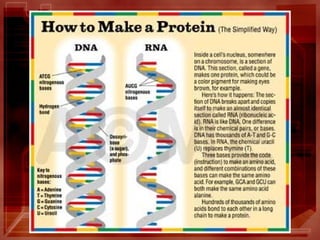
The document provides information about different types of cell reproduction and genetics concepts. It discusses asexual reproduction, which requires only one parent and produces genetically identical offspring through mitosis. The types of asexual reproduction include budding, vegetative reproduction, and binary fission. Sexual reproduction involves the production of gametes through meiosis and the fusion of egg and sperm to form a zygote. Punnett squares are used to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses and inheritance of traits or disorders. DNA, RNA, protein synthesis and gene technology concepts like gene splicing and genetic engineering are also summarized. Gel electrophoresis is described as a technique to determine relatedness between organisms based on separation of DNA bands by size.