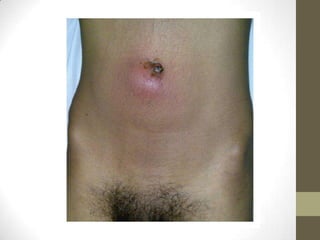
This document discusses several related umbilical disorders that can occur during fetal development or in infants:
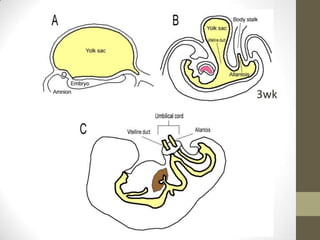
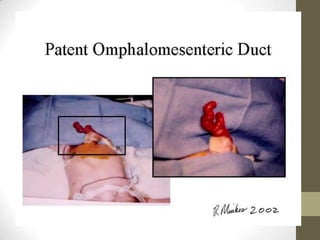
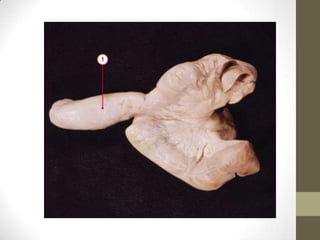
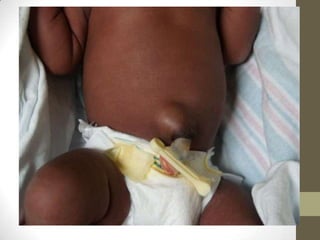
1) An omphalomesenteric duct is an extremely rare condition where the intestine remains connected to the umbilicus, sometimes causing fecal drainage.
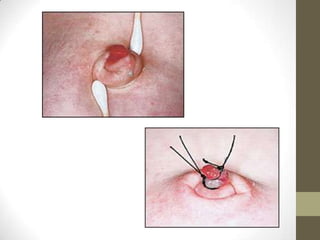
2) Partially patent omphalomesenteric ducts can cause sinus tracts or cysts that require excision.
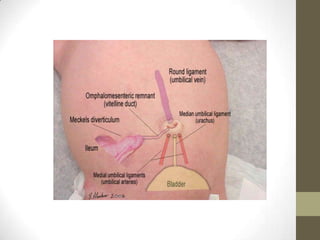
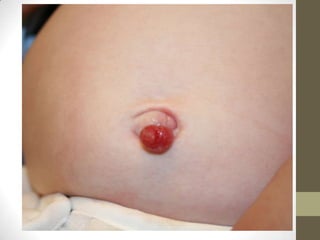
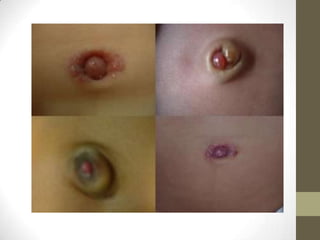
3) Meckel's diverticulum is a persistence of the proximal omphalomesenteric duct that opens into the ileum and may cause an umbilical polyp.