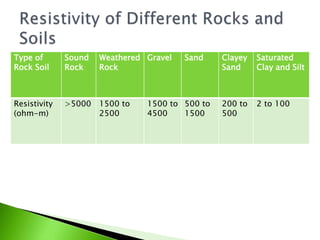
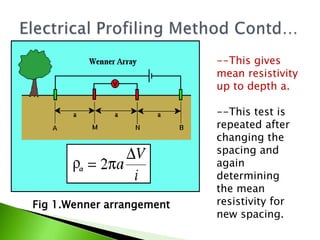
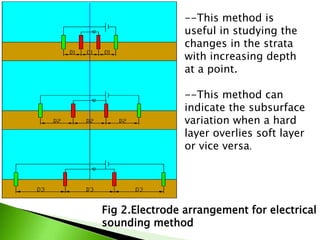
The electrical resistivity method uses four electrodes to measure the resistivity of soil and rock formations. Resistivity depends on factors like material type, water content, and salt concentration. Rocks have higher resistivity than saturated clays. This method involves expanding the electrode spacing to measure resistivity at increasing depths. It can detect subsurface variations and locate deposits like sand and gravel within fine-grained soils. Interpretation can be challenging as resistivity changes gradually at interfaces rather than abruptly.