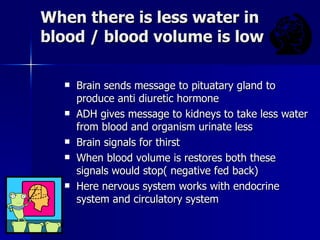
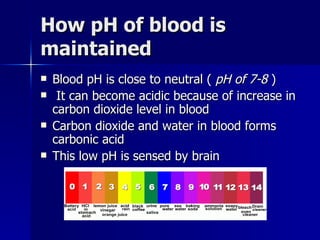
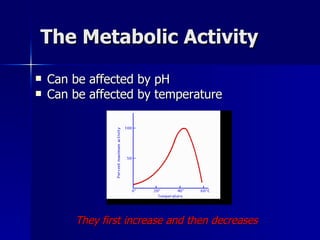
The document discusses how various organ systems work together to maintain homeostasis in the body. It provides examples of how temperature regulation is achieved through mechanisms like shivering, sweating, and vasoconstriction/dilation. It also explains how water balance and blood pH levels are regulated by signals between the brain, kidneys, lungs, and other organs to keep conditions in the optimal range for survival. The organ systems coordinate using negative feedback loops to restore homeostasis when environmental factors cause changes.