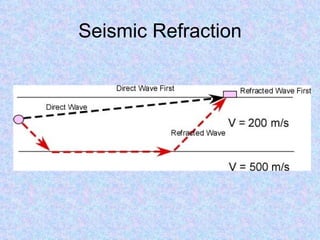
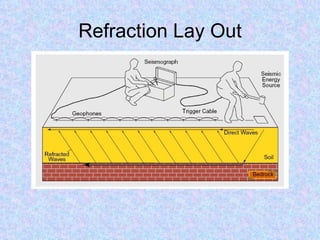
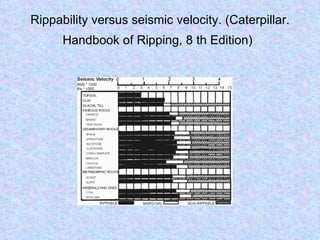
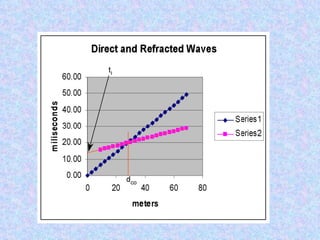
Seismic refraction is a geophysical method that uses seismic waves to determine subsurface layer properties like depth to bedrock or water tables. It works by measuring the refraction of seismic waves through subsurface layers with different velocities. Key uses include mapping bedrock depth, detecting faults or voids, and estimating material properties related to excavatability. The method has advantages of simple layout and analysis but is limited in resolving detailed subsurface structures. Interpretation involves analyzing refraction arrival times to calculate layer velocities and depths.