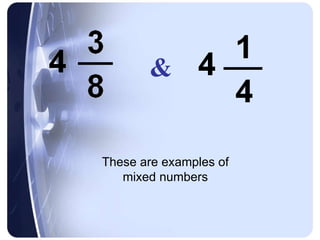
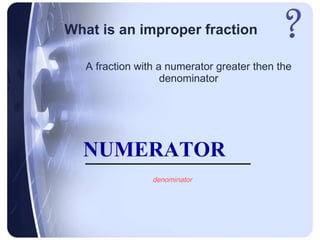
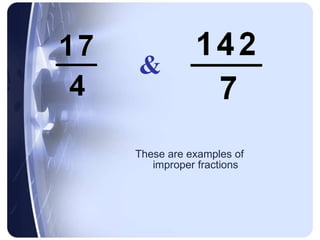
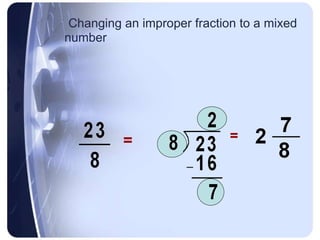
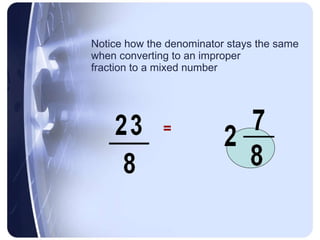
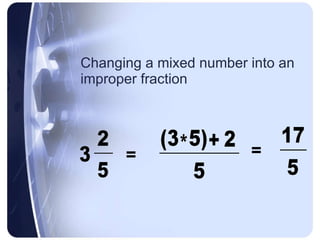
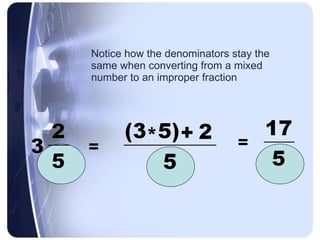
Rational numbers can be defined as any number that can be made by dividing one integer by another. This includes positive and negative numbers, whole numbers, fractions, and decimals.
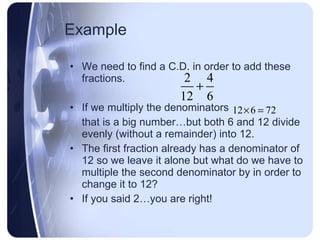
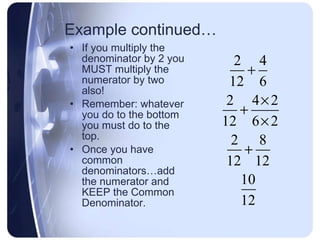
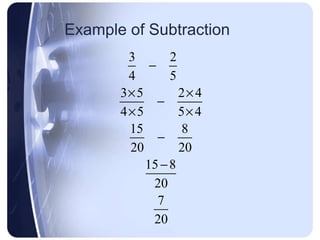
To add or subtract fractions, they must first be converted to have a common denominator. This is done by finding the least common multiple of the denominators and using it as the new common denominator.
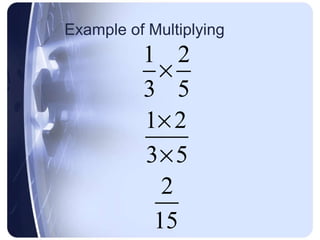
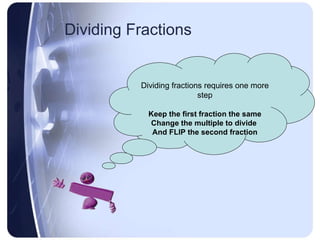
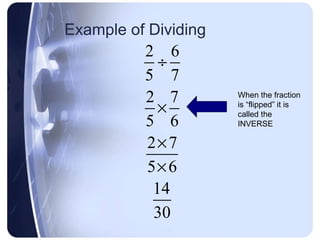
Multiplying and dividing fractions follows simple rules: for multiplication, multiply the numerators and multiply the denominators; for division, keep the first fraction the same, change the division symbol to multiplication, and flip the second fraction.