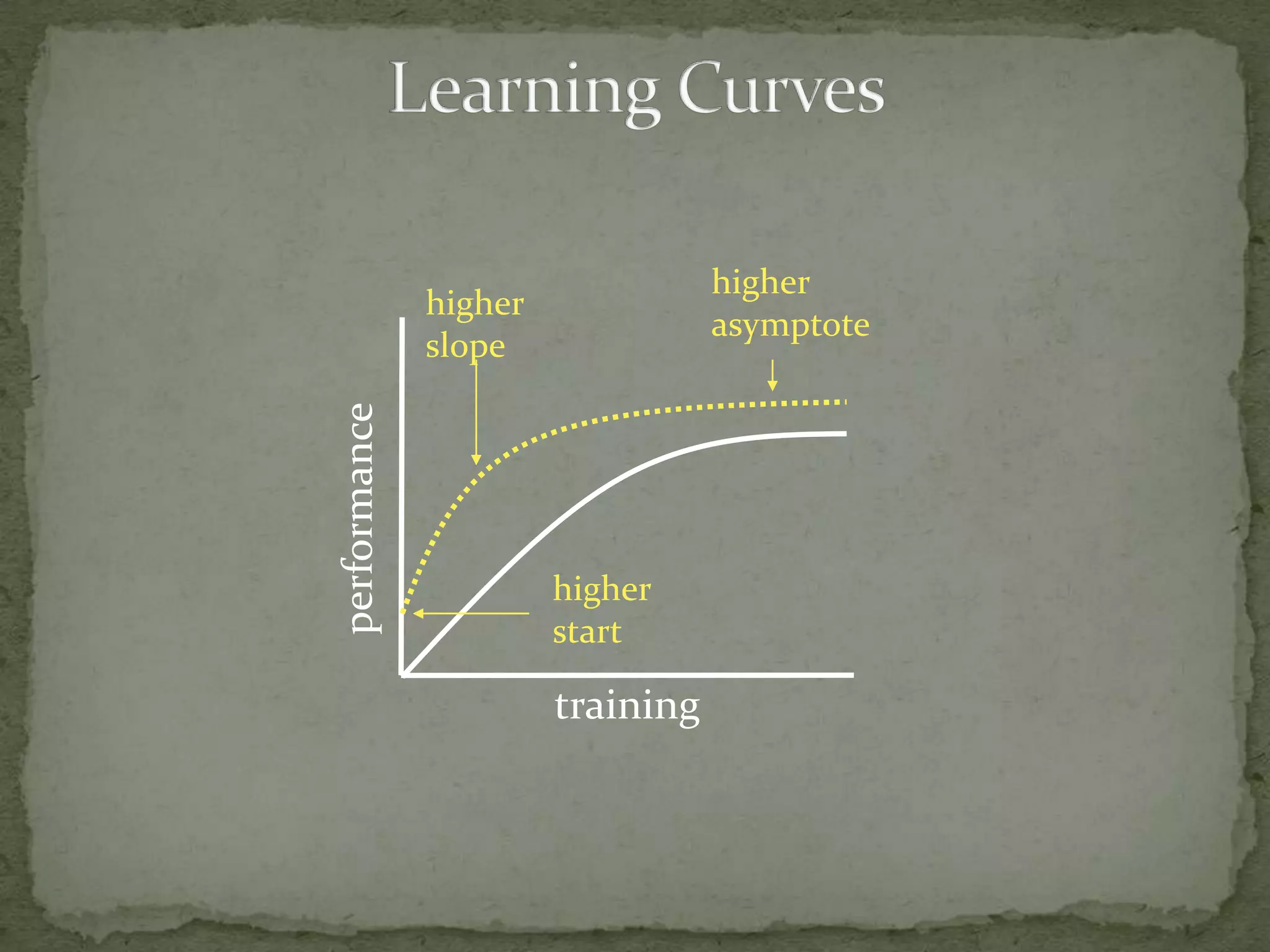
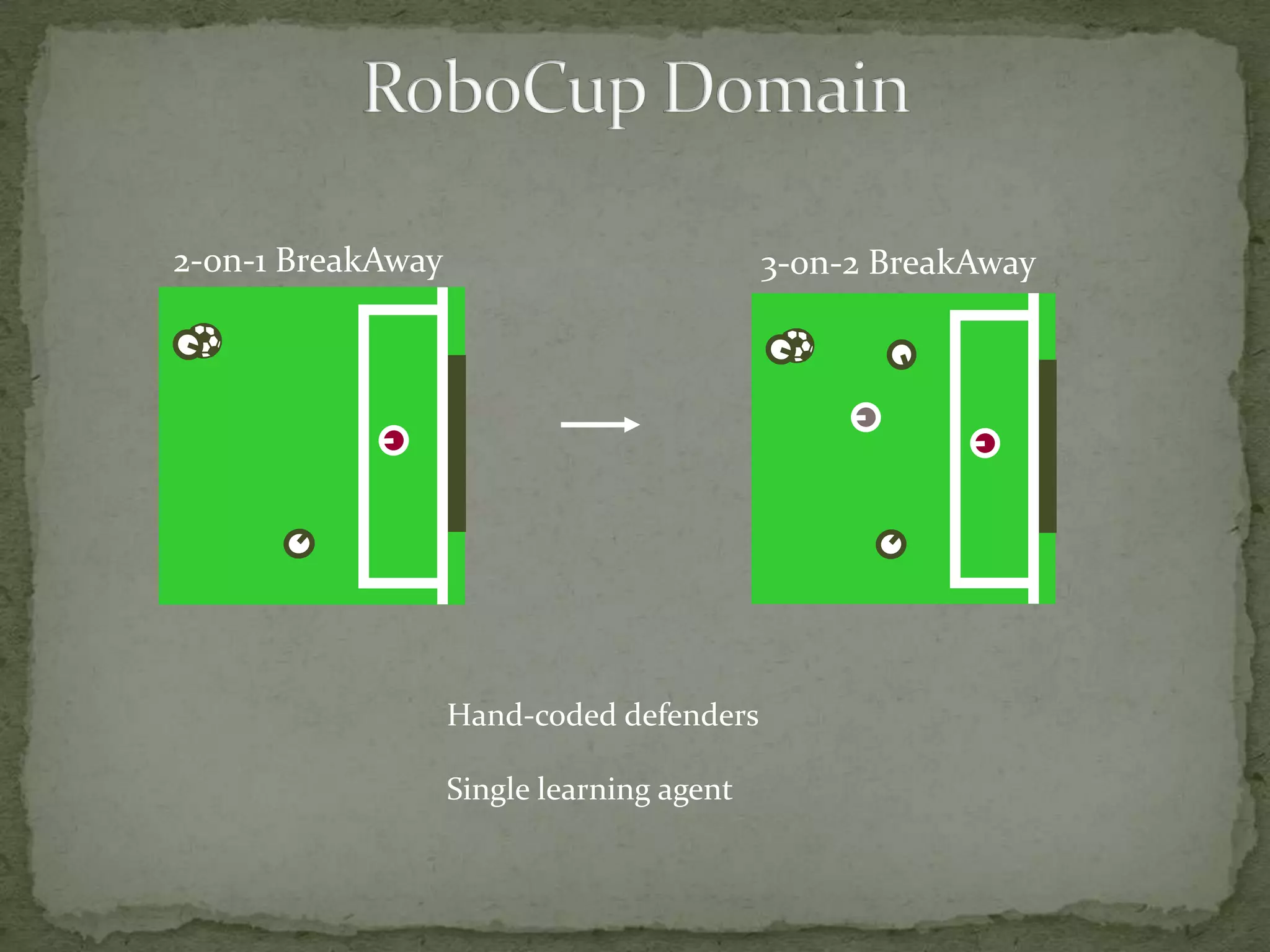
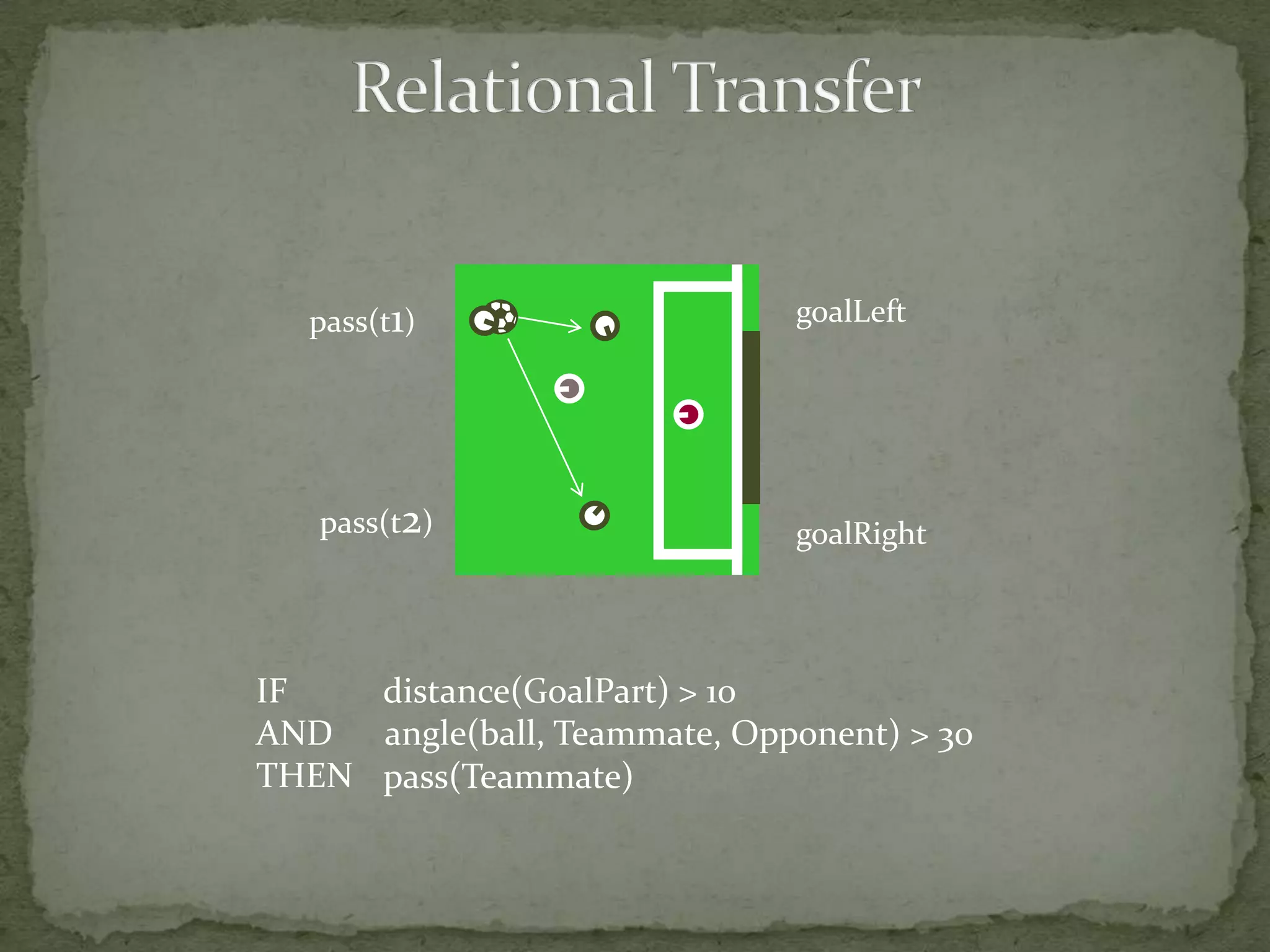
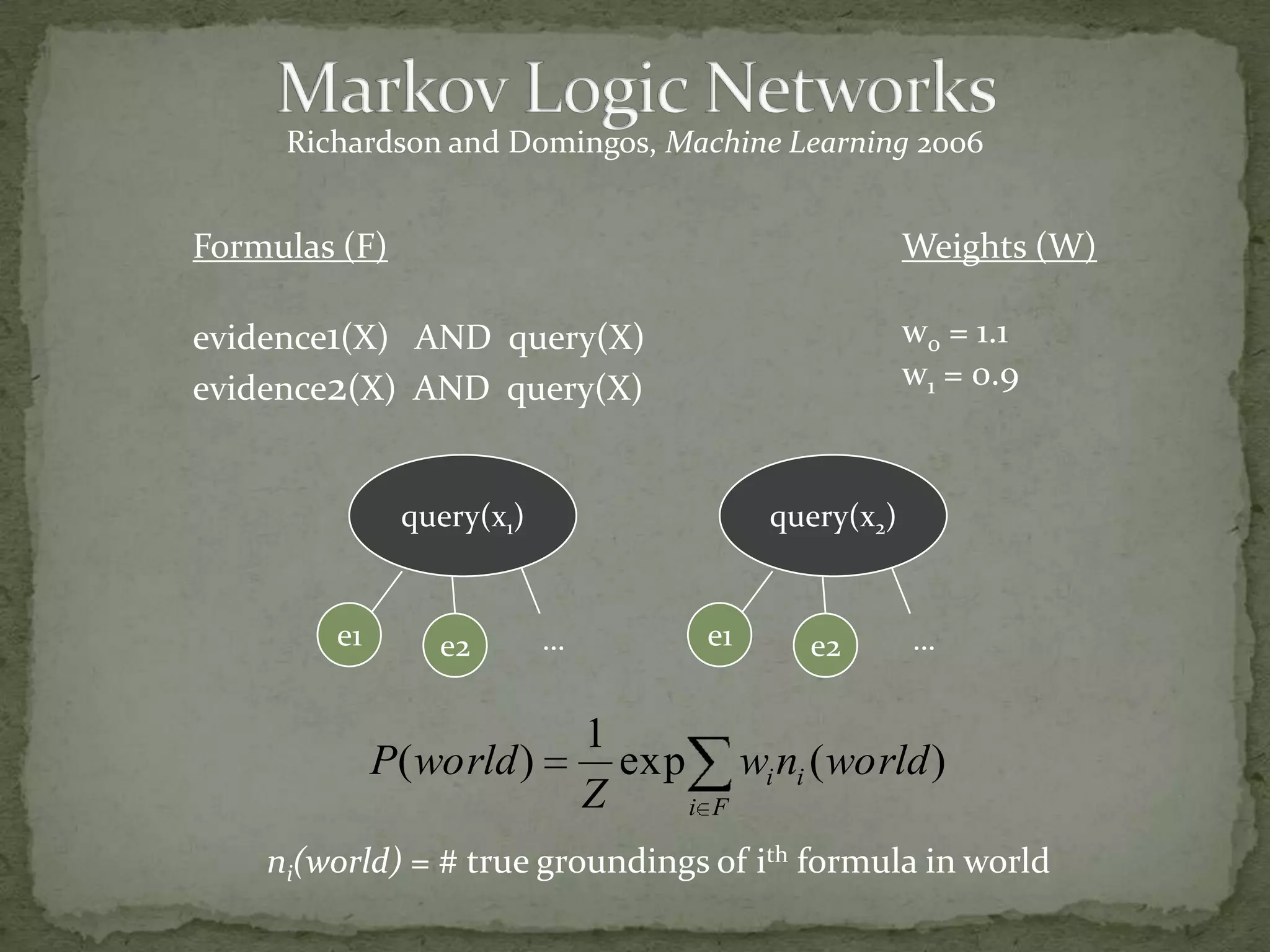
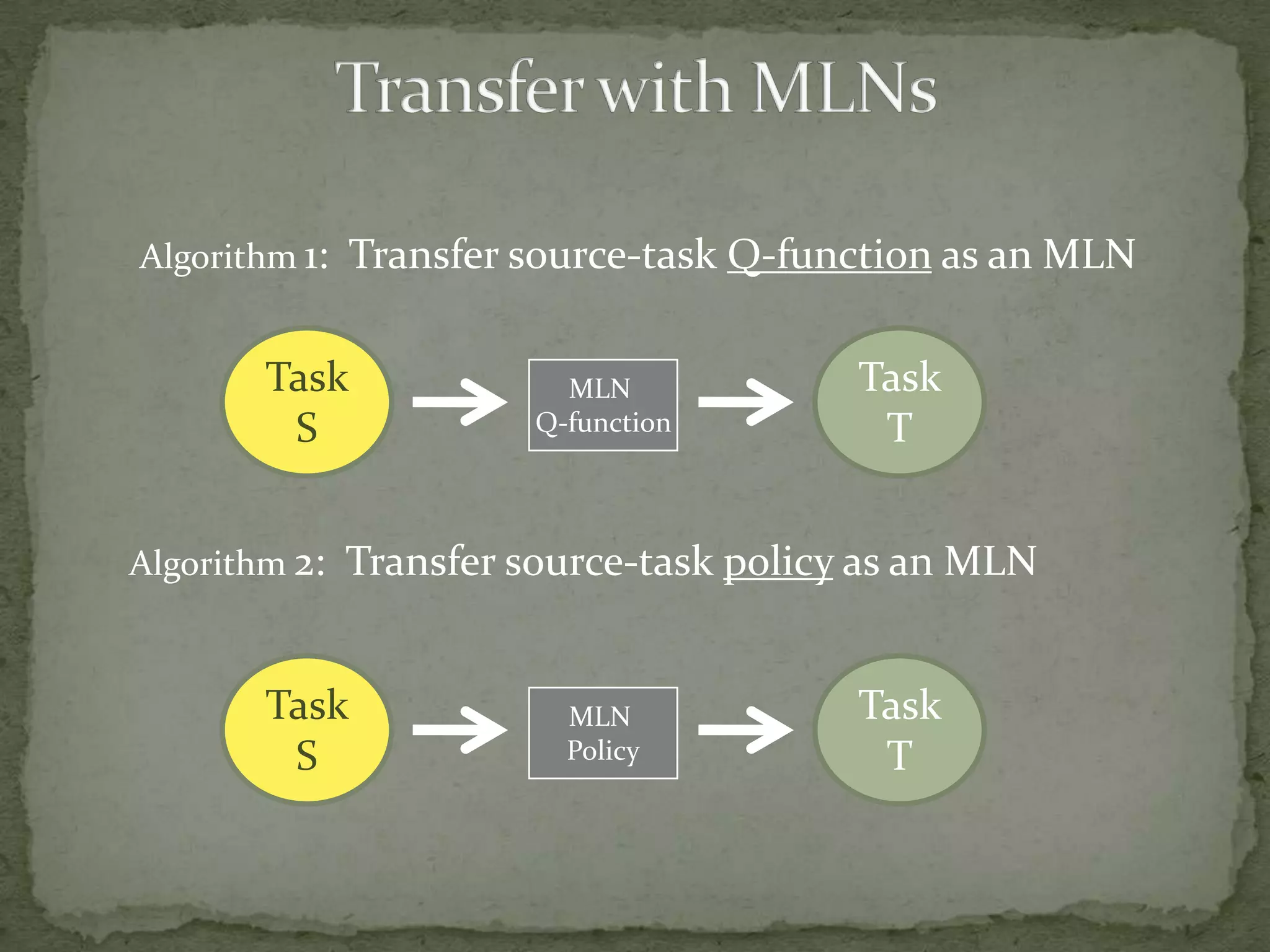
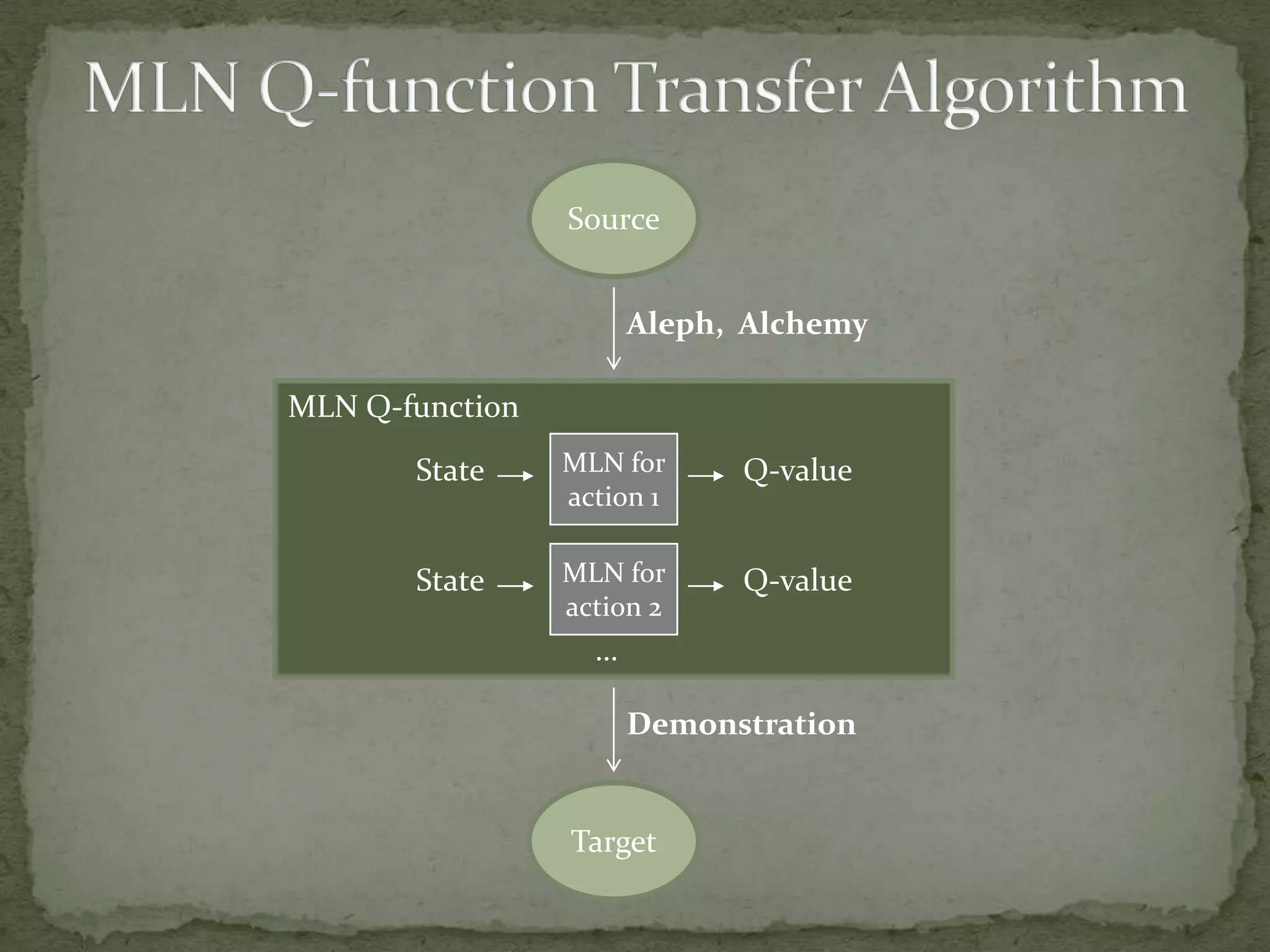
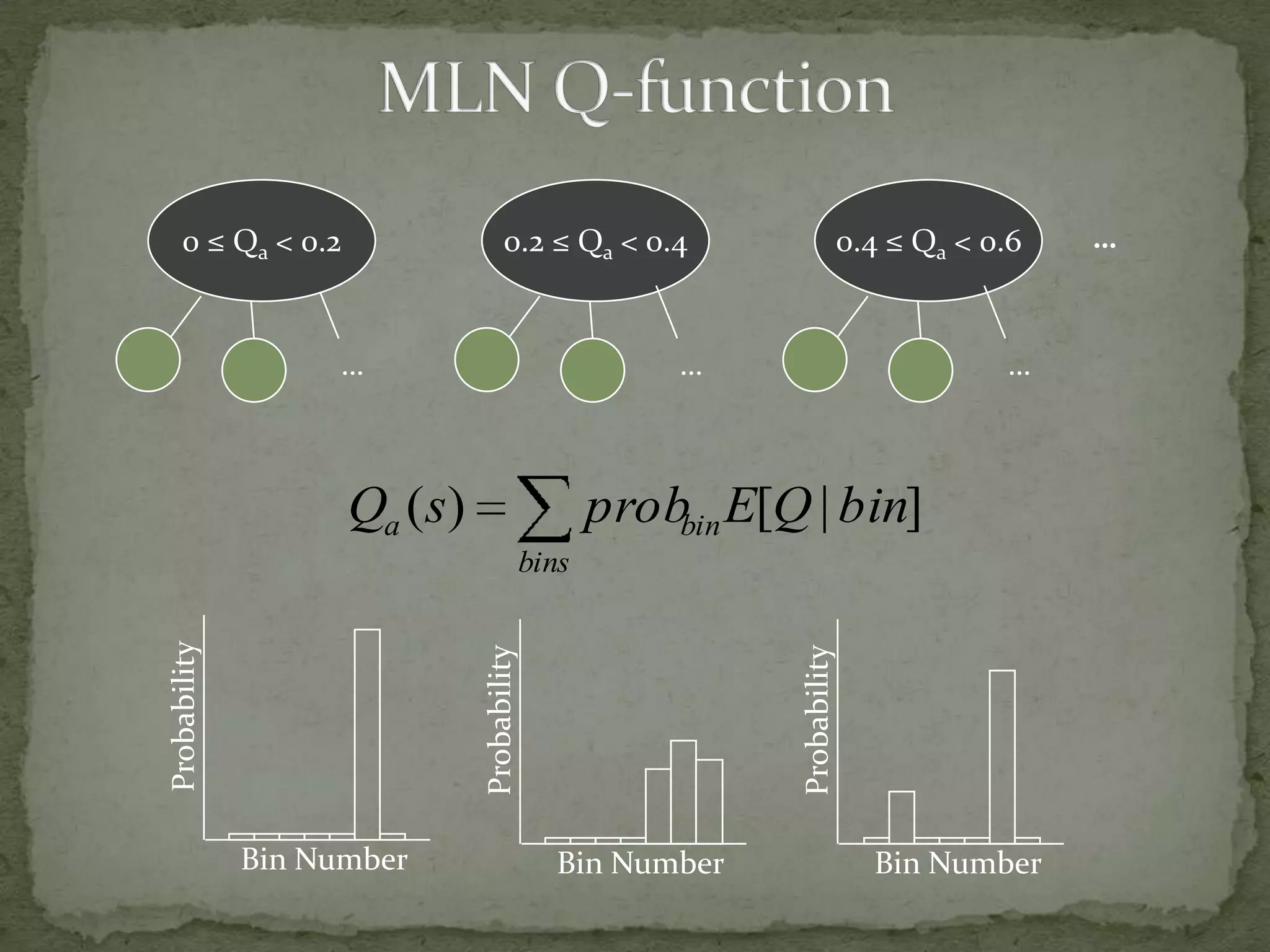
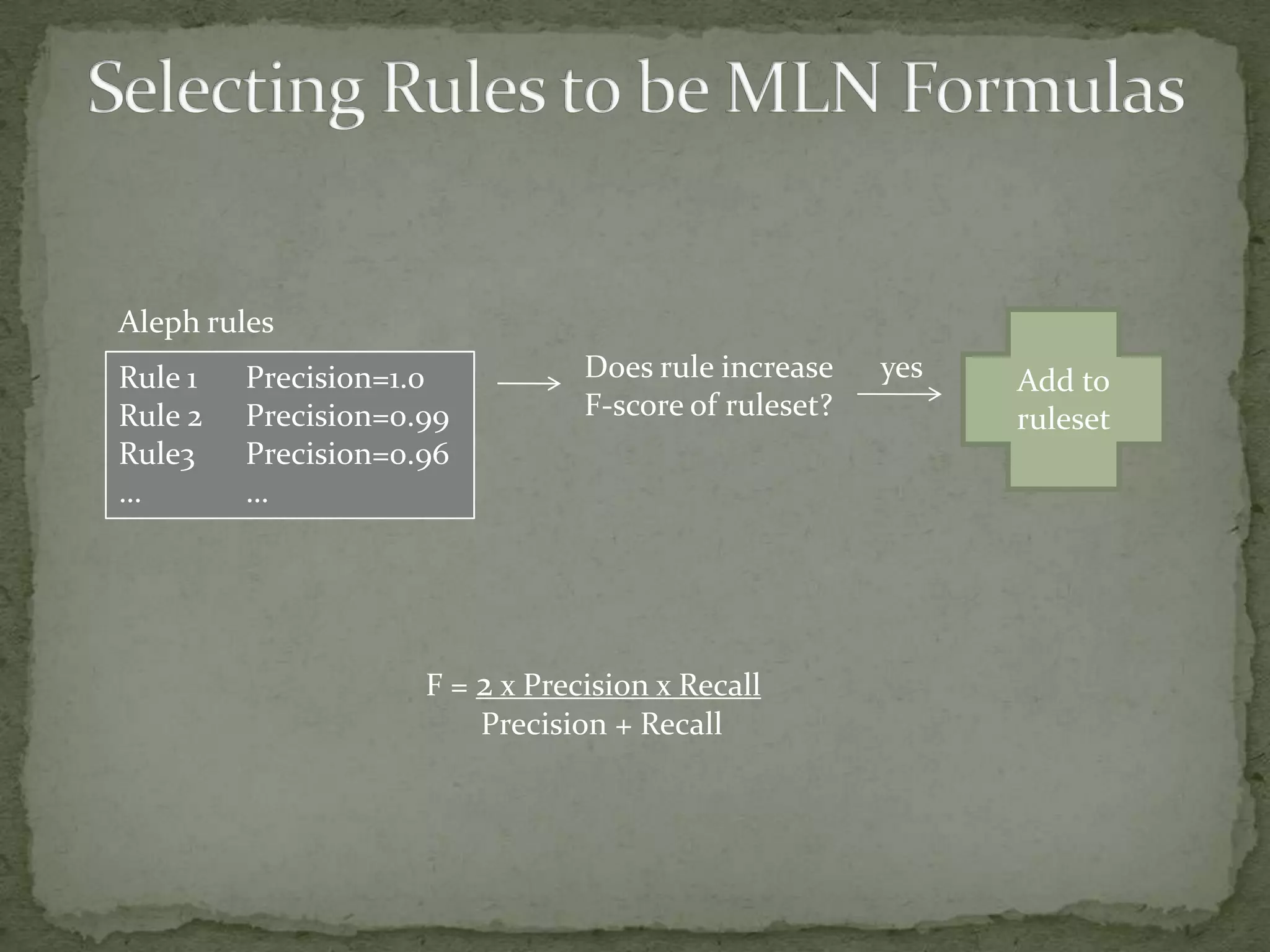
This document summarizes research on using Markov logic networks (MLNs) for transfer learning in reinforcement learning domains. It presents two new algorithms for transferring either a Q-function or policy from a source task to a target task via an MLN. Experimental results show that MLN transfer can improve learning performance in the target task compared to learning from scratch, and that policy transfer often works better than Q-function transfer. However, additional relational knowledge in MLN policies does not always further improve transfer. Future work areas include refining transferred knowledge and exploring relational reinforcement learning using MLNs.








![MLN Q-function RulesExamples for transfer from 2-on-1 BreakAway to 3-on-2 BreakAwayIF distance(me, GoalPart) ≥ 42 distance(me, Teammate) ≥ 39 THEN pass(Teammate) falls into [0, 0.11]IF angle(topRight, goalCenter, me) ≤ 42 angle(topRight, goalCenter, me) ≥ 55 angle(goalLeft, me, goalie) ≥ 20 angle(goalCenter, me, goalie) ≤ 30THEN pass(Teammate) falls into [0.11, 0.27]IF distance(Teammate, goalCenter) ≤ 9 angle(topRight, goalCenter, me) ≤ 85THEN pass(Teammate) falls into [0.27, 0.43]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relational-transfer-in-reinforcement-learning1862/75/Relational-Transfer-in-Reinforcement-Learning-20-2048.jpg)